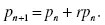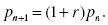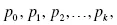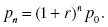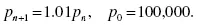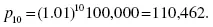Explorations of Mathematical Models in Biology with MATLAB
Mazen Shahin
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Explorations of Mathematical Models in Biology with MATLAB
Mazen Shahin
Informazioni sul libro
Explore and analyze the solutions of mathematical models from diverse disciplines
As biology increasingly depends on data, algorithms, and models, it has become necessary to use a computing language, such as the user-friendly MATLAB, to focus more on building and analyzing models as opposed to configuring tedious calculations. Explorations of Mathematical Models in Biology with MATLAB provides an introduction to model creation using MATLAB, followed by the translation, analysis, interpretation, and observation of the models.
With an integrated and interdisciplinary approach that embeds mathematical modeling into biological applications, the book illustrates numerous applications of mathematical techniques within biology, ecology, and environmental sciences. Featuring a quantitative, computational, and mathematical approach, the book includes:
- Examples of real-world applications, such as population dynamics, genetics, drug administration, interacting species, and the spread of contagious diseases, to showcase the relevancy and wide applicability of abstract mathematical techniques
- Discussion of various mathematical concepts, such as Markov chains, matrix algebra, eigenvalues, eigenvectors, first-order linear difference equations, and nonlinear first-order difference equations
- Coverage of difference equations to model a wide range of real-life discrete time situations in diverse areas as well as discussions on matrices to model linear problems
- Solutions to selected exercises and additional MATLAB codes
Explorations of Mathematical Models in Biology with MATLAB is an ideal textbook for upper-undergraduate courses in mathematical models in biology, theoretical ecology, bioeconomics, forensic science, applied mathematics, and environmental science. The book is also an excellent reference for biologists, ecologists, mathematicians, biomathematicians, and environmental and resource economists.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
CHAPTER 1
OVERVIEW OF DISCRETE DYNAMICAL MODELING AND MATLAB®
1.1. INTRODUCTION TO MODELING AND DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS
1.1.1. Model 1.1: Population Dynamics, A Discrete Dynamical System
Discussion