
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Focusing on basic lubrication problems this book offers specific engineering applications. The book introduces methods and programs for the most important lubrication problems and their solutions. It is divided into four parts. The first part is about the general solving methods of the Reynolds equation, including solutions of Reynolds equations with different conditions and their discrete forms, such as a steady-state incompressible slider, journal bearing, dynamic bearing, gas bearing and grease lubrication. The second part gives the 'energy equation solution'. The third part introduces methods and programs for elasto-hydrodynamic lurbication, which links the Reynolds equation with the elastic deformation equation. The final part presents application lubrication programs used in engineering.
- Provides numerical solution methodologies including appropriate software for the hydrodynamic and elasto-hydrodynamic lubrication of bearings
- Offers a clear introduction and orientation to all major engineering lubrication problems and their solutions
- Presents numerical programs for specific applications in engineering, with special topics including grease-lubricated bearings and gas bearings
- Equips those working in tribology and those new to the topic with the fundamental tools of calculation
- Downloadable programs are available at the companion website
With an emphasis on clear explanations, the text offers a thorough understanding of the numerical calculation of lubrication for graduate students on tribology and engineering mechanics courses, with more detailed materials suitable for engineers. This is an accessible reference for senior undergraduate students of tribology and researchers in thin-film fluid mechanics.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1.1 General Reynolds Equation and Its Boundary Conditions
1.1.1 Reynolds Equation
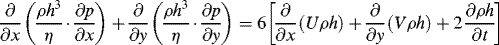
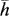
1.1.2 Definite Condition
1.1.2.1 Boundary Condition

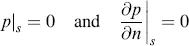
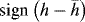

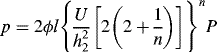
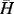
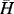
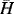
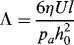
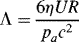
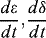
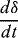
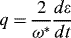
1.1.2.2 Initial Condition
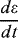
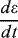
1.1.2.3 Connection Condition
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Part One: Numerical Method for Reynolds Equation
- Part Two: Numerical Method for Energy Equation
- Part Three: Numerical Method for Elastic Deformation and Thermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication
- Part Four: Calculation Programs for Lubrication Analysis in Engineering
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app