
An Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier Series
- 159 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
An Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier Series
About this book
This book arose out of the authors' desire to present Lebesgue integration and Fourier series on an undergraduate level, since most undergraduate texts do not cover this material or do so in a cursory way. The result is a clear, concise, well-organized introduction to such topics as the Riemann integral, measurable sets, properties of measurable sets, measurable functions, the Lebesgue integral, convergence and the Lebesgue integral, pointwise convergence of Fourier series and other subjects.
The authors not only cover these topics in a useful and thorough way, they have taken pains to motivate the student by keeping the goals of the theory always in sight, justifying each step of the development in terms of those goals. In addition, whenever possible, new concepts are related to concepts already in the student's repertoire.
Finally, to enable readers to test their grasp of the material, the text is supplemented by numerous examples and exercises. Mathematics students as well as students of engineering and science will find here a superb treatment, carefully thought out and well presented , that is ideal for a one semester course. The only prerequisite is a basic knowledge of advanced calculus, including the notions of compactness, continuity, uniform convergence and Riemann integration.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
The Riemann Integral
1. Definition of the Riemann Integral
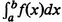
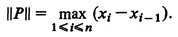
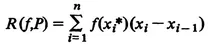
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- CHAPTER 1 - The Riemann Integral
- CHAPTER 2 - Measurable Sets
- CHAPTER3 - Properties of Measurable Sets
- CHAPTER 4 - Measurable Functions
- CHAPTER 5 - The Lebesgue Integral
- CHAPTER6 - Convergence and The Lebesgue Integral
- CHAPTER7 - Function Spaces and L2
- CHAPTER 8 - The L2 Theory of Fourier Series
- CHAPTER 9 - Pointwise Convergence of Fourier Series
- Appendix
- Bibliography
- INDEX
- A CATALOG OF SELECTED DOVER BOOKS IN SCIENCE AND MATHEMATICS
- CATALOG OF DOVER BOOKS