
- 256 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Elementary, yet authoritative and scholarly, this book offers an excellent brief introduction to the classical theory of differential geometry. It is aimed at advanced undergraduate and graduate students who will find it not only highly readable but replete with illustrations carefully selected to help stimulate the student's visual understanding of geometry. The text features an abundance of problems, most of which are simple enough for class use, and often convey an interesting geometrical fact. A selection of more difficult problems has been included to challenge the ambitious student.
Written by a noted mathematician and historian of mathematics, this volume presents the fundamental conceptions of the theory of curves and surfaces and applies them to a number of examples. Dr. Struik has enhanced the treatment with copious historical, biographical, and bibliographical references that place the theory in context and encourage the student to consult original sources and discover additional important ideas there.
For this second edition, Professor Struik made some corrections and added an appendix with a sketch of the application of Cartan's method of Pfaffians to curve and surface theory. The result was to further increase the merit of this stimulating, thought-provoking text — ideal for classroom use, but also perfectly suited for self-study. In this attractive, inexpensive paperback edition, it belongs in the library of any mathematician or student of mathematics interested in differential geometry.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
CURVES
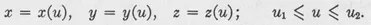

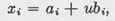
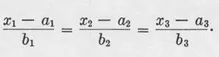
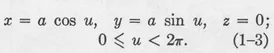

Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- PREFACE
- BIBLIOGRAPHY
- CHAPTER 1 - CURVES
- CHAPTER 2 - ELEMENTARY THEORY OF SURFACES
- CHAPTER 3 - THE FUNDAMENTAL EQUATIONS
- CHAPTER 4 - GEOMETRY ON A SURFACE
- CHAPTER 5 - SOME SPECIAL SUBJECTS
- SOME PROBLEMS AND PROPOSITIONS
- APPENDIX - THE METHOD OF PFAFFIANS IN THE THEORY OF CURVES AND SURFACES
- ANSWERS TO PROBLEMS
- APPENDIX
- INDEX
- A CATALOG OF SELECTED DOVER BOOKS IN SCIENCE AND MATHEMATICS
- DOVER BOOKS ON MATHEMATICS
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app