![]()
Diagnosis
______________________
Abstract
Diagnostic procedures of microtia/atresia of the external auditory canal include: (1) classification of shapes of the auricle and the external auditory canal by shape, (2) imaging assessment for revealing the condition of the external canal and middle ear by CT, and reconstructing the surface of temporal bone to confirm the positions for pinnaplasty and auditory canalplasty in order, (3) auditory assessment by pure tone audiometry, air and bone conduction ABR and ASSR and sound lateralization test, (4) evaluation of development of the auricle and the external auditory canal and rib cartilage for pinnaplasty and auditory canalplasty, (5) deciding on the correct position for auricular reconstruction for later auditory canalplasty, (6) evaluation of anomalies of the auditory ossicles for improving hearing by tympanoplasty, and (7) psychological changes in patients before and after pinnaplasty and auditory canalplasty.
![]()
Diagnosis
Kaga K, Asato H (eds): Microtia and Atresia – Combined Approach by Plastic and Otologic Surgery.
Adv Otorhinolaryngol. Basel, Karger, 2014, vol 75, pp 10–12 (DOI: 10.1159/000350495)
______________________
Classification of Shapes (Auricle/External Auditory Canal)
Yasutoshi Suzuki
Department of Plastic Surgery, Dokkyo Medical University, Shimotsuga-gun, Tochigi, Japan
Classification of Shapes of the Auricle
Microtia is a congenital anomaly of the auricle in which the components of the auricle are small or missing. The severity and states vary. Its incidence is 1 in 10,000-15,000 births, and male patients outnumber female patients (approximately 2:1). Microtia develops more frequently on the right than the left side (approximately 5:3), and the reported incidence of bilateral microtia is approximately 10%. Many cases are complicated by stenosis or occlusion of the EAC in addition to the morphological abnormality of the auricle.
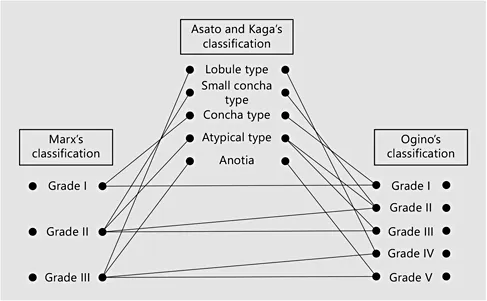
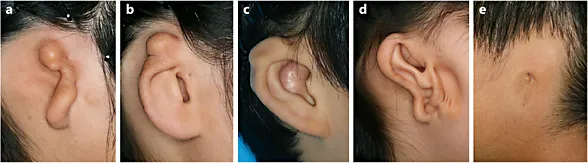
Auricular shape in microtia can be classified by conventional methods using the characteristics of the residual auricle, and by methods using qualitative differences related to embryology in addition to quantitative differences. The former includes the three-grade classification of Marx [1] and the five-grade classification of Ogino et al. [2] (table 1), and the 10-type classification of Fukuda [3] is an example of the latter. These criteria are widely used in Japan for diagnosis, treatment and surgery of microtia. In addition, Asato and Kaga classified microtia into five types from the perspective of simultaneous reconstruction of the EAC with auricular projection, in addition to auricular reconstruction by costal cartilage transplantation (fig. 1, 2). The incidence of lobule-type (a) microtia is highest, accounting for approximately 60% of cases, followed by the concha-type (c) and the small-concha type (b), with a combined incidence of approximately 15%. Atypical-type (d) and anotia-type (e) microtia, which are not included in a, b or c are rare.
Fig. 1. Correlation between classification systems for microtia.
Fig. 2. Classification of microtia according to Asata and Kaga. a Lobule type. b Small concha type. c Concha type. d Atypical type. e Anotia type.
Table 1. Clinical classification of microtia
Classification of the External Auditory Canal by Shape
Many cases of microtia are complicated by atresia of the EAC, which may occur as complete occlusion or EAC stenosis, which is incomplete occlusion. Atresia or stenosis of the EAC is either limited to cartilage or osseous occlusion. Stenosis is classified as: (1) stenosis of the entire bone, (2) stenosis of the lateralis osseous, and (3) stenosis of the cartilage.
Osseous occlusion is often observed in microtia patients and is commonly complicated by a middle ear anomaly. In such cases, a deformation or deficit of the auditory ossicle or osseous adhesion to the surrounding tissues is observed, and formation of the middle ear cavity and development of the tympanic antrum are variable. From the viewpoint of treatment and prognosis, classification of cases by combining development of the middle ear with the occlusion of the EAC has been reported. The grading system of Jahrsdoerfer et al. [4] is especially useful, where higher scores indicate expected improvement of auditory acuity (see ‘Imaging diagnosis’, this vol., p. 15).
