
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Statistical Hypothesis Testing with SAS and R
About this book
A comprehensive guide to statistical hypothesis testing with examples in SAS and R
When analyzing datasets the following questions often arise:
Is there a short hand procedure for a statistical test available in SAS or R?
If so, how do I use it?
If not, how do I program the test myself?
This book answers these questions and provides an overview of the most common
statistical test problems in a comprehensive way, making it easy to find and perform
an appropriate statistical test.
A general summary of statistical test theory is presented, along with a basic
description for each test, including the necessary prerequisites, assumptions, the
formal test problem and the test statistic. Examples in both SAS and R are provided,
along with program code to perform the test, resulting output and remarks
explaining the necessary program parameters.
Key features:
• Provides examples in both SAS and R for each test presented.
• Looks at the most common statistical tests, displayed in a clear and easy to follow way.
• Supported by a supplementary website http://www.d-taeger.de featuring example
program code.
Academics, practitioners and SAS and R programmers will find this book a valuable
resource. Students using SAS and R will also find it an excellent choice for reference
and data analysis.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
Introduction
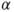
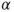
Chapter 1
Statistical hypothesis testing
1.1 Theory of statistical hypothesis testing

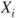
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Preface
- Part I: Introduction
- Part II: Normal Distribution
- Part III: Binomial Distribution
- Part IV: Other Distributions
- Part V: Correlation
- Part VI: Nonparametric Tests
- Part VII: Goodness-of-Fit Tests
- Part VIII: Tests on Randomness
- Part IX: Tests on Contingency Tables
- Part X: Tests on Outliers
- Part XI: Tests in Regression Analysis
- Appendix A: Datasets
- Appendix B: Tables
- Glossary
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app