
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Heterocyclic Chemistry
About this book
Heterocyclic chemistry comprises at least half of all organic chemistry research worldwide. In particular, the vast majority of organic work done in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries is heterocyclic chemistry.
The fifth edition of Heterocyclic Chemistry maintains the principal objective of earlier editions – to teach the fundamentals of heterocyclic reactivity and synthesis in a way that is understandable to second- and third-year undergraduate chemistry students. The inclusion of more advanced and current material also makes the book a valuable reference text for postgraduate taught courses, postgraduate researchers, and chemists at all levels working with heterocyclic compounds in industry.
Fully updated and expanded to reflect important 21st century advances, the fifth edition of this classic text includes the following innovations:
- Extensive use of colour to highlight changes in structure and bonding during reactions
- Entirely new chapters on organometallic heterocyclic chemistry, heterocyclic natural products, especially in biochemical processes, and heterocycles in medicine
- New sections focusing on heterocyclic fluorine compounds, isotopically labeled heterocycles, and solid-phase chemistry, microwave heating and flow reactors in the heterocyclic context
Essential teaching material in the early chapters is followed by short chapters throughout the text which capture the essence of heterocyclic reactivity in concise resumés suitable as introductions or summaries, for example for examination preparation. Detailed, systematic discussions cover the reactivity and synthesis of all the important heterocyclic systems. Original references and references to reviews are given throughout the text, vital for postgraduate teaching and for research scientists. Problems, divided into straightforward revision exercises, and more challenging questions (with solutions available online), help the reader to understand and apply the principles of heterocyclic reactivity and synthesis.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Heterocyclic Nomenclature
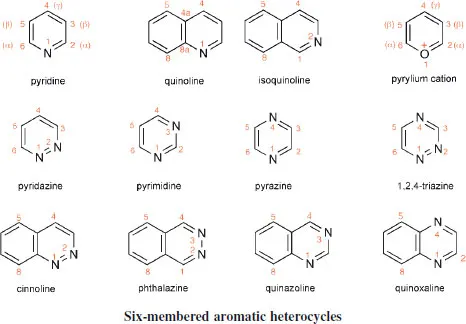
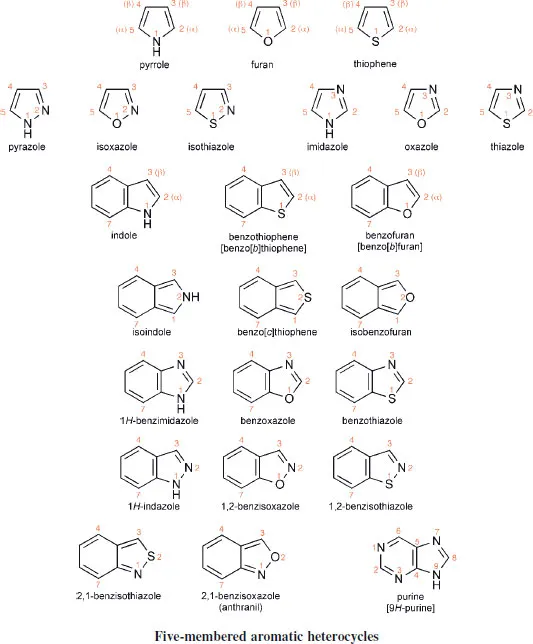
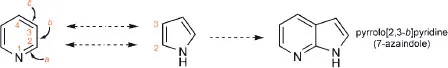
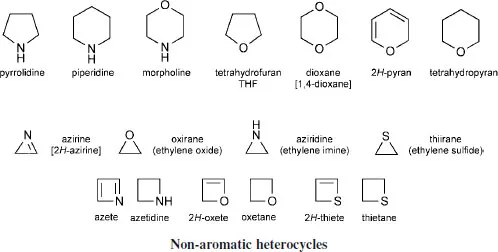
2
Structures and Spectroscopic Properties of Aromatic Heterocycles
2.1 Carbocyclic Aromatic Systems
2.1.1 Structures of Benzene and Naphthalene
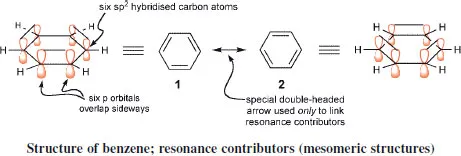
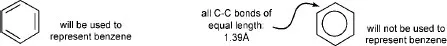
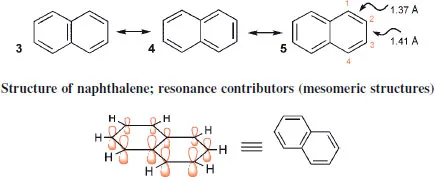
2.1.2 Aromatic Resonance Energy3
Table of contents
- Cover
- Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface to the Fifth Edition
- Biography
- Definitions of Abbreviations
- 1 Heterocyclic Nomenclature
- 2 Structures and Spectroscopic Properties of Aromatic Heterocycles
- 3 Substitutions of Aromatic Heterocycles
- 4 Organometallic Heterocyclic Chemistry
- 5 Methods in Heterocyclic Chemistry
- 6 Ring Synthesis of Aromatic Heterocycles
- 7 Typical Reactivity of Pyridines, Quinolines and Isoquinolines
- 8 Pyridines: Reactions and Synthesis
- 9 Quinolines and Isoquinolines: Reactions and Synthesis
- 10 Typical Reactivity of Pyrylium and Benzopyrylium Ions, Pyrones and Benzopyrones
- 11 Pyryliums, 2- and 4-Pyrones: Reactions and Synthesis
- 12 Benzopyryliums and Benzopyrones: Reactions and Synthesis
- 13 Typical Reactivity of the Diazine: Pyridazine, Pyrimidine and Pyrazine
- 14 The Diazines: Pyridazine, Pyrimidine, and Pyrazine: Reactions and Synthesis
- 15 Typical Reactivity of Pyrroles, Furans and Thiophenes
- 16 Pyrroles: Reactions and Synthesis
- 17 Thiophenes: Reactions and Synthesis
- 18 Furans: Reactions and Synthesis
- 19 Typical Reactivity of Indoles, Benzo[b]thiophenes, Benzo[b]furans, Isoindoles, Benzo[c]thiophenes and Isobenzofurans
- 20 Indoles: Reactions and Synthesis
- 21 Benzo[b]thiophenes and Benzo[b]furans: Reactions and Synthesis
- 22 Isoindoles, Benzo[c]thiophenes and Isobenzofurans: Reactions and Synthesis
- 23 Typical Reactivity of 1,3- and 1,2-Azoles and Benzo-1,3- and-1,2-Azoles
- 24 1,3-Azoles: Imidazoles, Thiazoles and Oxazoles: Reactions and Synthesis
- 25 1,2-Azoles: Pyrazoles, Isothiazoles, Isoxazoles: Reactions and Synthesis
- 26 Benzanellated Azoles: Reactions and Synthesis
- 27 Purines: Reactions and Synthesis
- 28 Heterocycles Containing a Ring-Junction Nitrogen (Bridgehead Compounds)
- 29 Heterocycles Containing More Than Two Heteroatoms
- 30 Saturated and Partially Unsaturated Heterocyclic Compounds: Reactions and Synthesis
- 31 Special Topics
- 32 Heterocycles in Biochemistry; Heterocyclic Natural Products
- 33 Heterocycles in Medicine
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app