![]()
1. INTRODUCTION: STATE OF WATER AND INTERSTATE WATER RELATIONS
Objectives
This chapter sets the stage for most of the concepts and jargon a ‘water person’ uses. It considers global water issues, sectoral use patterns, and other water-related concepts such as water scarcity. The chapter will likewise demonstrate the link between a basin’s water situation and the potential conflict that can arise between the riparians. You will also be introduced to concepts relevant to international water agreements. You will find a very short introduction explaining the likely impact of climate change (global warming) on the hydrological cycle. Finally, you will note the distribution of international river basins and the nature of various conflicts over water.
Main Terminology
Access to water; Acre-foot (af) (1 af = 1235 m3); Brackish water; Conflict; Consumptive use; Cooperation; Cusec (cubic meters per second); Desalinization; Downstream riparian; Electrical conductivity (EC); Evaporation; Externality; Fresh water; Flow variability; Groundwater; Hydrological cycle; International water; Irrigation; m3 (cubic meter); Nonconsumptive use; Parts per million (PPM); Peace; Precipitation; Recycling (Water reuse); River runoff; Salt water; Treaties; Upstream riparian; War; Water cycle; Water in circulation; Water supply variability.
This chapter will set the basis for understanding the problem of water availability and variability supply in the world, its regional distribution, and how humankind may affect it with human interventions. We will link in this chapter the notion of water scarcity to the evidence on water conflicts among nations and try to set the stage for the remaining chapters of the book. The chapter helps in establishing some of the language and concepts to communicate without getting too wet. The reader will not only be able to get a ‘free access’ to the rest of the book’s chapters but also to other literature on water.
THE STATE OF WATER IN THE WORLD
Our world witnesses several phenomena that individually and jointly have led to an increase in water dependency among sectors and segments of society, as well as among nations. Population growth, increase in urbanization and industrialization, and technological progress, just to name a few, have led to deforestation, water quality deterioration, and this affects the availability of water for human uses and ecological needs. As the, more or less, fixed amounts of the world’s natural resources, such as land, water, forests, and other environmental amenities, have to be shared by a larger number of humans over time, increased competition and strategic decisions become more apparent at all levels of decision-making, starting with the household and ending with state level water managers. Recently, we became aware also of the impacts of changing precipitation patterns on annual river runoff. The impact of climate change on increased water supply variability is widely seen as a possible deterrence to the stability of existing water allocation agreements.
How Much Water Is There and How Is It Used?
There is plenty of water in our globe. The problem is that it is either hard/expensive to extract or is available at the ‘wrong time’ and/or at the ‘wrong places.’ Countries that share the same water source may have different levels of access and this, alone, could be a source of conflict.
Box 1.1: Access to water
What does ‘access’ mean? For example, a river that is shared by two countries may constitute an upstream country with a steep terrain. Consequently, reasonable use of the water for production of any benefit is made difficult. Nevertheless, the water flows across the border and reaches the flat terrain of the downstream riparian, where it can be fully utilized. A good example is the case of the Blue Nile and two of its major riparians, Ethiopia and Egypt. While 85% of the water originates upstream, Ethiopia’s terrain makes utilization of the resource difficult. For several decades, the two riparians have been conflicting over the amount of water allocated to Egypt in a water treaty. Alternative, approaches other than the allocation of the water among the riparian states have to be considered.
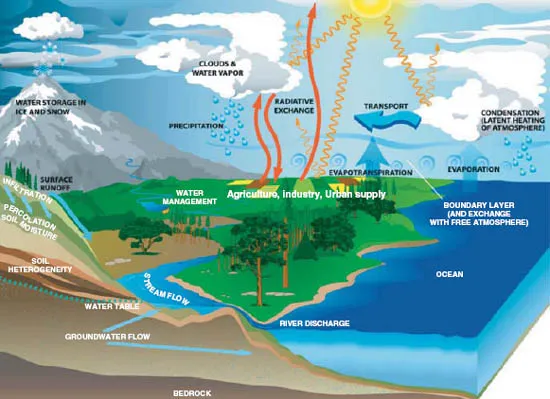
Most of the available water is generated in a continuous process called ‘the water cycle.’ Figure 1.1 notes the many water-consuming sectors, interactions among them, and physical relationships that affect the water cycle — the way that water is generated, moves, and stored. In addition, Fig. 1.1 points to many interdependencies, or what economists term externalities, among sources, users, and locations. In other words, what one user does affects the availability of water to others. This makes water unique relative to other natural resources.
