
eBook - ePub
ABC of Hypertension
D. Gareth Beevers, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Eoin T. O'Brien
This is a test
Condividi libro
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
ABC of Hypertension
D. Gareth Beevers, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Eoin T. O'Brien
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
High blood pressure is a common chronic medical problem encountered in primary care, yet it is commonly under diagnosed. ABC of Hypertension is a long established, practical guide to the investigation, treatment and management of hypertensive patients. This sixth edition:
- Provides practical guidance on measurement of blood pressure and the investigation and management of hypertensive patients
- Explains new developments in measurement and automated measurement of blood pressure and
- Updates coverage on treatment of the elderly and explains of the implications of recent trials
- Incorporates current British Hypertension Society and NICE guidelines
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
ABC of Hypertension è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a ABC of Hypertension di D. Gareth Beevers, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Eoin T. O'Brien in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Medicina e Cardiología. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Chapter 1
The prevalence and causes of hypertension
OVERVIEW
- The distribution of blood pressure in the general population is as a continuous variable forming a roughly normal of ‘Gaussian’ curve, with no clear dividing lines between low, normal or high readings.
- The dividing lines above which an individual is considered to have hypertension are pragmatic, based on the results of the many placebo-controlled trials of antihypertensive drug therapy.
- From a practical point of view, blood pressures of 140/90 mm Hg or more are considered to be raised and some individuals whose pressures are persistently in this range would be considered to require drug treatment.
- The prevalence of ‘clinical’ hypertension increases with advancing age. Five to ten percent of teenagers have a blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or more at first screening. At the age of 80 years, this figure rises to a 70–75%.
- Average blood pressures and the prevalence of hypertension are higher in people of African origin in Western countries. Hypertension is rapidly becoming commoner in all developing countries.
- In about 5% of all hypertensives, underlying renal or adrenal diseases are identifiable (secondary hypertension). In the remaining 95%, no underlying cause can be found (essential or primary hypertension).
- Essential hypertension runs in families and part of this tendency is related to genetic factors. No single gene is related to essential hypertension; to date, around 27 candidate genes have been investigated, but they only explain a 1–2 mm Hg variation in blood pressure.
- Several lifestyle factors are implicated in the causation of hypertension. These include obesity, heavy alcohol consumption, a low intake of fruit and vegetables and lack of exercise.
- The most important lifestyle factor causing hypertension is a diet with a high salt content as is common in almost all developing countries.
Blood pressure in populations
In the population, blood pressure is a continuous, normally distributed variable. No separate subgroups of people with and without hypertension exist. A consistent continuous gradient exists between usual levels of blood pressure and the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke, and this gradient continues down to blood pressures that are well below the average for the population (Figure 1.1). Above blood pressures of 115/70 mmHg, the risk of developing cardiovascular events doubles for every 20/10mmHg rise in blood pressure. This means that much of the burden of renal disease and cardiovascular disease (CVD) related to blood pressure can be attributed to blood pressures within the so-called ‘normotensive’ or average range for Western populations. Most cardiovascular events are therefore blood pressure-related rather than hypertension-related.
