
Financial Modelling in Practice
A Concise Guide for Intermediate and Advanced Level
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Financial Modelling in Practice: A Concise Guide for Intermediate and Advanced Level is a practical, comprehensive and in-depth guide to financial modelling designed to cover the modelling issues that are relevant to facilitate the construction of robust and readily understandable models.
Based on the authors extensive experience of building models in business and finance, and of training others how to do so this book starts with a review of Excel functions that are generally most relevant for building intermediate and advanced level models (such as Lookup functions, database and statistical functions and so on). It then discusses the principles involved in designing, structuring and building relevant, accurate and readily understandable models (including the use of sensitivity analysis techniques) before covering key application areas, such as the modelling of financial statements, of cash flow valuation, risk analysis, options and real options. Finally, the topic of financial modelling using VBA is treated. Practical examples are used throughout and model examples are included in the attached CD-ROM.
Aimed at intermediate and advanced level modellers in Excel who wish to extend and consolidate their knowledge, this book is focused, practical, and application-driven, facilitating knowledge to build or audit a much wider range of financial models.
Note: CD-ROM/DVD and other supplementary materials are not included as part of eBook file.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
- AVERAGE calculates the average of a set of numbers.
- COUNT counts the number of cells that contain numbers (COUNTA counts the number of non-empty cells, and so includes the counting of text fields).
- MIN and MAX calculate the minimum and maximum of a set of values.
- PRODUCT multiplies its arguments.
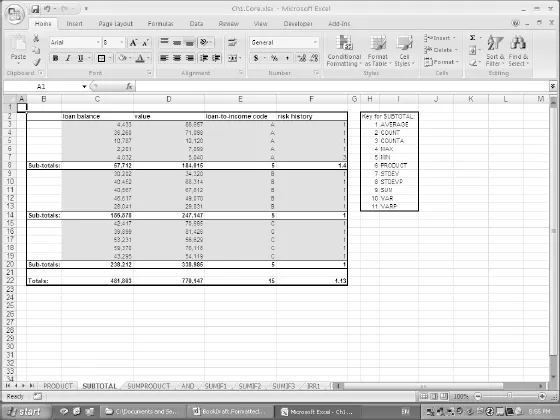
- SUBTOTAL calculates the sum (or other values) of a range of cells, ignoring other SUBTOTAL functions, so avoiding potential double-counting of values.
- SUM adds up a set of numbers.
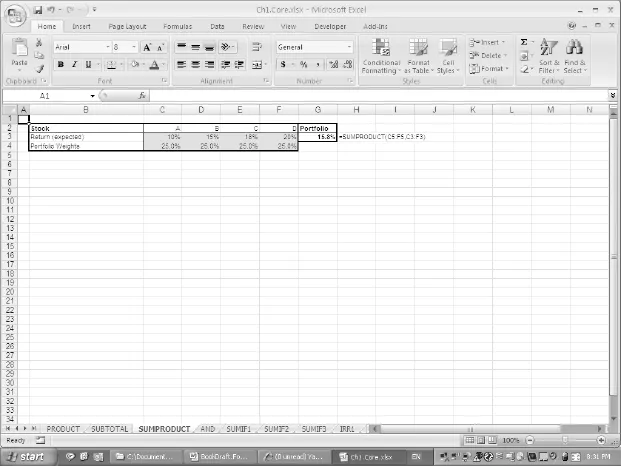
- SUMPRODUCT multiplies the corresponding elements of two ranges and forms their sum.
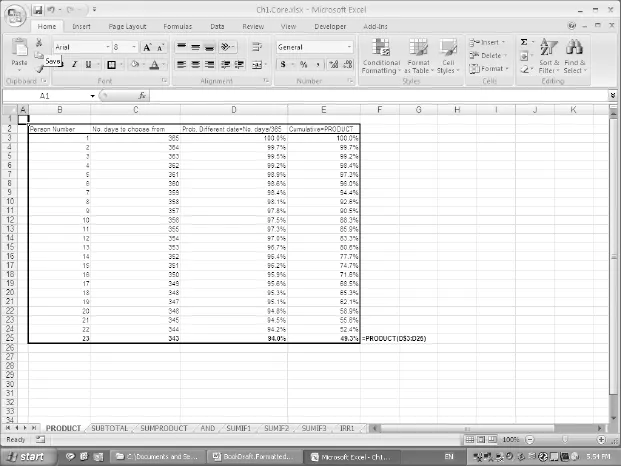
- The creation of subtotals in a large list of data that is sorted into categories.
- In financial statement modelling, where a company’s total assets may be calculated from the (subtotal) of its fixed and current assets, which may themselves each be calculated as the subtotal of a more detailed breakdown (such as equipment, working capital, etc.).
- The analysis of sets of filtered data (see later), where the function ignores any hidden rows that result from a list having been filtered (unlike SUM, COUNT).
- AND checks if two conditions both hold, and returns TRUE or FALSE accordingly. Similarly OR and NOT functions exist. These can be useful to avoid writing embedded IF statements when checking multiple conditions.
- IF checks whether a condition is true or not and returns a specified value in each case. Its use is implicit in a direct comparison expression such as = F7>F6, which would evaluate to either TRUE or FALSE (these are not text strings, but when used in any subsequent formulae, are interpreted by Excel as 1 or 0 respectively). Therefore = 50*(F7>F6) would return either 50 or 0. Similarly, while one may write = IF(F7>F6,1,0), this would not be the same as = IF(F7>F6,“TRUE”,“FALSE”), which returns text strings (and is therefore generally inconvenient when the results of such expressions are to be used in further numerical calculations).
- SUMIF (classified in the Math & Trig category) adds the values of cells in a given range according to whether a criterion is met in another range. Excel 2007 also has a SUMIFS function in which a range is summed according to multiple criteria being met; an example is shown later in this chapter. In addition, in some cases the use of Database functions, PivotTables, or the Conditional Sum Wizard can provide more appropriate alternatives (see later).
- COUNTIF (classified in the Statistical category) counts the number of cells that meet a specified criterion. In Excel 2007, the AVERAGEIF function exists, as do AVERAGEIFS and COUNTIFS when multiple criteria are to be met.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title page
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Dedication
- Background, Objectives and Approach
- About the Author
- Acknowledgements
- Chapter 1: Building Blocks: Selected Excel Functions and Tools
- Chapter 2: Principles of Modelling
- Chapter 3: Financial Statement, Cash Flow and Valuation Modelling
- Chapter 4: Risk Modelling
- Chapter 5: Introduction to Options and Real Options Modelling
- Chapter 6: VBA for Financial Modelling
- Further Reading
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app