
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Solid Waste Technology and Management
About this book
The collection, transportation and subsequent processing of waste materials is a vast field of study which incorporates technical, social, legal, economic, environmental and regulatory issues. Common waste management practices include landfilling, biological treatment, incineration, and recycling – all boasting advantages and disadvantages. Waste management has changed significantly over the past ten years, with an increased focus on integrated waste management and life-cycle assessment (LCA), with the aim of reducing the reliance on landfill with its obvious environmental concerns in favour of greener solutions. With contributions from more than seventy internationally known experts presented in two volumes and backed by the International Waste Working Group and the International Solid Waste Association, detailed chapters cover:
- Waste Generation and Characterization
- Life Cycle Assessment of Waste Management Systems
- Waste Minimization
- Material Recycling
- Waste Collection
- Mechanical Treatment and Separation
- Thermal Treatment
- Biological Treatment
- Landfilling
- Special and Hazardous Waste
Solid Waste Technology & Management is a balanced and detailed account of all aspects of municipal solid waste management, treatment and disposal, covering both engineering and management aspects with an overarching emphasis on the life-cycle approach.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Introduction
Introduction to Waste Management
value for the owner and which the owner wants to discard.’
- Time: If supplies are scarce, for example during war time and embargos, the owner will spend more time and effort repairing an item since the alternative may be costly and hard to find.
- Location: Farming communities may easily make use of food waste for animal feeding, while this is less feasible in a highrise in an urban area.
- State: The item may be repairable depending on its state (price, age, type of damage) and thereby avoid being discarded.
- Income level: The higher your income the more food you may discard or the more items you may discard because they no longer are in fashion or up to date.
- Personal preferences: Certain types of items may be collector’s items or possess veneration for some individuals.
- Oxidizing in contact with other materials resulting in highly exothermic reactions.
- Flammable in contact with air having flashpoint less than 55°C (highly flammable, with a flashpoint less than 21°C).
- Irritant: causing inflammation through contact with skin or mucous membrane.
- Harmful: causing limited health risks through inhalation, ingestion or penetration of skin.
- Toxic: causing serious, acute or chronic health risks and even death through inhalation, ingestion or penetration of skin.
- Carcinogenic: inducing cancer or increasing cancer incidence through inhalation, ingestion or penetration of skin.
- Explosive under the effect of flame, shock or friction.
- Corrosive by destroying living tissue on contacts.
- Infectious due to viable microorganism or their toxins known or reliably believed to cause disease in man or other living organisms.
- ‘Toxic for reproduction’: substances and preparations which, if they are inhaled or ingested or if they penetrate the skin, may induce nonhereditary congenital malformations or increase their incidence.
- Mutagenic: inducing hereditary genetic defects or increasing their incidence through inhalation, ingestion or penetration of skin.
- Releasing toxic gases in contact with water, air or an acid.
- ‘Sensitizing’: substances and preparations which, if they are inhaled or if they penetrate the skin, are capable of eliciting a reaction of hypersensitization such that on further exposure to the substance or preparation, characteristic adverse effects are produced.
- Ecotoxic: presenting any immediate or delayed risks for any sector of the environment.
- Substances capable by any means after disposal of yielding another substance which possesses any of the characteristics listed above.
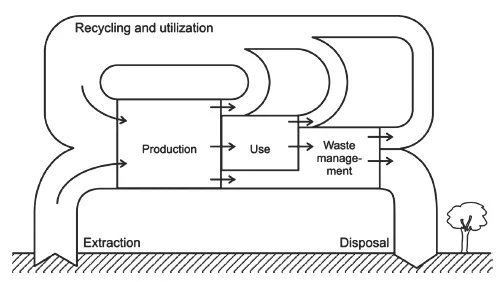
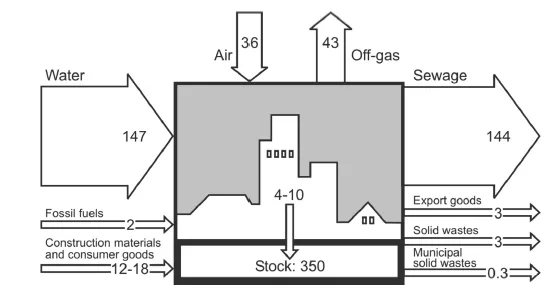
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- List of Contributors
- 1 INTRODUCTION
- 2 WASTE GENERATION AND CHARACTERIZATION
- 3 LCA OF WASTE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
- 4 WASTE MINIMIZATION
- 5 MATERIAL RECYCLING
- 6 COLLECTION
- 7 MECHANICAL TREATMENT
- 8 THERMAL TREATMENT
- 9 BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT
- 10 LANDFILLING
- 11 SPECIAL AND HAZARDOUS WASTE
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app