
Strategies to the Prediction, Mitigation and Management of Product Obsolescence
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Strategies to the Prediction, Mitigation and Management of Product Obsolescence
About this book
Supply chains for electronic products are primarily driven by consumer electronics. Every year new mobile phones, computers and gaming consoles are introduced, driving the continued applicability of Moore's law. The semiconductor manufacturing industry is highly dynamic and releases new, better and cheaper products day by day. But what happens to long-field life products like airplanes or ships, which need the same components for decades? How do electronic and also non-electronic systems that need to be manufactured and supported of decades manage to continue operation using parts that were available for a few years at most? This book attempts to answer these questions.
This is the only book on the market that coversobsolescence forecasting methodologies, includingforecasting tactics for hardware and software that enable cost-effective proactive product life-cycle management. This book describes how to implement a comprehensive obsolescence management system within diverse companies. Strategies to the Prediction, Mitigation and Management of Product Obsolescence is a must-have work for all professionals in product/project management, sustainment engineering and purchasing.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
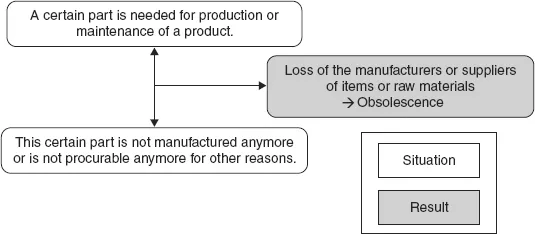
- Rapid technological development makes a product or part unusable for technical, economical, or legal reasons (Feldmann and Sandborn, 2007)
- The original component manufacturer (OCM) or original equipment manufacturer (OEM) disappears from the market for various reasons (Atterbury, 2005)
- The OCM or OEM is not willing to continue producing a part for economic reasons (usually precipitated by a drop in demand for the part) (Atterbury, 2005)
- Chemical or physical aging processes of parts placed in storage can destroy parts or make it impossible to use existing part inventories in products
- Logistical Loss of the ability to procure the parts, materials, manufacturing, or software necessary to manufacture and/or support a product.
- Functional The product or subsystem still operates as intended and can still be manufactured and supported, but the specific requirements for the product have changed; as a result the product’s current function, performance, or reliability (level of qualification) become obsolete. For consumer products, functional obsolescence is the customer’s problem; for more complex systems (such as avionics) it is both the manufacturer’s and customer’s problem. For complex systems, the functional obsolescence of a subsystem is often caused by changes made to other portions of the system.
- Technological More technologically advanced components have become available. This may mean that inventory still exists or can be obtained for older parts that are used to manufacture and support the product, but it becomes a technological obsolescence problem when suppliers of older parts no longer support them.
- Functionality Improvement Dominated Obsolescence (FIDO) Manufacturers cannot maintain market share unless they evolve their products in order to keep up with competition and customer expectations (manufacturers are forced to change their products by the market). Note that this differs from functional obsolescence in that for commercial products FIDO obsolescence is forced upon the manufacturers and functional obsolescence is forced upon the customers.
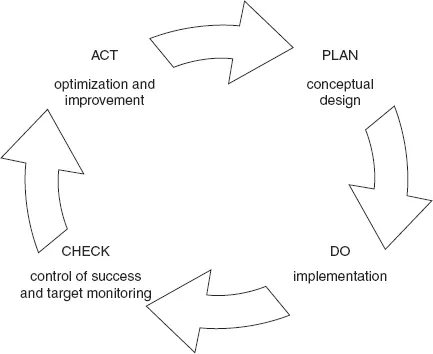
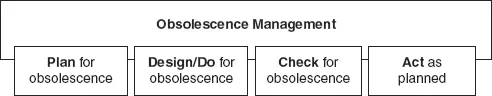
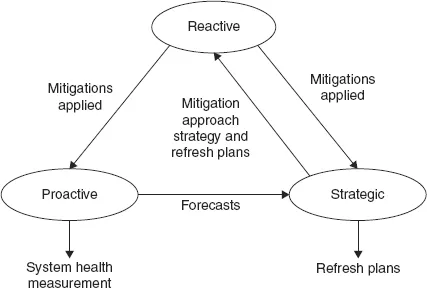
Table of contents
- Cover
- Contents
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Obsolescence Problems
- Chapter 2: Part Change and Discontinuation Management
- Chapter 3: Introduction to Electronic Part Product Life Cycles
- Chapter 4: Obsolescence Forecasting Methodologies
- Chapter 5: Case Study Hardware Forecasts and Trends
- Chapter 6: Software Obsolescence
- Chapter 7: Reactive Obsolescence Management
- Chapter 8: Proactive Obsolescence Management
- Chapter 9: Strategic Obsolescence Management
- Chapter 10: Obsolescence Management Standards and Organizations
- References
- Index