
eBook - ePub
High Temperature Superconductors
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
High Temperature Superconductors
About this book
This essential reference provides the most comprehensive presentation of state-of-the-art research being conducting worldwide today in this growing field of research and applications. HTS are currently being supported by numerous governmental and industrial initiatives in the USA and Asia and Europe to overcome energy distribution issues and are now being commercialised for power-delivery devices, such as power transmission lines and cables, motors, and generators. Applications in electric utilities include energy-storing devices to help industries avoid dips in electric power, current limiters, and long transmission lines. The technology is particularly thought out for highly-populated and densed areas.
Both editors are leading experts in the field from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. This book can be used as a companion teaching tool, and also as as a research and professional reference.
Both editors are leading experts in the field from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. This book can be used as a companion teaching tool, and also as as a research and professional reference.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Edition
11
General Theory of High-Tc Superconductors
Twenty years after the discovery of high-temperature superconductors, practical superconducting wires made of these materials are now being manufactured, and trials of electrical and industrial applications including a train supported by magnetic levitation, a transmission line, a ship’s engine, and many others are being implemented. High-temperature superconductors have again taken central stage as a dream material after long research and development. To give a better understanding of the latest results, the general theory of superconductors is explained in this chapter.
1.1 Fundamental Properties of Superconductors
1.1.1 The Superconducting Phenomenon
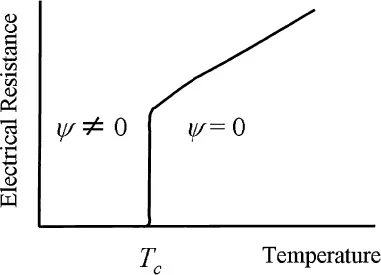
What is the superconducting phenomenon? Figure 1.1 shows the temperature dependence of the electrical resistance of a superconductor. This falls gradually as the superconductor is cooled, before it vanishes suddenly. The temperature at which this occurs is called the critical temperature Tc.
When we consider the process whereby water is changed into ice at its freezing point, the state of water and the state of ice are recognized as different phases. The change between two phases is called a phase transition, and, in a similar way, the superconducting phenomenon is also a kind of phase transition. The super-conductor at temperatures above Tc is in its normal conducting state and has electrical resistance. Here, the electron system does not have order; that is to say, if the order is denoted by ψ, ψ = 0. In contrast, by cooling the superconductor to temperatures below Tc, it enters into the superconducting state, and a certain order in the electron system arises. Then, ψ ≠ 0. When two electrons are united, a Cooper pair is generated, and many such pairs are formed in the cooled superconductor. These pairs are expressed by wave functions with exactly the same amplitude and phase, and these overlap each other, resulting in a macroscopic wave function. The macroscopic wave function is given by the above-mentioned order ψ. The electrical resistance vanishes in the case of ψ ≠ 0; moreover, a variety of other aspects of superconducting phenomena like the persistent current, the Meissner effect, the Josephson effect, and so on, appear. Many textbooks on superconductivity have already been published, and some of these are listed in Refs. [1–6].
Figure 1.1 A typical temperature dependence of an electrical resistance of a superconductor. Tc is the critical temperature. When ψ ≠ 0 (T < Tc) the material is in the superconducting state, whereas ψ = 0 (T > Tc) corresponds to the normal conducting state.
A heat loss due to electrical resistance occurs when a current flows in a metal like copper or aluminum. Such a disadvantageous energy loss in an electric power cable cannot be disregarded. The copper wire could melt by the heating which occurs when a large current is applied to a copper coil to generate a strong magnetic field, whereas no energy loss occurs at all even if a large current is applied to a superconductor below Tc, since the superconductor has zero electrical resistance. Thus, a strong magnetic field can be generated by a superconducting coil and power can be transmitted by a cable without energy loss.
Figure 1.2 shows the evolution of the critical temperature Tc of superconductors. The superconductivity of mercury was discovered first by Kamerlingh-Onnes in 1911 [7]. Further discoveries of superconducting materials followed, and Tc rose slowly. Cuprate superconductor was discovered in 1986 [8, 9], and, after this, Tc increased rapidly [10], reaching 164 K at the high pressure of 30 GPa [11]. This means that the maximum Tc had already reached halfway toward room temperature (~ 300 K). These materials are called high-Tc superconductors. The metallic superconductor MgB2, with Tc = 39 K, was discovered in 2001 [12], becoming a favorite topic in recent years. Even more surprising, a new material group with Tc ≈ 56 K was discovered in 2008, this being an iron pnictide, containing iron and arsenide instead of copper and oxygen [13, 14], and this advance led to renewed interest in high-Tc superconductors.
Conventional Nb–Ti and Nb3Sn superconducting wires are already being put to practical use [15], and the effectiveness of these superconductors has been confirmed by the development of a magnetic levitation train, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), particle accelerators, and so forth. These metallic wires are also essential for the construction of the large-scale superconducting coil of a nuclear fusion device, but they need to be cooled to 4.2 K with the aid of expensive liquid helium.
Figure 1.2 The evolution of the critical temperature Tc of superconductors. The series of high-Tc cuprate superc...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- List of Contributors
- Chapter 1: General Theory of High-Tc Superconductors
- Chapter 2: Characterizing Current Conduction in Coated Conductors Using Transport and Contact-Free Magnetic Methods
- Chapter 3: Characterization: Raman Spectroscopy Measurements and Interpretations
- Chapter 4: YBa2Cu3O7−x Coated Conductors
- Chapter 5: Flux Pinning Enhancement in YBa2Cu3O7–x Films for Coated Conductor Applications
- Chapter 6: Thallium-Oxide Superconductors
- Chapter 7: Recent Progress in Fabrication, Characterization, and Application of Hg-Based Oxide Superconductors
- Chapter 8: Superconductivity in MgB2
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access High Temperature Superconductors by Raghu N. Bhattacharya, M. Parans Paranthaman, Raghu N. Bhattacharya,M. Parans Paranthaman,Raghu N. Bhattacharya in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.