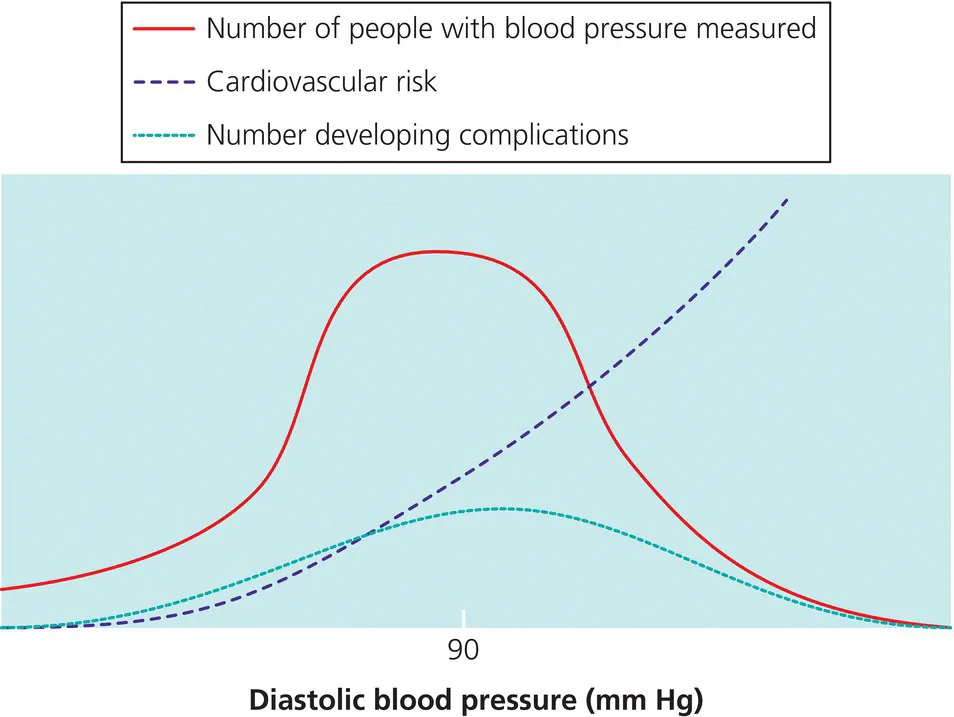
Figure 1.1 The distribution of diastolic blood pressure in the general population, the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and the number of people who develop CVD.
The main concern for clinicians is what level of blood pressure needs drug treatment. The pragmatic definition of hypertension is the level of blood pressure at which treatment is worthwhile. This level varies from patient to patient and balances the risks of untreated hypertension in different types of patients and the known benefits of reducing blood pressure, while taking into account the disadvantages of taking drugs and the likelihood of side effects.
Hypertension: a disease of quantity not quality
‘In an operational sense, hypertension should be defined in terms of a blood pressure level above which investigation and treatment do more good than harm.’ Grimley Evans J, Rose G. Hypertension. Br Med Bull1971;27:37–42
Systolic blood pressure continues to rise with advancing age, so the prevalence of hypertension (and its complications) also increases with age. By contrast, diastolic pressures tend to level off at the age of about 50 years and tend to decline thereafter (Figure 1.2).
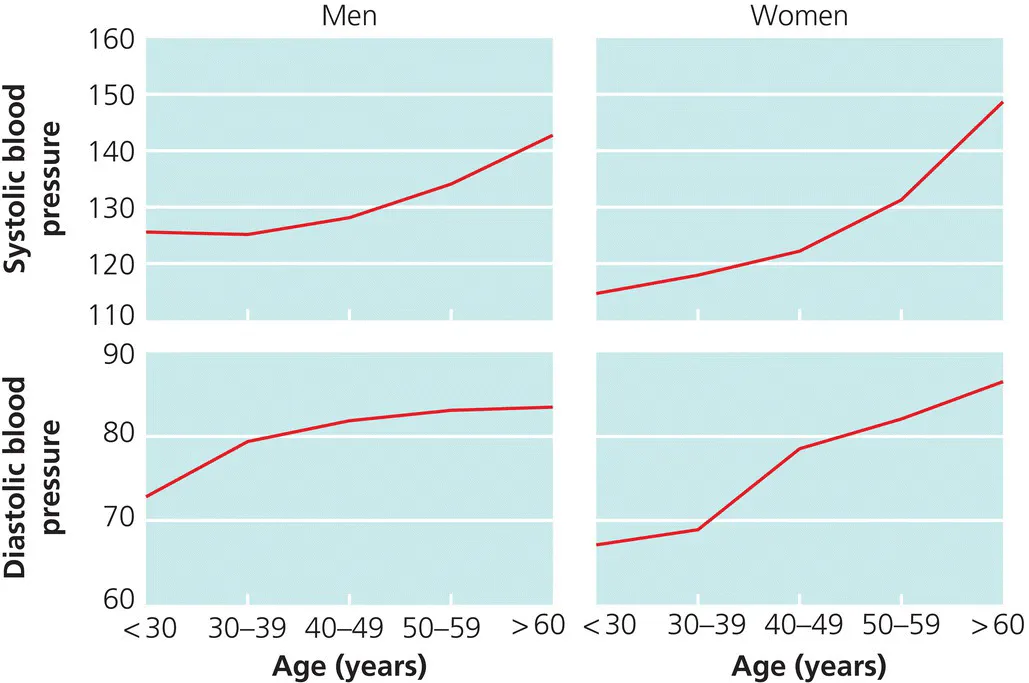
Figure 1.2 Average systolic and diastolic blood pressures in men and women in the Birmingham Factory Screening Project. This figure excludes 165 patients who were receiving antihypertensive drugs.
