
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Biochemistry for Sport and Exercise Metabolism
About this book
The book opens with some basic information on the subject, including an overview of energy metabolism, some key aspects of skeletal muscle structure and function, and some simple biochemical concepts. It continues by looking at the three macromolecules which provide energy and structure to skeletal muscle - carbohydrates, lipids, and protein. The last section moves beyond biochemistry to examine key aspects of metabolism - the regulation of energy production and storage. Beginning with a chapter on basic principles of regulation of metabolism it continues by exploring how metabolism is influenced during high-intensity, prolonged, and intermittent exercise by intensity, duration, and nutrition.
Key Features:
- A clearly written, well presented introduction to the biochemistry of muscle metabolism.
- Focuses on sport to describe the relevant biochemistry within this context.
- In full colour throughout, it includes numerous illustrations, together with learning objectives and key points to reinforce learning.
Biochemistry for Sport and Exercise Metabolism will prove invaluable to students across a range of sport-related courses, who need to get to grips with how exercise mode, intensity, duration, training status and nutritional status can all affect the regulation of energy producing pathways and, more important, apply this understanding to develop training and nutrition programmes to maximise athletic performance.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
- outline the key energy sources for exercise;
- distinguish between anaerobic and aerobic sources of energy;
- describe the essential structure of ATP;
- draw and explain the components of the energy continuum;
- describe the role of PCr in ATP synthesis;
- explain how PCr is resynthesized;
- describe the involvement of carbohydrates and fats as energy sources for exercise;
- explain reasons why an athlete is unable to sprint a marathon;
- describe the amounts and sources of energy in the body and their rates of energy formation;
- discuss how amino acids can be used as an energy source during exercise.
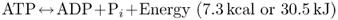
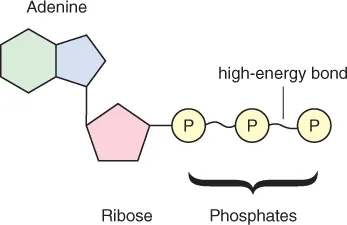
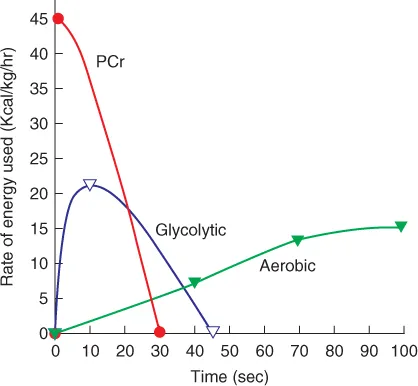
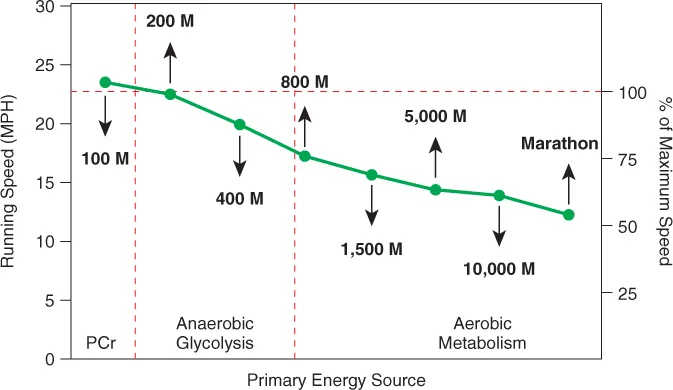
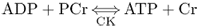
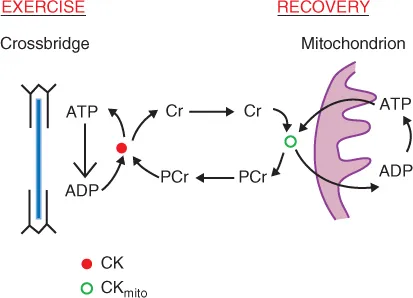
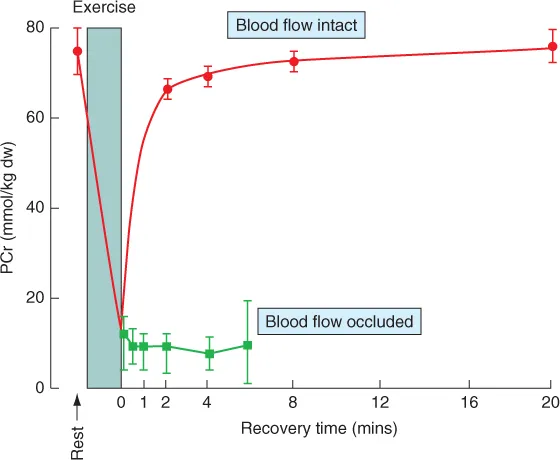
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Part One: Basic Muscle Physiology and Energetics
- Part Two: Fundamentals of Sport and Exercise Biochemistry
- Part Three: Metabolic Regulation in Sport and Exercise
- References and Suggested Readings
- Index