
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Exotic Options Trading
About this book
Written by an experienced trader and consultant, Frans de Weert's Exotic Options Trading offers a risk-focused approach to the pricing of exotic options. By giving readers the necessary tools to understand exotic options, this book serves as a manual to equip the reader with the skills to price and risk manage the most common and the most complex exotic options.
De Weert begins by explaining the risks associated with trading an exotic option before dissecting these risks through a detailed analysis of the actual economics and Greeks rather than solely stating the mathematical formulae. The book limits the use of mathematics to explain exotic options from an economic and risk perspective by means of real life examples leading to a practical interpretation of the mathematical pricing formulae.
The book covers conventional options, digital options, barrier options, cliquets, quanto options, outperformance options and variance swaps, and explains difficult concepts in simple terms, with a practical approach that gives the reader a full understanding of every aspect of each exotic option. The book also discusses structured notes with exotic options embedded in them, such as reverse convertibles, callable and puttable reverse convertibles and autocallables and shows the rationale behind these structures and their associated risks.
For each exotic option, the author makes clear why there is an investor demand; explains where the risks lie and how this affects the actual pricing; shows how best to hedge any vega or gamma exposure embedded in the exotic option and discusses the skew exposure.
By explaining the practical implications for every exotic option and how it affects the price, in addition to the necessary mathematical derivations and tools for pricing exotic options, Exotic Options Trading removes the mystique surrounding exotic options in order to give the reader a full understanding of every aspect of each exotic option, creating a useable tool for dealing with exotic options in practice.
" Although exotic options are not a new subject in finance, the coverage traditionally afforded by many texts is either too high level or overly mathematical. De Weert's exceptional text fills this gap superbly. It is a rigorous treatment of a number of exotic structures and includes numerous examples to clearly illustrate the principles. What makes this book unique is that it manages to strike a fantastic balance between the theory and actual trading practice. Although it may be something of an overused phrase to describe this book as compulsory reading, I can assure any reader they will not be disappointed. "
—Neil Schofield, Training Consultant and author of Commodity Derivatives: Markets and Applications
"Exotic Options Trading does an excellent job in providing a succinct and exhaustive overview of exotic options. The real edge of this book is that it explains exotic options from a risk and economical perspective and provides a clear link to the actual profit and pricing formulae. In short, a must read for anyone who wants to get deep insights into exotic options and start trading them profitably. "
—Arturo Bignardi
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
2.1 CALL AND PUT OPTIONS AND FORWARDS
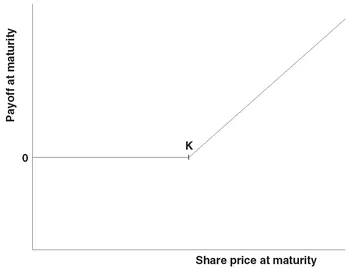
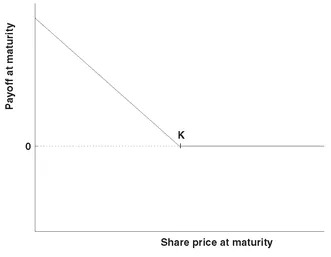
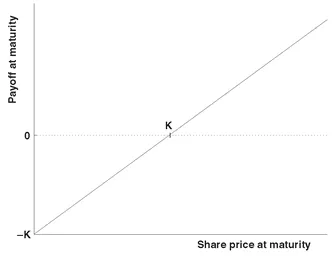
2.2 PRICING CALLS AND PUTS
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Chapter 1 - Introduction
- Chapter 2 - Conventional Options, Forwards and Greeks
- Chapter 3 - Profit on Gamma and Relation to Theta
- Chapter 4 - Delta Cash and Gamma Cash
- Chapter 5 - Skew
- Chapter 6 - Simple Option Strategies
- Chapter 7 - Monte Carlo Processes
- Chapter 8 - Chooser Option
- Chapter 9 - Digital Options
- Chapter 10 - Barrier Options
- Chapter 11 - Forward Starting Options
- Chapter 12 - Ladder Options
- Chapter 13 - Lookback Options
- Chapter 14 - Cliquets
- Chapter 15 - Reverse Convertibles
- Chapter 16 - Autocallables
- Chapter 17 - Callable and Puttable Reverse Convertibles
- Chapter 18 - Asian Options
- Chapter 19 - Quanto Options
- Chapter 20 - Composite Options
- Chapter 21 - Outperformance Options
- Chapter 22 - Best of and Worst of Options
- Chapter 23 - Variance Swaps
- Chapter 24 - Dispersion
- Chapter 25 - Engineering Financial Structures
- Appendix A - Variance of a Composite Option and Outperformance Option
- Appendix B - Replicating the Variance Swap
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app