
Trading the Fixed Income, Inflation and Credit Markets
A Relative Value Guide
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Trading the Fixed Income, Inflation and Credit Markets
A Relative Value Guide
About this book
Trading the Fixed Income, Inflation and Credit Markets is a comprehensive guide to the most popular strategies that are used in the wholesale financial markets, answering the question: what is the optimal way to express a view on expected market movements? This relatively unique approach to relative value highlights the pricing links between the different products and how these relationships can be used as the basis for a number of trading strategies.
The book begins by looking at the main derivative products and their pricing interrelationships. It shows that within any asset class there are mathematical relationships that tie together four key building blocks: cash products, forwards/futures, swaps and options. The nature of these interrelationships means that there may be a variety of different ways in which a particular strategy can be expressed. It then moves on to relative value within a fixed income context and looks at strategies that build on the pricing relationships between products as well as those that focus on how to identify the optimal way to express a view on the movement of the yield curve. It concludes by taking the main themes of relative value and showing how they can be applied within other asset classes. Although the main focus is fixed income the book does cover multiple asset classes including credit and inflation.
Written from a practitioner's perspective, the book illustrates how the products are used by including many worked examples and a number of screenshots to ensure that the content is as practical and applied as possible.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
- Bank treasuries with excess cash who are looking to match floating-rate liabilities.
- Central Banks, retail investors and credit-conscious fund managers will buy sovereign-issued FRNs.
- Money market funds and corporates can earn an enhanced yield compared to alternatives such as cash and commercial paper.
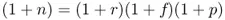
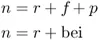
- A required real yield that investors demand over and above expectations of inflation.
- Inflationary expectations over a particular period of time (“breakeven inflation”).
- A factor that captures the combination of a risk premium and a liquidity discount.
- The risk premium is the compensation an investor earns for accepting undesirable inflation risk when holding nominal bonds. One interpretation is that it represents the risk premium demanded by nominal bond investors for unexpected inflation.
- The liquidity discount represents the yield premium that investors demand to hold a less liquid inflation-linked bond.
- If the investor expects inflation to average less than 3.0% over the period, they should hold the nominal bond.
- If the investor expects inflation to average more than 3.0% over the period, they should hold the inflation-linked bond.
- If the investor expects inflation to average 3.0% over the period, they will be indifferent between the two assets.
- A real rate of interest reflects the amount earned or paid after taking into account the impact of inflation.
- It is the market clearing rate of return in excess of expected future inflation that ensures supply meets demand for a particular investment opportunity.
- The return for forgoing consumption today to consume more goods and services tomorrow.
- Reflect the growth in an economy's productivity.
- Represent the rate at which investments are rewarded. Investments compete for capital on the basis of the real yield they offer given their associated risk.
- Slower economic growth prospects, which lowered rates of expected returns across investments.
- The US Federal Reserve was expected to cut interest rates such that inflation would be greater than nominal rates.
- A “flight to quality” by investors, which drove up the price of government securities, reducing their nominal returns.
- An asset is not considered a productive use o...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- About the Authors
- Chapter 1: Product Fundamentals
- Chapter 2: Pricing Relationships
- Chapter 3: Market Risk Management
- Chapter 4: Expressing Views on the Interrelationships between Products
- Chapter 5: Identifying Value in Sovereign Bonds
- Chapter 6: Trading the Yield Curve
- Chapter 7: Relative Value in Credit
- Chapter 8: Relative Value in Inflation
- Chapter 9: Trading Axioms: An A to Z
- Notes
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app