![]()
PART I
Banking Business, Bank Capital and Debt Market Instruments
Part I is something of a primer on banking, and is designed to set the scene for beginners, be they students or practitioners. We need to be familiar with the nature of banking business, as well as the types of instruments used in money market trading. We also need to be familiar with banking capital and financial statements, the former preparatory to a discussion of regulatory capital and the Basel rules, the latter simply for general knowledge purposes. So the first part of this book covers all these areas.
We begin with a look at the fundamentals of banking business, and the different elements of bank capital. This is essentially an introduction into the nature of banking. We then look at financial statements, which comprise balance sheet and profit and loss account. The contents of this chapter may appear more at home in a textbook on accounting, but an understanding of ratio analysis is vital for the ALM practitioner, who is concerned with issues such as return on capital.
The remainder of Part I looks at financial market debt instruments, which are the main products issued and traded by banks. Chapter 3 discusses money market instruments and Chapter 4 is concerned with capital market instruments or bonds. For undergraduate students and junior practitioners we cover elements of financial arithmetic, which are essential to an understanding of ALM, in the Appendix at the back of the book.
“[Cassandra is] a bit like me – an achiever. I’ve always been an achiever ... ...I’ve never actually achieved anything, mind...but I’ve always been up there with a shout.”
— Derek ‘Del-Boy’ Trotter, “The Jolly Boys Outing”
Only Fools and Horses
BBC TV 1989
![]()
CHAPTER 1
Bank Business and Bank Capital
Banking has a long and honourable history. Today it encompasses a wide range of activities, of varying degrees of complexity. Whatever the precise business, the common denominators of all banking activities are those of risk, return and the bringing together of the providers of capital. Return on capital is the focus of banking activity. The coordination of all banking activity could be said to be the focus of asset and liability management (ALM), although some practitioners will give ALM a narrower focus. Either way, we need to be familiar with the wide-ranging nature of banking business, and the importance of bank capital. This then acts as a guide for what follows.
In this introductory chapter of the first part of the book, we place ALM in context by describing the financial markets and the concept of bank capital. Subsequent chapters look at money market instruments and the basics of bank financial statements. We begin with a look at the business of banking. We then consider the different types of revenue generated by a bank, the concept of the banking book and the trading book, and financial statements. The chapter concludes with an introduction to the money market, the key area of involvement for an ALM desk.
Banking business
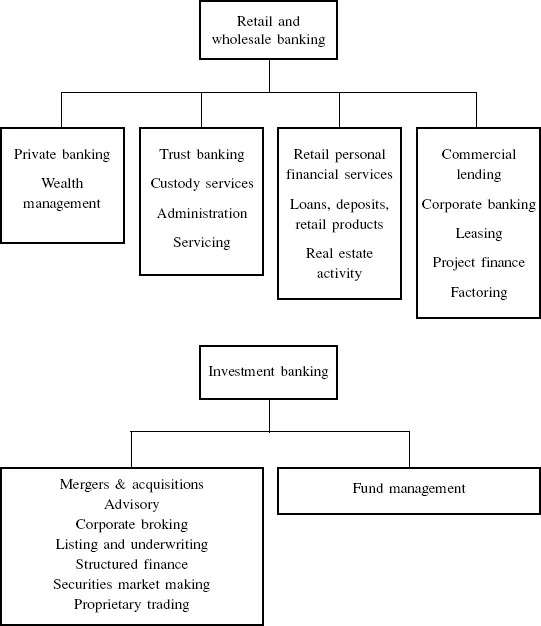
We introduced the different aspects of banking business in the Preface. For the largest banks these aspects are widely varying in nature. For our purposes we may group them together in the form shown in Figure 1.1. Put very simply, “retail” or “commercial” banking covers the more traditional lending and trust activities, while “investment” banking covers trading activity and fee-based income such as stock exchange listing and mergers and acquisition (M&A). The one common objective of all banking activity is return on capital. Depending on the degree of risk it represents, a particular activity will be required to achieve a specified return on the capital it uses. The issue of banking capital is vital to an appreciation of the banking business; entire new business lines (such as securitisation) have been originated in response to a need to generate more efficient use of capital.
As we can see from Figure 1.1, the scope of banking business is vast. The activities range from essentially plain vaNIIla activity, such as corporate lending, to complex transactions such as securitisation and hybrid products trading. There is a vast literature on all these activities, so we do not need to cover them here. However, it is important to have a basic general knowledge of the basic products, so subsequent chapters will introduce these.
ALM is concerned with, among other things, the efficient management of banking capital. It therefore concerns itself with all banking operations, even if the day-to-day contact between the ALM desk (or Treasury desk) with other parts of the bank is remote. The ALM desk will be responsible for the treasury and money markets activities of the entire bank. So if we wish, we could draw a box with ALM in it around the whole of Figure 1.1. This is not to say that the ALM function does all these activities; rather, it is just to make clear that all the various activities represent assets and liabilities for the bank, and one central function is responsible for this side of these activities.
For capital management purposes a bank’s business is organised into a “banking book” and a “trading book”. We consider them next; first though, a word on bank capital.
Capital
Bank capital is the equity of the bank. It is important as it is the cushion that absorbs any unreserved losses that the bank incurs. By acting as this cushion, it enables the bank to continue operating and thus avoid insolvency or bankruptcy during periods of market correction or economic downturn. When the bank suffers a loss or writes off a loss-making or otherwise economically untenable activity, the capital is used to absorb the loss. This can be done by eating into reserves, freezing dividend payments or (in more extreme scenarios) a write-down of equity capital. In the capital structure, the rights of capital creditors, including equity holders, are subordinated to senior creditors and deposit holders.
Banks occupy a vital and pivotal position in any economy, as suppliers of credit and financial liquidity, so bank capital is important. As such, banks are heavily regulated by central monetary authorities, and their capital is subject to regulatory rules governed by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), based in Basel, Switzerland. For this reason its regulatory capital rules are often called the Basel rules. Under the original Basel rules (“Basel I”) a banking institution was required to hold a minimum ca...