![]()
Chapter 1
Barriers to Oral Bioavailability—an Overview
Ming Hu
Department of Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Houston, Houston, TX
Xiaoling Li
Department of Pharmaceutics and Medicinal Chemistry, University of the Pacific, Stockton, CA
1.1 Introduction
Oral bioavailability of a drug is a measure of the rate and extent of the drug reaching the systemic circulation and is a key parameter that affects its efficacy and adverse effects. Therefore, study of oral bioavailability has received considerable attention in scientific arena. Unfortunately, we are unable to predict bioavailability as a priori to this date, although we have made significant progress in understanding various components of this complex puzzle, including solubility (e.g., aqueous solubility), partition coefficients (e.g., octanol/water), absorption (e.g., permeability across the Caco-2 cell membrane), metabolism (e.g., microsome-mediated phase I metabolism), and excretion (e.g., efflux via p-glycoprotein). However, understanding a few of these components would not allow us to accurately predict a drug candidate's bioavailability in humans. Therefore, oral bioavailability remains to be a highly experimental parameter that eludes prediction from modern computational or experimental approaches, although some preliminary progress has been made in recent years. Continued progress to develop a better and more thorough understanding of physicochemical and biochemical profiling of drug or drug-like molecules would be needed to alleviate the problems associated with bioavailability, and some progress has been made in the last decade (Ho and Chien, 2009). Poor oral bioavailability is also one of the leading causes of failures in clinical trials. This is because compounds with low bioavailability would have a highly variable exposure between individuals. If a compound has an average bioavailability of 5%, it would easily vary in the range of 0.5–10%, a 20-fold difference. This difference makes the selection of an appropriate dose particularly difficult since too little may yield no impact and too much could result in toxicity, which is not acceptable for most drugs that desire chronic administration.
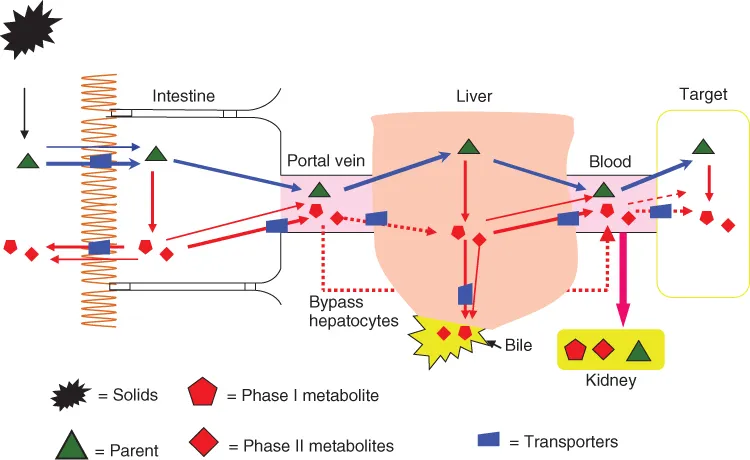
The reasons why oral bioavailability is such a challenge for development of drugs or drug-like substances (e.g., nutraceuticals) are several-fold: first, many physicochemical and biological factors contribute to the bioavailability of a compound; second, many scientific disciplines are involved but few, if any, scientists are good at more than one specific area; third, reliable scaling from animal models to humans is often absent; and fourth, oral bioavailability is often seriously affected by diet and polypharmacy, neither of which can be adequately controlled in a standard clinical trial, considering the diversity of the population—the elderly and seriously ill patients. In addition, we are normally able to gain access only to limited body fluids such as blood and urine, and fluids surrounding the target tissues/cells are often not accessible. This limitation makes bioavailability, a measure of the extent and rate of absorption and the elimination processes, really representing only systemic blood exposure to drugs (Fig. 1.1). Therefore, it is not surprising that bioavailability would sometimes not satisfactorily correlate with efficacy.
Oral bioavailability remains a major challenge to the development of nutraceuticals and naturally derived chemopreventive agents. For example, many scientists are interested in developing plant-derived polyphenols into chemopreventive agents. Polyphenols are derived from plants and consumed in the form of fruits, vegetables, spices, and herbs. In different regions of the world, a large percentage of dietary polyphenols are consumed in the form of flavonoids from various sources of food intake, although cultural and dietary habit dictates which forms of polyphenols are consumed (Fletcher, 2003; Slavin, 2003; Aggarwal et al., 2007). On the other hand, a large percentage of population do not take sufficient quantities of fruits and vegetables for a variety of reasons (Adhami and Mukhtar, 2006). Therefore, scientists are interested in developing a pill that will mimic the effects of ingesting fruits and vegetables. Yet, today their effort has not produced a single polyphenolic chemopreventive agent; the unsuccessful attempt may be attributed to the poor bioavailability of polyphenols (usually <5%). Poor bioavailability makes the evaluation of a chemopreventive agent a particular challenge, since the clinical trials for chemopreventive agents often involve a large population for a prolonged period and extremely high costs.
