
LTE, WiMAX and WLAN Network Design, Optimization and Performance Analysis
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
LTE, WiMAX and WLAN Network Design, Optimization and Performance Analysis
About this book
LTE, WiMAX and WLAN Network Design, Optimization and Performance Analysis provides a practical guide to LTE and WiMAX technologies introducing various tools and concepts used within. In addition, topics such as traffic modelling of IP-centric networks, RF propagation, fading, mobility, and indoor coverage are explored; new techniques which increase throughput such as MIMO and AAS technology are highlighted; and simulation, network design and performance analysis are also examined. Finally, in the latter part of the book Korowajczuk gives a step-by-step guide to network design, providing readers with the capability to build reliable and robust data networks.
By focusing on LTE and WiMAX this book extends current network planning approaches to next generation wireless systems based on OFDMA, providing an essential resource for engineers and operators of fixed and wireless broadband data access networks. With information presented in a sequential format, LTE, WiMAX and WLAN Network Design, Optimization and Performance Analysis aids a progressive development of knowledge, complementing latter graduate and postgraduate courses while also providing a valuable resource to network designers, equipment vendors, reference material, operators, consultants, and regulators.
Key Features:
- One of the first books to comprehensively explain and evaluate LTE
- Provides an unique explanation of the basic concepts involved in wireless broadband technologies and their applications in LTE, WiMAX, and WLAN before progressing to the network design
- Demonstrates the application of network planning for LTE and WiMAX with theoretical and practical approaches
- Includes all aspects of system design and optimization, such as dynamic traffic simulations, multi-layered traffic analysis, statistical interference analysis, and performance estimations
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
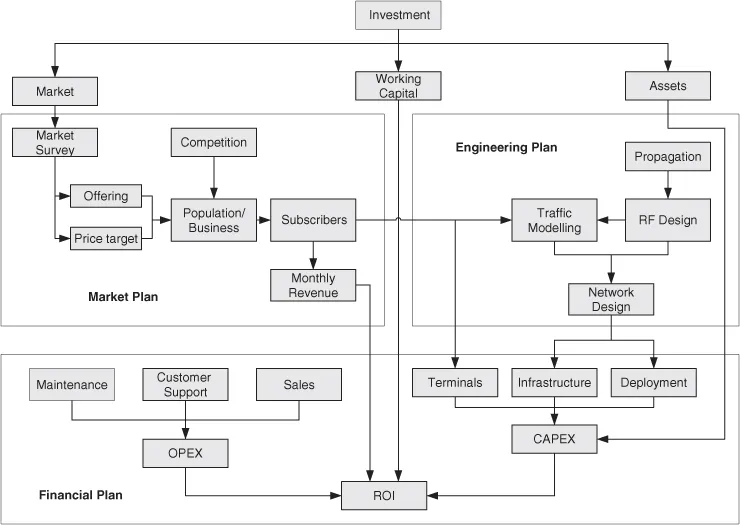
- the market plan;
- the engineering plan;
- the financial plan.
- In the exploratory case, options are left wide open and the results from the research will define the outcome.
- In the confirmatory case, a set of assumptions is made and are confirmed or not by the research.
- market information: where information is collected;
- market segmentation: where demographic, psychographic, ethnographic and lifestyle information is gathered;
- market trends: where market evolution over time is predicted.
- Market scan: collection and analysis of available data that can contribute to the subject. Optionally customer visits can be done at the location where they use the service (businesses or residences), to ask broad questions about their satisfaction with existing services and their willingness to accept alternative offerings.
- Options generation: unconstrained options should be formulated to define all possible offerings.
- Option selection: each option should be evaluated based on the previously collected data and the best ones selected. The proper technique for this selection is choice modeling, which categorizes the data for each choice.
- Selected options evaluation: a customer survey should be done, with questions specific to each option.
- Service target area (STA): area in which service should be provided. It can constitute a single continuous area or several separate areas. These areas should be then divided in sub-areas classified by characteristics such as type of service expected and demand.
- Product: product to be offered, its features and restrictions. This includes service plans and its SLA (service level agreement).
- Service coverage: coverage area.
- Client demographics for the STA.
- Client evolution over the years.
- RF signal propagation, which depends on the environment and is mistakenly used as the sole criterion.
- Location where service will be provided (rooftop, outdoor, indoor).
- Spectrum availability and, consequently, expected interference.
- Equipment to be used.
- Amount of traffic to be carried in each location and its distribution.
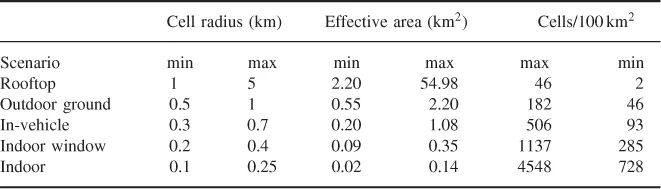
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- About the Author
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- List of Abbreviations
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: The Business Plan
- Chapter 2: Data Transmission
- Chapter 3: Market Modeling
- Chapter 4: Signal Processing Fundamentals
- Chapter 5: RF Channel Analysis
- Chapter 6: RF Channel Performance Prediction
- Chapter 7: OFDM
- Chapter 8: OFDM Implementation
- Chapter 9: Wireless Communications Network (WCN)
- Chapter 10: Antenna and Advanced Antenna Systems
- Chapter 11: Radio Performance
- Chapter 12: Wireless LAN
- Chapter 13: WiMAX
- Chapter 14: Universal Mobile Telecommunication System—Long Term Evolution (UMTS-LTE)
- Chapter 15: Broadband Standards Comparison
- Chapter 16: Wireless Network Design
- Chapter 17: Wireless Market Modeling
- Chapter 18: Wireless Network Strategy
- Chapter 19: Wireless Network Design
- Chapter 20: Wireless Network Optimization
- Chapter 21: Wireless Network Performance Assessment
- Chapter 22: Basic Mathematical Concepts Used in Wireless Networks
- Appendix
- Further Reading
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app