Fig. 1.1: The water cycle.
Source: Modified from US Climate Change Science Program (with permission to use), http://www.usgcrp.gov/usgcrp/images/ocp2003/ocpfy2003-fig5-1.htm (Visited July 7, 2006).
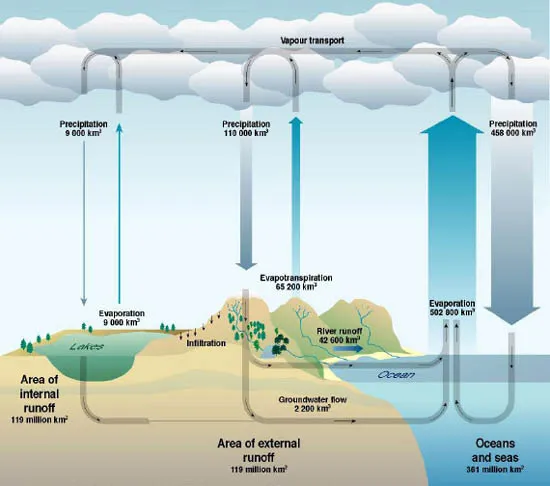
Since water can be transported, ownership becomes an issue and may affect relationships between riparians. Figure 1.2 demonstrates the contribution of oceans, rivers, and vegetation, and lakes to the global water cycle. In addition, it explains the transport of water from one place to another, not via the traditional conduits (of pipes and rivers) but rather through space.
What are the main sources of water available for extraction, and how is water stored? There are four major water sources for human use: surface (rivers, lakes); groundwater (renewable, nonrenewable, fossil, brackish); reused treated wastewater; desalinized water (sea and brackish groundwater).
What are the water-using sectors and how do they utilize water? We will see that the distribution of water use by sectors across continents and countries varies a great deal. The composition of sectoral use of water may affect the relationship (conflict/cooperation) among riparian states. This happens for various reasons. First, time of use varies across sectors. While agriculture requires water for irrigation mainly during the summer season, hydropower utilizes the available water during the winter. Second, quality of water needs varies across sectors. While agriculture can use water of relatively low quality, residential uses are quite sensitive to water quality standards. In addition, water ‘quality’ is actually a vector of various components, and may differ in nature among sectors. For example, level of minerals in the water affects the ‘salinity’ of the water and its suitability for irrigation of salt-sensitive crops. For residential uses, quality takes into consideration stricter standards such as level of nutrients, and other chemical elements that make water harmful for residential use.
Fig. 1.2: The dynamic nature of the global water cycle.
Source: United Nations Environmental Programme (with permission to use), UNEP (2002) http://www.unep.org/vitalwater/03-water-cycle.htm (Visited August 20, 2006).
Table 1.1: Sectoral water withdrawals by region, rounded numbers (%).
Region | Residential | Industry | Agriculture |
Africa | 7 | 5 | 88 |
Europe | 14 | 55 | 31 |
North America | 13 | 47 | 49 |
Central America | 6 | 8 | 86 |
South America | 18 | 23 | 59 |
Asia | 6 | 9 | 85 |
Oceania | 64 | 2 | 34 |
Source : World Resources Institute (1998).
In the following paragraphs, we provide a very general description of water use by sectors. But first, take a look at the information in Table 1.1.
One immediate observation from Table 1.1 is the unequal distribution of water withdrawals among the continents, especially the share of agriculture. One rule of thumb is that the higher the share of agricultural use in the economy, the less developed the country. In addition, to the implications based on the share of water used by agriculture, as is explained below, the shares of water withdrawals also imply the sectoral power relations and the status quo solutions, which may not necessarily be the most efficient ones.
Irrigation consumes the lion share of the available water, depending on the country. Therefore, irrigation dictates many of the characteristics of the water situation in the world. Soil is watered using various application methods such as flood, furrow, sprinkler, and drip, just to name a few. Some of the irrigation water is consumed by the plants, the reminder percolates, and evaporates. In most locations, 50% of the water that is being ‘sent’ to the fields is lost to percolation and evaporation even before reaching its destination. Irrigation may cause many negative consequences, e.g., soil and groundwater pollution by pesticides and fertilizers. Although the irrigation season could be long, most of the irrigation demand for water occurs during the summer months. Irr...