
eBook - ePub
Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices
About this book
Energy storage devices are considered to be an important field of interest for researchers worldwide. Batteries and supercapacitors are therefore extensively studied and progressively evolving. The book not only emphasizes the fundamental theories, electrochemical mechanism and its computational view point, but also discusses recent developments in electrode designing based on nanomaterials, separators, fabrication of advanced devices and their performances.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices by Poulomi Roy, S. K. Srivastava, Poulomi Roy,S. K. Srivastava,S. K. Srivastava in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Energy. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Part 1
GENERAL INTRODUCTION TO BATTERY AND SUPERCAPACITOR, FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS CHARACTERIZATION TECHNIQUES
Chapter 1
Electrochemistry of Rechargeable Batteries Beyond Lithium-Based Systems
Brij Kishore, Shyama Prasad Mohanty and Munichandraiah Nookala*
Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India
*Corresponding author: [email protected]
Abstract
The state-of-art, Li-ion battery is the most preferred system among electrochemical energy conversion devices in recent years. The other battery systems based on Li such as Li-S and Li-O2 are either at commercialization or prototype stage. The specific energy of systems based on Li is the greatest among all known battery systems. However, the global raw material resources of Li are limited (0.007% in earth crust), and they are unevenly distributed on the earth. As a consequence, it is likely that there can be lithium crisis in the future affecting the production of Li-based rechargeable batteries for large scale applications such as electrical vehicles. Rechargeable batteries based on Na, Mg and K are expected to be viable substitutes for Li based batteries. Research activities are in progress on several electrode materials, which provide high specific capacity, cycling stability, long cycle-life, etc. The cathode materials for Na-ion batteries include layered sodium transition metal oxides, sodium transition metal polyanions such as phosphates, pyrophosphates, and fluorophosphates. Among the anodes, the most studied materials are hard carbons, low potential transition metal oxides and phosphates, and alloys of Sn, Sb, Ge, etc. The research activities for K-ion batteries are still in infancy, and K-S and K-O2 have attracted attention in recent years. The cathode materials of interest are Prussian green and Prussian blue. Several other materials analogous to Li and Na based materials may soon pick up as research interest. For the anode materials, carbon and potassium titanates are good contenders. The chapter reviews major advances in Li-based systems, detailed studies on electrode materials for emerging Na- and K-based systems, and also Mg-based rechargeable batteries.
Keywords: Cathode, anode, electrolyte, Li-based batteries, Na-based batteries, K-based batteries, Mg-based batteries
Ever since the demonstration of Voltaic piles by Alessando Volta in 1800, batteries have been under use for a variety of applications. Their importance has gained rapid strides with the advancement of electronics and also due to dwindling resources for fossil fuels. Although rechargeable batteries such as lead-acid batteries have been widely used over more than 150 years, the recently invented Li-ion batteries have started dominating the battery market. In the present chapter, the research progress made in recent years on future battery systems beyond Li-based batteries is reviewed.
1.1 Lithium-Based Batteries
The position of lithium in periodic table and in electrochemical series projects it as an excellent electrode material for battery application. Lithium-based cells can deliver high voltage (~4 V), high volumetric as well as gravimetric energy density and hence occupy a leading position in usage for portable electronic devices. The evolution of Li metal-based cells started with primary batteries and extended to secondary batteries unsuccessfully. At present, lithium–sulfur and lithium–air batteries employing Li metal are envisioned as future high energy density batteries.
1.1.1 Lithium Primary Batteries
A lithium primary battery utilizes Li metal as the anode [1]. The electrochemical reactions are irreversible. Energy density of 200 Wh kg–1 or 400 Wh l–1 can be obtained from Li-based primary batteries. Advantages of such batteries include a wide operating temperature (70 to –40°C) and good shelf life. Depending on the cathode and electrolyte used, the Li primary batteries are classified into different categories. One type is soluble cathode based battery where the cathode is either liquid (SOCl2) or gas (SO2). An organic solvent along with a Li salt serves as the electrolyte. In SOCl2 based battery, SOCl2 performs the role of solvent and a porous carbon at cathode provides the framework for electrochemical reaction. The following reactions occur, which lead to generation of electrical energy.
(1.1)
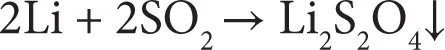
(1.2)
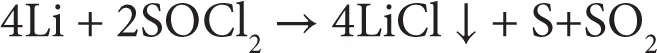
Another type is solid cathode based battery where materials such as CuO, MnO2, FeS2, (CF)n, etc., have been utilized. Such active materials are combined with conducting carbon...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Preface
- Part 1: General Introduction to Battery and Supercapacitor, Fundamental Physics Characterization Techniques
- Part 2: Battery: Anode, Cathode and Non-Li-Ion Batteries
- Part 3: Supercapacitor: Pseudocapacitor, EDLC
- Part 4: Outlook and Conclusion
- Index
- End User License Agreement