New Approach to the Diabetic Foot
Diabetes has reached epidemic proportions, and with it has come a growing number of complex diabetic foot problems. This book is written to help practitioners tackle these problems. It attempts to give enough simple practical information to enable practitioners to understand the natural history of the diabetic foot, rapidly diagnose its problems and confidently undertake appropriate interventions in a timely manner.
Three great pathologies come together in the diabetic foot: neuropathy, ischaemia and infection. Their combined impact results in a swift progression to tissue necrosis, which is the fundamental hallmark of the natural history of the diabetic foot. Progress towards necrosis can be so rapid and devastating that it has come to be regarded as a ‘diabetic foot attack’, similar to the heart and brain attacks of the coronary and cerebrovascular systems. A ‘diabetic foot attack’ can quickly reach the point of no return, with overwhelming necrosis. Thus, it is vital to diagnose it early and provide rapid and intensive treatment. Furthermore, it is important to achieve early recognition of the at-risk foot so as to institute prompt measures to prevent the onset of the ‘diabetic foot attack’. Although there have been many advances in the management of the diabetic foot, it nevertheless remains a major global public health problem. All over the world, health-care systems have failed the diabetic foot patient and a major amputation occurs every 20 s. However, amputations are not inevitable.
In this book we describe a system of multidisciplinary care that has been shown to reduce the number of amputations. It is easily reproducible and has been developed as a successful model of care throughout the world. This system is always being improved and refined, and this book describes the modern version of our diabetic foot management.
One important facet of this approach is the realization that neuropathy revolutionizes the practice of medicine and surgery. Classical symptoms and signs of disease are often absent because their expression depends on an intact peripheral nervous system. Thus, in traditional medical practice, a patient has a symptom, complains of this to their practitioner, who then makes a diagnosis. However, this approach may not work in the patient who has neuropathy. Instead, there must be a meticulous assessment of the patient to elicit subtle symptoms and signs that are clues to disease. Furthermore, an intact nervous system usually reflects symptomatically a ‘picture’ of what is going on inside the body, but in the presence of neuropathy this picture is absent and prompt use of imaging is required. Also, particular attention must be paid to inflammatory markers. Overall, it is important to practise what we call ‘neuropathic medicine’. All practitioners looking after diabetic feet should understand this and adapt their practice of working with diabetic foot patients.
Modern Management of the Diabetic Foot
This consists of four simple steps: assessment, classification, staging and intervention.
Assessment
A simple assessment of the diabetic foot is described to classify and stage the foot, looking for eight clinical features (Table 1.1). This assessment should take no longer than 5 min.
Table 1.1 Eight clinical features in the assessment of the foot.
| Neuropathy |
| Ischaemia |
| Deformity |
| Callus |
| Swelling |
| Skin breakdown |
| Infection |
| Necrosis |
Classification
The diabetic foot can be classified into two groups:
1 Neuropathic foot with palpable pulses
2 Ischaemic foot without pulses and a varying degree of neuropathy.
The neuropathic foot may be further divided into two clinical scenarios:
1 Foot with neuropathic ulceration
2 Charcot foot, which may be secondarily complicated by ulceration.
The ischaemic foot may be divided into four clinical scenarios:
1 Neuroischaemic foot characterized by both ischaemia and neuropathy and complicated by ulcer
2 Critically ischaemic foot
3 Acutely ischaemic foot
4 Renal ischaemic foot characterized by digital necrosis.
Staging
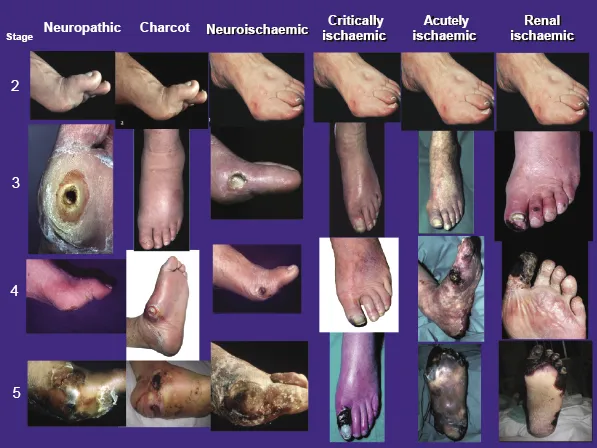
Each of these six clinical scenarios (two neuropathic and four ischaemic) have specific stages in their natural history, and these stages have been described in a simple staging system (Fig. 1.1). This system covers the whole spectrum of diabetic foot disease and describes six stages in the natural history of each of the six clinical scenarios and emphasizes the relentless progression to the end stage necrosis. The stages are briefly summarized in Table 1.2 and will be described in detail in subsequent chapters devoted to each stage.
Table 1.2 Staging the diabetic foot.
|
| 1 | Normal |
| 2 | High risk |
| 3 | Ulcerated |
| 4 | Infected |
| 5 | Necrotic |
| 6 | Unsalvageable |
Intervention
A simple management plan is described for each stage, outlining six aspects of patient treatment within a multidisciplinary framework (Table 1.3).
Table 1.3 Six aspects of patient treatment, within a multidisciplinary framework.
| Wound control |
| Microbiological control |
| Mechanical control |
| Vascular control |
| Metabolic control |
| Educational control |
Assessing the Diabetic Foot
The initial approach to the diabetic foot starts with a simple assessment to enable the practitioner to make a basic classification and staging.
There is a specific search for eight factors, as shown in Table 1.1. Many of these features can be detected by an examination that includes:
- Simple inspection
- Palpation
- Sensory testing.
A complicated examination is not necessary. This chapter describes the search for these individual features and then presents an integrated examination. It is often helpful to detect abnormalities by comparing one foot with the other.
Shoe inspection should be included in the foot assessment and this is described in Chapter 2.
Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common complication of diabetes, affecting 50% of all diabetic patients. Although neuropathy may present with tingling and a feeling of numbness, it is asymptomatic in the majority of patients and neuropathy will only be detected by clinical examination. An important indication of neuropathy will be a patient who fails to complain of pain, even when significant foot lesions are present. Neuropathic patients are at increased risk of injury while walking because of impaired sensation and motor function. Neuropathy also damages proprioception and falls are common.
The presentation of peripheral neuropathy is determined by the impairment of sensory, motor and autonomic nerves. Simple inspection will usually reveal signs of motor and autonomic neuropathy of the feet, but sensory neuropathy must be detected by screening or by a simple sensory examination.
The diabetic patient with peripheral neuropathy affecting the feet and legs may also have syste...