
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Using LEDs, LCDs and GLCDs in Microcontroller Projects
About this book
Describing the use of displays in microcontroller based projects, the author makes extensive use of real-world, tested projects. The complete details of each project are given, including the full circuit diagram and source code. The author explains how to program microcontrollers (in C language) with LED, LCD and GLCD displays; and gives a brief theory about the operation, advantages and disadvantages of each type of display.
Key features:
- Covers topics such as: displaying text on LCDs, scrolling text on LCDs, displaying graphics on GLCDs, simple GLCD based games, environmental monitoring using GLCDs (e.g. temperature displays)
- Uses C programming throughout the book – the basic principles of programming using C language and introductory information about PIC microcontroller architecture will also be provided
- Includes the highly popular PIC series of microcontrollers using the medium range PIC18 family of microcontrollers in the book.
- Provides a detailed explanation of Visual GLCD and Visual TFT with examples.
- Companion website hosting program listings and data sheets
- Contains the extensive use of visual aids for designing LED, LCD and GLCD displays to help readers to understand the details of programming the displays: screen-shots, tables, illustrations, and figures, as well as end of chapter exercises
Using LEDs, LCDS, and GLCDs in Microcontroller Projects is an application oriented book providing a number of design projects making it practical and accessible for electrical & electronic engineering and computer engineering senior undergraduates and postgraduates. Practising engineers designing microcontroller based devices with LED, LCD or GLCD displays will also find the book of great use.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1.1 Microcontrollers and Microprocessors
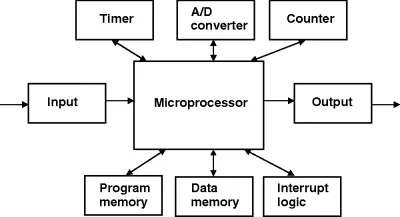
- A microprocessor is a single chip CPU microcontroller containing a CPU, memory, I/O, timers, counters and much of the remaining circuitry of a complete computer system on a single chip.
- The power consumption of a microprocessor based computer is very large, in the order of amperes. On the other hand, the power consumption of a microcontroller based computer is in the range of several hundred milliamperes. In addition, microcontrollers can be operated in sleep modes, which consume currents as low as tens of nanoamperes.
- A microprocessor based computer costs much more than a microcontroller based system.
- Because a microcontroller based system consists of a single chip, it has higher reliability.
- Microprocessor based systems can easily be expanded, for example by adding more memory or I/O chips. It is usually not possible to expand a microcontroller system. If an application requires more memory, more I/O or higher processing power, then a different model microcontroller is usually chosen.
- Offices: in typewriters, computers, calculators, photocopiers, scanners, plotters, elevators, and so on;
- Homes: in microwave ovens, washing machines, alarm clocks, dish washers, hi-fi equipment, DVD players, digital televisions, and so on;
- Industry: in automatic control systems, safety systems, robotics, motor control, and so on;
- Transportation systems: in vehicles, traffic signals, road signs, speed cameras, GPS systems, and so on;
- Supermarkets: in weighing scales, cash registers, electronic signs, card readers, and so on;
- Play: in electronic toys, MP3 players, video games, mobile phones, and so on;
- Education: in electronic white-boards, photocopiers, projectors, calculators, and so on.
1.2 Evolution of the Microcontroller
1.3 Parts of a Microcontroller
1.3.1 Address
1.3.2 ALU
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Microcontrollers and Display Systems
- Chapter 2: PIC18F Microcontrollers
- Chapter 3: C Programming Language
- Chapter 4: PIC Microcontroller Development Tools – Including Display Development Tools
- Chapter 5: Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
- Chapter 6: Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) and mikroC Pro for PIC LCD Functions
- Chapter 7: Graphics LCD Displays (GLCD)
- Chapter 8: Microcontroller Program Development
- Chapter 9: LED Based Projects
- Chapter 10: 7-Segment LED Display Based Projects
- Chapter 11: Text Based LCD Projects
- Chapter 12: Graphics LCD Projects
- Chapter 13: Touch Screen Graphics LCD Projects
- Chapter 14: Using the Visual GLCD Software in GLCD Projects
- Chapter 15: Using the Visual TFT Software in Graphics Projects
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app