
Leadership for Innovation
Three Essential Skill Sets for Leading Employee-Driven Innovation
David Masumba
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Leadership for Innovation
Three Essential Skill Sets for Leading Employee-Driven Innovation
David Masumba
About This Book
Leadership for Innovation takes a look at organizations' desire to make innovation every employee's responsibility and teaches organizational leaders to create an innovative climate.
Studies have revealed that although organizations desire to make innovation every employee`s responsibility, the major challenge is how to create a climate where every employee across functional units is involved in advancing innovation. Employee-driven innovation does not happen naturally, or by relaying on traditional management tools and approaches. Organizational leaders must possess the necessary innovation skills to develop and implement crosscutting innovation-support systems and practices. With over 10 years of experience focusing on designing workforce innovation-support systems, David Masumba shares strategies and policies that help companies create a climate of innovation. Leadership for Innovation offers tools that organizational leaders across industries, individuals aspiring to assume leadership roles, and undergraduate and graduate students can apply to develop essential innovation skill sets and bring themselves or their company to a whole new level.
Frequently asked questions
Information
PART I
INNOVATIVE THINKING SKILLS
Overview
- Chapter 1: Understanding Innovative Thinking Skills
- Chapter 2: Approaches: How Do You Develop Innovative Thinking Skills?
- Chapter 3: Why Is It Important for Organizational Leaders to Have Innovative Thinking Abilities in Leading Workforce Innovation?

CHAPTER 1
Understanding Innovative Thinking Skills
1. The Definition of Innovative Thinking Skills
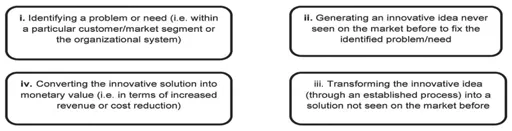
- i.The ability to identify problems, needs, and challenges
- ii.The ability to turn the problems and needs into innovative opportunities by generating innovative ideas or solutions (i.e., solutions not seen on the market before) to fix the identified problems or needs
2. The Importance of Understanding What Innovative Thinking Skills Entail
- i.Innovative thinking is now a crosscutting practice in organizations. According to a number of studies, it’s widely believed across industries (e.g., manufacturing, technology, financial, hospitality, health, aviation, auto, retail) that innovation is a predictor of growth and profitability. Thus, in an effort to scale innovation performance across all functional units, many organizations are adopting the practice of making innovation every employee’s business. The introduction to this book cites a 2010 study by the US-based Institute for Corporate Productivity on the topic of innovation in which virtually all 641 respondents representing organizations with a thousand or more employees agreed that innovation had increased in importance across their organizations and further predicted that innovation would become even more important in coming years. In order to scale the practice of innovative thinking across the organization, one vital aspect that the top leadership has to clarify and instill in the hearts and minds of workforces is that innovative thinking is not an area reserved for specific persons or functional units. That is, innovative thinking is a skill that all employees can attain or develop, irrespective of their level in the organizational structure or the functional unit under which they fall. This fact is backed by numerous studies. To instill this message in the hearts and minds of workforces and influence or drive innovative thinking practices across functional units, first and foremost, it is important for organizational leaders to understand what innovative thinking skills entail. Further, the message can be leveraged by leadership as a motivational instrument for rallying the workforces to contribute toward generating diverse innovative ideas and to help build a culture of innovation across all the functional units of the organization.
- ii.Understanding what innovative thinking entails helps leaders to interpret how innovative thinking skills are expressed. According to the Human Capital Trends—2012 report by Deloitte LLP, many companies are now defining innovation broadly to include such aspects as services, processes, business models, communication, and cost-structure improvements across the enterprise. Similarly, in an article published in the online innovation management magazine InnovationManagement.se, Jean-Philippe Deschamps, a renowned innovation expert and professor at Switzerland’s prestigious IMD management school, observed that one of the key roles of management in governing innovation is to ensure that innovation is defined very broadly across the organization. Thus, understanding innovative thinking skills helps leaders to interpret how innovative thinking skills are applied and expressed across the various components of an organization’s value chain such as research and development, design, manufacturing, sales, marketing, IT, procurement, distribution, HR, finance and accounting.
3. The Interpretation and Expression of Innovative Thinking Skills
- Product-development unit, with the following segments:
- Body-lotions segment

- Skin-cleansing segment

- Hair-care segment

- Hand-washing segment

- Manufacturing-processes department (the manufacturing-processes department comprises the same segments as the product-development unit)
- Marketing department, with the following units:
- Pricing unit

- Product-promotion unit

- Product-delivery unit

- New-markets unit

- Packaging unit

- Customer service department
- Procurement department
- HR department
- Finance and accounting department
- IT department
- Corporate affairs department
Product categories and segments | How do you define or express innovative thinking skills in the context of the product-development functional unit? |
Body lotions | Innovative thinking skills in the context of the product-development functional unit would be interpreted as the ability to do the following:
|