
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Fundamentals of Stochastic Networks
About this book
An interdisciplinary approach to understanding queueing and graphical networks
In today's era of interdisciplinary studies and research activities, network models are becoming increasingly important in various areas where they have not regularly been used. Combining techniques from stochastic processes and graph theory to analyze the behavior of networks, Fundamentals of Stochastic Networks provides an interdisciplinary approach by including practical applications of these stochastic networks in various fields of study, from engineering and operations management to communications and the physical sciences.
The author uniquely unites different types of stochastic, queueing, and graphical networks that are typically studied independently of each other. With balanced coverage, the book is organized into three succinct parts:
-
Part I introduces basic concepts in probability and stochastic processes, with coverage on counting, Poisson, renewal, and Markov processes
-
Part II addresses basic queueing theory, with a focus on Markovian queueing systems and also explores advanced queueing theory, queueing networks, and approximations of queueing networks
-
Part III focuses on graphical models, presenting an introduction to graph theory along with Bayesian, Boolean, and random networks
The author presents the material in a self-contained style that helps readers apply the presented methods and techniques to science and engineering applications. Numerous practical examples are also provided throughout, including all related mathematical details.
Featuring basic results without heavy emphasis on proving theorems, Fundamentals of Stochastic Networks is a suitable book for courses on probability and stochastic networks, stochastic network calculus, and stochastic network optimization at the upper-undergraduate and graduate levels. The book also serves as a reference for researchers and network professionals who would like to learn more about the general principles of stochastic networks.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
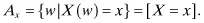
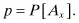
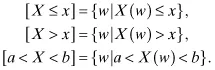
- P[X ≤ x] is the probability that X takes a value less than or equal to x.
- P[X > x] is the probability that X takes a value greater than x; this is equal to 1 – P[X ≤ x].
- P[a < X < b] is the probability that X takes a value that strictly lies between a and b.
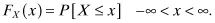
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Copyright page
- PREFACE
- 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN PROBABILITY
- 2 OVERVIEW OF STOCHASTIC PROCESSES
- 3 ELEMENTARY QUEUEING THEORY
- 4 ADVANCED QUEUEING THEORY
- 5 QUEUEING NETWORKS
- 6 APPROXIMATIONS OF QUEUEING SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
- 7 ELEMENTS OF GRAPH THEORY
- 8 BAYESIAN NETWORKS
- 9 BOOLEAN NETWORKS
- 10 RANDOM NETWORKS
- REFERENCES
- Index
- Download CD/DVD content