References
1 Marx H: Die Missbildungen des Ohres. Denker-Kahler’sche Handbuch der Hals-Nasen und Ohren-heilkunde, Gehörogan 1. Berlin, Julius Springer, 1926, pp 131-169.
2 Ogino Y, Nishimura Y, Horii M, et al: Congenital microtia – multidirectional tomographic and remnant auricular forms. Pract Otol 1976;69:792-801.
3 Fukuda O: Shoujishou no bunrui; in Soeda S (eds): Zusetsu rinshou keiseigekagaku kouza 4. Tokyo, Medical View, 1988, pp 16-17.
4 Jahrsdoerfer RA, Yeakley JW, Aguilar EA, et al: Grading system for the selection of patients with congenital aural atresia. Am J Otol 1992;13:6-12.
Yasutoshi Suzuki
Department of Plastic Surgery, Dokkyo Medical University
880 Kitakobayashi, Mibu-Machi
Shimotsuga-gun, Tochigi 320-0293 (Japan)
E- Mail
[email protected]![]()
Diagnosis
Kaga K, Asato H (eds): Microtia and Atresia – Combined Approach by Plastic and Otologic Surgery.
Adv Otorhinolaryngol. Basel, Karger, 2014, vol 75, pp 13–19 (DOI: 10.1159/000350594)
______________________
Imaging Diagnosis
Hideki Takegoshi
National Institute of Sensory Organs, National Tokyo Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan
The temporal bone is a part of the cranial bone that constitutes the ear. Vital organs for hearing such as the external auditory canal (EAC), eardrum, auditory ossicles, cochlea, semicircular duct, otolithic organ, internal auditory canal, facial nerve, and internal carotid are crammed in this narrow space. Although simple X-ray of the middle and inner ear (Schüller method and Stenvers method) provide some findings and is still generally performed at present, it is difficult to observe the structure of the temporal bone clearly. Subsequent to the introduction of computed tomography (CT) in the 1970s, helical scanning was developed in the latter half of the 1980s, allowing the temporal bone to be shown more in detail [1]. Many patients with microtia/atresia of the EAC also have a middle ear anomaly, and a CT scan is essential for understanding the condition of the middle ear.
Age for CT Scanning
Babies are sometimes referred to our outpatient department with CT images at several months of age. The timing for performing CT differs among medical institutions. CT is performed within several months of birth for the following reasons: (1) it is the best method for revealing the condition of the external and middle ear; (2) it shows the presence or absence of an inner ear anomaly and enables identification of the cause of hearing loss; (3) it shows the presence or absence of congenital cholestea-tomatous otitis media, and (4) it is used to understand the severity of the temporal bone anomaly at an early age in order to confirm the possibility of EAC reconstruction and to reassure the patient’s family. Thanks to recent progress in CT equipment, the dose of radiation is decreasing, but the radioactivity exposure with CT is still dozens of times higher than that with simple radiography. Furthermore, because of their smaller body size, the level of exposure per organ is 2-5 times higher for children than adults, under the same conditions [2]. Also, image contrast is generally poorer in children because they have less fat and smaller organs than adults. Thus, the dose of radioactivity must be increased when a higher contrast image is desired. CT in children should therefore be carefully planned considering the above.
It was reported that congenital cholesteatomatous otitis media was observed in 4-7% of patients with congenital stenosis or occlusion of the EAC [3, 4]. With progression of cholesteatomatous otitis media, surrounding bones are destroyed, and inner ear disorders and facial palsy are induced; serious symptoms associated with meningitis and brain abscess develop when the lesion reaches the cranium. It is therefore better to perform a CT scan as soon as possible to rule out congenital cholesteatomatous otitis media. However, diagnosis of cholesteatomatous otitis media based on CT images is sometimes difficult because fetal remnants and exudation are often retained in the middle ear cavity within 1 year of birth. Also, it may take several years before the disease becomes advanced enough to manifest obvious symptoms even if a diagnosis was made during infancy. MRI is useful diagnostically to help differentiate congenital cholesteatoma from other soft-density exudation of the middle ear. On MRI, cholesteatoma will appear with low signal intensity on T1-weighted images and high signal intensity on T2-weighted images.
...