
- 256 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Calculus of Variations
About this book
Based on a series of lectures given by I. M. Gelfand at Moscow State University, this book actually goes considerably beyond the material presented in the lectures. The aim is to give a treatment of the elements of the calculus of variations in a form both easily understandable and sufficiently modern. Considerable attention is devoted to physical applications of variational methods, e.g., canonical equations, variational principles of mechanics, and conservation laws.
The reader who merely wishes to become familiar with the most basic concepts and methods of the calculus of variations need only study the first chapter. Students wishing a more extensive treatment, however, will find the first six chapters comprise a complete university-level course in the subject, including the theory of fields and sufficient conditions for weak and strong extrema. Chapter 7 considers the application of variational methods to the study of systems with infinite degrees of freedom, and Chapter 8 deals with direct methods in the calculus of variations. The problems following each chapter were made specially for this English-language edition, and many of them comment further on corresponding parts of the text. Two appendices and suggestions for supplementary reading round out the text.
Substantially revised and corrected by the translator, this inexpensive new edition will be welcomed by advanced undergraduate and graduate students of mathematics and physics.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
ELEMENTS
OF THE THEORY
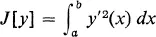
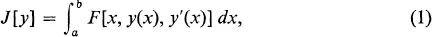
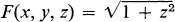
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Authors’ Preface
- Translator’s Preface
- Table of Contents
- 1 Elements of the Theory
- 2 Further Generalizations
- 3 The General Variation of a Functional
- 4 The Canonical form of the Euler Equations and Related Topics
- 5 The second Variation. Sufficient Conditions for a weak Extremum
- 6 Fields. Sufficient Conditions for a Strong Extremum
- 7 Variational Problems Involving Multiple Integrals
- 8 Direct Methods in the Calculus of Variations
- Appendix I Propagation of Disturbances and the Canonical Equations
- Appendix II Variational methods in Problems of optimal control
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app