Source: Reproduced with permission from Lane, D.A., et al. (2002) Journal of Human Hypertension, 16, 267–273.© Nature Publishing.
Hypertension thus is as much a disorder of populations as of individual people. Globally, high blood pressure and its vascular consequences, heart attack and stroke, account for more deaths than any other common medical condition and is a major burden of disease (Figure 1.3).
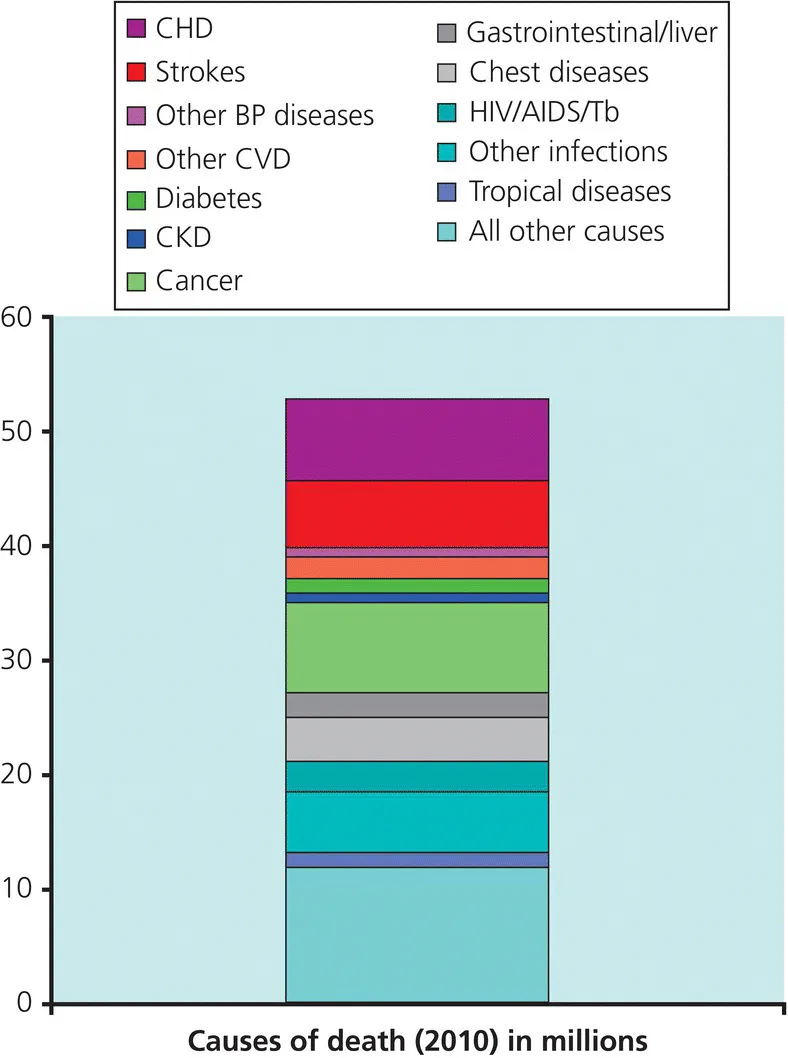
Figure 1.3 Worldwide causes of death in 2002 in millions. CKD: chronic kidney disease.
Source: Adapted from Mackay, J., & Mensah, G.A. (2004) The Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke. World Health Organisation, Geneva.
As hypertension is the most important risk factor for CVD, achievement of a universal target systolic blood pressure of 140 mm Hg or ...