
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Economic growth and rising levels of consumption in developing and developed countries has been observed as being deeply coupled with natural resource usage and material consumption. The increasing need for natural resources has raised concerns regarding issues such as resource scarcity, undesirable environmental impacts due to material extraction, primary production, and suboptimal product disposal, and social or political tensions. Product End-of-Life (EoL) options, such as reusing or recycling, attempt to limit or reduce the amount of waste sent to a landfill, providing strategic means to decouple the link between economic growth and resource usage. These EoL options have the potential to close material loops, further utilizing wastes as resources, reducing environmental impacts, conserving natural resources, reducing material prices, and providing job opportunities in developing countries. Remanufacturing, on the other hand, is a unique EoL option due to increasing the number of life cycles of a product before final disposal. First, recurring environmental benefits, such as emission and raw material extraction avoidance are obtained with each additional product life cycle. Second, individual resource efficiency yields increase through product remanufacture. Resource efficiency or, using more with less will continue to compound with each additional life cycle. Third, recirculating products decreases the demand and dependency for primary resource production, further closing the material loop and creating a more circular economy. In addition, remanufacturing can initiate more preferable EoL options such as recovery, recycling, and waste reduction.
While remanufacturing offers numerous benefits, there is significant lack of literature and books covering the fundamentals of operations, technologies and business models. The proposed book will provide in-depth coverage of remanufacturing fundamentals and its strong link to circular economy and resource efficiency.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Value-Retention Processes within the Circular Economy
Abstract
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Overview and Evaluation of Value-Retention Processes
1.2.1 Defining Value-Retention Processes
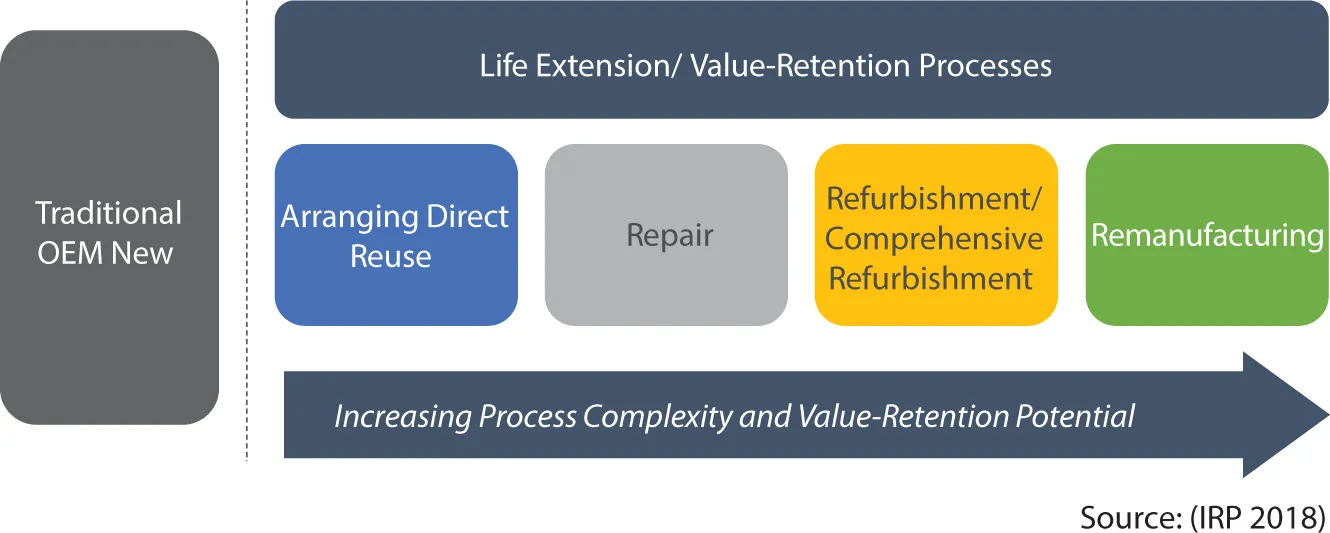
1.2.1.1 Arranging Direct Reuse
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Value-Retention Processes within the Circular Economy
- Chapter 2: The Role of Remanufacturing in a Circular Economy
- Chapter 3: Remanufacturing Business Models
- Chapter 4: Remanufacturing, Closed-Loop Systems and Reverse Logistics
- Chapter 5: Product Service and Remanufacturing
- Chapter 6: Design for Remanufacturing
- Chapter 7: Global Challenges and Market Transformation in Support of Remanufacturing
- End User License Agreement