When all of the above-mentioned challenges are taken into consideration in the product development of drugs or chemopreventive agents, it is obvious that developing an appropriate oral dosage form for drug candidate or candidate of chemopreventive agent is not a trivial or straight forward task. Although pharmaceutical scientists have great difficulty in predicting and enhancing bioavailability, the reward is also immense as the vast majority of top revenue and prescription leaders are orally administered drugs. Therefore, we devote this chapter to briefly introduce each of the factors that influence bioavailability and guide the readers to the appropriate chapters in this book where they can obtain in-depth contents of each related topic.
As an oral dosage form enters the oral cavity and then the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, several barriers must be overcome before it can reach the systemic circulation and the therapeutic target. On its way to the therapeutic target, a drug in a given dosage form will need to first overcome the preabsorption barrier formed by the hostile acidic and enzymatic environment in the stomach and intestine. Then the drug would encounter the primary barrier formed by the biological membrane, that is, the wall of the GI tract. Once a drug successfully passes the intestinal epithelium barrier, the drug will need to overcome another barrier consisting of transporters and enzymes, which utilize the efflux mechanism to pump the drug back to the intestine and degrade the drug via the first-pass effect. There are many factors that will affect a drug molecule's ability to overcome these barriers to reach and remain in the systemic circulation. These factors include the inherent physicochemical properties of the drug molecules, biological characteristics of the GI tract, pathophysiological state, drug–drug or drug–food interactions, etc.
1.1.1 Physicochemical Factors
Various physicochemical factors will affect the oral bioavailability of a drug. The importance of physicochemical properties of a drug molecule in drug absorption or permeation was illustrated by Lipinski's “rule of 5” (Lipinski et al., 2001). Because of the importance of physicochemical properties, a thorough characterization of drug substance would provide fundamental information for drug discovery, as well as for formulation and dosage form development. The characterization of key physicochemical properties of drug substances is described in Chapter 2. One of the key physicochemical properties that play a crucial role in the drug absorption/permeation is solubility. Solubility defines the maximum concentration of a drug available for absorption or permeation, while another important physicochemical property, dissolution rate, controls the rate of the drug available for absorption or permeation. Factors that affect solubility and dissolution rate surely will also influence the bioavailability of the drug. Variation of pH in the GI tract causes drugs to behave differently in terms of solubility and dissolution rate along the GI tract. For an acidic drug, a low solubility and slow dissolution rate in the stomach, where pH is low, can be expected, while for a basic drug, poor solubility owing to precipitation in the intestinal fluids, where pH is high, would happen. An understanding of the basic concept of solubility and dissolution rate forms a solid foundation for comprehending bioavailability. Physicochemical factors also dictate the permeability of drug molecules. Solubility and permeability of a drug are such important factors for drug absorption or bioavailability. The combined effect of these two factors would determine the developability and bioavailability of a compound to a certain extent. Chapters 3 and 4 discuss the two important factors related to drug absorption, namely, solubility and dissolution rate. Chapter 6 provides the fundamentals for drug permeation or absorption. Chapter 7 correlates the physicochemical parameters in vitro and in vivo.
1.1.2 Biological Factors
Oral delivery is a preferred route for the administration of small molecule drugs, because the intestine has a very large surface area, in excess of 200 m2, which is the size of a tennis court. Since oral absorption is limited by the drugs with molecular weight <600 Da and effective absorption window in the GI tract, permeability of drug through intestinal membrane, physiology of GI tract, and metabolism of drugs in absorption and transport have become important factors with respect to bioavailability.
