
eBook - ePub
Managing Financial Risk and Its Interaction with Enterprise Risk Management
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Managing Financial Risk and Its Interaction with Enterprise Risk Management
About this book
This chapter first discusses financial risk management from a broad perspective, including possible definitions and examples of industry applications of financial hedging. The discussion then moves to a basic review of the theoretical rationales for managing (financial) risk and the related empirical findings.
The potential for the interaction of financial hedging with other areas of risk management (such as operational and strategic) is then explored. Finally, there is a discussion regarding the lessons that can be applied to Enterprise Risk Management from the knowledge base about financial hedging.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Managing Financial Risk and Its Interaction with Enterprise Risk Management by Daniel A. Rogers in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Finance. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
CHAPTER 18
Managing Financial Risk and Its Interaction with Enterprise Risk Management
INTRODUCTION
Financial risk management encompasses corporate strategies of employing financial transactions to eliminate or reduce measurable risks. Most businesses face financial risks of some sort, such as currency price volatility, interest rate changes, commodity price fluctuations, or from some other source.
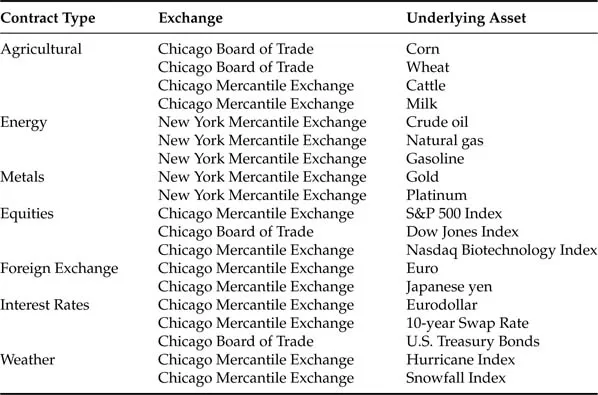
A key attribute of a financial risk is that it can be managed by entering into some form of contract that can be settled in cash. Classic forms of contracts with these characteristics include forward contracts privately arranged between two parties or futures contracts traded on exchanges located around the world. Exhibit 18.1 includes an overview of some of the types of contracts traded at several of the largest futures exchanges in the United States. As may be seen from the wide array of contract types and underlying assets, futures markets exist to manage risks as disparate as those arising from the stock market (i.e., S&P 500) to the amount of snowfall in Boston or New York City.
Financial risk management strategies, often called financial “hedging,” can be considered as a predecessor in the evolution of enterprise risk management (ERM) programs. ERM addresses a far broader array of risks than those that can easily be hedged using financial contracts. However, hedging of financial risk by firms around the world has been sufficiently commonplace that this behavior has been well studied, especially over the last 15 years. Given the considerable amount of research that has been completed on the benefits of financial hedging, the findings are relevant to firms considering the implementation of broader risk management strategies such as ERM.
In this chapter the discussion first provides additional background on financial risk management, including possible definitions and examples of industry applications of financial hedging. The discussion then moves to a basic review of the theoretical rationales for managing (financial) risk and the related empirical findings. The potential for the interaction of financial hedging with other areas of risk management (such as operational and strategic) is then explored. Finally, there is a discussion regarding the lessons that can be applied to ERM from the knowledge base about financial hedging.
Exhibit 18.1 Examples of Contracts Traded at Major U.S. Futures Exchanges
WHAT IS FINANCIAL RISK AND HOW IS IT MANAGED?
In the context of corporate risk management, financial risk has two necessary characteristics. The first characteristic of financial risk is that it is an exogenous event (i.e., outside the company’s control) having the potential to affect a financial outcome. Any (or all) of the following are potential consequences of the realization of a corporate financial risk:
- Reduced cash flow.
- Reduced market value.
- Reduced accounting income.
The second characteristic of financial risk is that it can be reduced by entering into a financial contract with cash settlement. The most common means for corporations to manage financial risk is by using derivative financial instruments, such as forward or futures contracts, swap contracts, and/or option contracts. Derivative contracts used can be exchange-traded or over-the-counter (OTC) contracts that are privately negotiated.
In this section, there are straightforward examples of various types of financial risks that are commonly experienced by corporations. For each case, there is an example as to how the risk can be managed by using a specific derivative contract.
Case 1: Currency Price Risk: The Multinational Corporation
At the end of 2007, Coca-Cola Company generates revenues in more than 200 countries. Given the multinational flavor of its operations, it is natural to expect Coca-Cola to be significantly affected by currency fluctuations. Box 18.1 shows the general currency risk disclosure contained in Coca-Cola’s 10-K filing for 2007.1
Box 18.1 Coca-Cola’s Currency Risk Disclosure in SEC 10-K Filing
Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange could affect our financial results.
We earn revenues, pay expenses, own assets and incur liabilities in countries using currencies other than the U.S. dollar, including the euro, the Japanese yen, the Brazilian real and the Mexican peso. In 2007, we used 67 functional currencies in addition to the U.S. dollar and derived approximately 74 percent of our net operating revenues from operations outside of the United States. Because our consolidated financial statements are presented in U.S. dollars, we must translate revenues, income...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Chapter 18: Managing Financial Risk and Its Interaction with Enterprise