GI tract is not always a hospitable place for drug absorption. Enzymes are secreted in the GI tract at a rate of about 45 g per day in adult humans. Although the primary functions of these enzymes are to digest nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, and nucleotides, their presence is one of the primary reasons why protein and genetic materials (for gene therapy) cannot be delivered orally, unless special formulation approaches are used. In addition to surviving in the hostile environment, a drug needs to overcome the barriers posted by the intestinal epithelium. Intestinal epithelium is a complex tissue with advanced cellular structures and metabolic functionality. The presence of cellular junctions, especially tight junction, severely impedes the passage of molecules with molecular weight >200 Da via the paracellular route. Therefore, the vast majority of the drug molecules must use the transcellular route. Transcellular route is affected by a myriad of interrelated but sometimes competing biological factors. Although it was always believed that lipophilic molecules have an easy access to the transcellular route, the presence of various efflux transporters that preferentially bind with lipophilic molecules could seriously limit the absorption of lipophilic molecules. In addition, if a molecule is too lipophilic (e.g., log P > 5), it may be retained in the cellular membrane. Because intestinal epithelial cells have a functional existence of only three to four days (near or at the tip of the intestinal villus), molecules that bind too tightly will be eventually lost when the epithelial cells slough off. Hydrophilic drug molecules with molecular weight >200 Da cannot penetrate the intestinal epithelium by passive diffusion; they must have special structural motifs that make them attractive for the nutrient transporters such as amino acid transporters (Chapter 17), the small peptide transporter 1 (or PepT1) (Chapter 18), organic ion transporters (Chapter 19), and nucleobases transporters. Assuming drug molecules get into the epithelial cells, there are intestinal first-pass metabolisms capable of further degrading their chance to reach the systemic circulation. These metabolisms are primary phase II metabolism although CYP3A4 is thought to be decently active in the enterocytes. In Chapters 5, 6, 8, and 10, the barriers to oral bioavailability have been described in greater details, with emphasis on GI biology (Chapters 5 and 16), drug absorption (Chapter 6) and metabolism pathways (Chapter 8), and drug excretion by the enterocytes (Chapter 9).
The last major barrier to oral bioavailability, perhaps the most well-known one, is the first-pass metabolism in the liver. Since all drugs absorbed via the GI tract (except the last few centimeters of the rectum) have to enter the portal vein and encounter hepatocytes (each of which can be called metabolic superstar), escaping liver metabolism is the last step in the oral absorption process.
In addition to these important factors, protein binding, which affects drug distribution and free drug available for metabolism, has also featured in this book (Chapter 11). Lastly, another general factor that affects the systemic exposure, elimination via urine, is discussed in Chapter 12. Taken together, substantial information is provided on the pharmacokinetic behaviors of drugs following oral administration (Chapter 13), many of which can be explained using the information learned from previous chapters.
1.1.3 Diet and Food Effects
Development of drugs is becoming more global and multidimensional. The day where a standard diet is appropriate for clinical trials across the globe is probably over. Traditionally, diet and food effects have focused on the protein content, caloric intake, and fat amounts, and few if any have carefully examined the effects of other more exotic dietary components such as spices. More recently, consumers are taking ever large quantities of dietary supplements with increasing frequency and variety. Although we are unable to completely address how these changes in the diet will impact drug bioavailability, various attempts have been made. Chapter 14 has shed some light on this topic.
1.1.4 Drug Interactions
Drug interactions remain a serious concern for the development of new drugs. On the basis of the target patient population, certain types of drug interactions are not acceptable to the manufacturer, FDA (Food and Drug Administration of the United States of America), or both. Traditionally, drug interactions are classified into pharmacodynamic interactions and pharmacokinetic interactions and this book mainly deals with the latter in Chapter 15, since it is a book focused on oral bioavailability.
Classical pharmacokinetic drug interactions typically involve phase I metabolic enzymes, and clinical examples of this type of interactions are well documented in the literature. From a pharmacokinetic point of view, drug interaction may cause a rise or a fall in body exposure of drug, that is, change in Cmax (maximal drug concentration) and/or AUC (area under the curve) values. From a mechanistic point of view, a rise in exposure is typically related to inhibition of enzyme activities or down regulation of relevant metabolic enzymes, whereas a fall in exposure is typically related to activation of dormant enzymes or induction of relevant metabolic enzymes.
More recently, FDA is contemplating the inclusion of efflux transporters into the drug interaction universe, and provisional guidance has been issued. This could further complicate the drug development process and increase the complexity and cost of development. The reasons are several-fold. First, many drugs undergo efflux and phase I metabolism simultaneously and therefore it is difficult to sort out the precise mechanisms of drug interactions. Second, there are few demonstrated clinical cases where interactions with efflux transporters have been confirmed as the sole source of drug interactions. Third, metabolic enzymes may develop significant interplay with the efflux transporters such that it would be necessary to interact with both components of the disposition in order to display clinically significant effects. Many of these are discussed in Chapter 26.
1.1.5 Formulation Factors
Based on the physicochemical and biological factors that affect the bioavailability, we can use different strategies to overcome the barriers for bioavailability (Chaubal, 2004). One can design a dosage form that can avoid the harsh environment in the stomach or optimally utilize the absorption window. For example, an enteric-coated dosage form will not dissolve until it reaches the intestine while a gastroretentive drug delivery system can prolong the resident time of dosage forms in the GI tract. Oral dosage forms can ...