
Introductory Electrical Engineering With Math Explained in Accessible Language
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Introductory Electrical Engineering With Math Explained in Accessible Language
About this book
Offers an understanding of the theoretical principles in electronic engineering, in clear and understandable terms
Introductory Electrical Engineering With Math Explained in Accessible Language offers a text that explores the basic concepts and principles of electrical engineering. The author—a noted expert on the topic—explains the underlying mathematics involved in electrical engineering through the use of examples that help with an understanding of the theory. The text contains clear explanations of the mathematical theory that is needed to understand every topic presented, which will aid students in engineering courses who may lack the necessary basic math knowledge.
Designed to breakdown complex math concepts into understandable terms, the book incorporates several math tricks and knowledge such as matrices determinant and multiplication. The author also explains how certain mathematical formulas are derived. In addition, the text includes tables of integrals and other tables to help, for example, find resistors' and capacitors' values. The author provides the accessible language, examples, and images that make the topic accessible and understandable. This important book:
• Contains discussion of concepts that go from the basic to the complex, always using simplified language
• Provides examples, diagrams, and illustrations that work to enhance explanations
• Explains the mathematical knowledge that is crucial to understanding electrical concepts
• Contains both solved exercises in-line with the explanations
Written for students, electronic hobbyists and technicians, Introductory Electrical Engineering With Math Explained in Accessible Language is a much-needed text that is filled with the basics concepts of electrical engineering with the approachable math that aids in an understanding of the topic.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Scientific Method: General Concepts
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Powers of 10
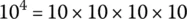
1.3 Roots
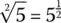
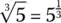
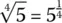
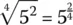
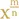
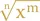
1.4 Scientific Notation as a Tool
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- About the Author
- Preface
- Acknowledgement
- Introduction
- Conventions
- 1 Scientific Method
- 2 Infinitesimal Calculus
- 3 Atom
- 4 Voltage and Current
- 5 Resistors
- 6 Ohm’s Laws
- 7 Delta–Wye Conversions
- 8 Capacitors
- 9 Electromagnetism
- 10 Inductors
- 11 Transformers
- 12 Generators
- 13 Semiconductors
- 14 Diodes and Transistors
- 15 Voltage and Current Sources
- 16 Source Transformations
- 17 Impedance and Phase
- 18 Power
- 19 Kirchhoff’s Laws
- 20 Nodal Analysis
- 21 Thévenin’s Theorem
- 22 Norton’s Theorem
- 23 Superposition Theorem
- 24 Millman’s Theorem
- 25 RC Circuits
- 26 RL Circuits
- 27 RLC Circuits: Part 1
- 28 RLC Circuits: Part 2
- 29 Transistor Amplifiers
- 30 Operational Amplifiers
- 31 Instrumentation and Bench
- Appendix A: International System of Units (SI)International System of Units (SI)
- Appendix B: Color Code: ResistorsColor Code: Resistors
- Appendix C: Root Mean Square (RMS) ValueRoot Mean Square (RMS) Value
- Appendix D: Complex NumbersComplex Numbers
- Appendix E: Table of IntegralsTable of Integrals
- Appendix F: AWG Versus Metric System: Wire Cross Sections AWG Versus Metric System: Wire Cross Sections
- Appendix G: Resistors: Commercial ValuesResistors: Commercial Values
- Appendix H: Capacitors: Commercial ValuesCapacitors: Commercial Values
- Appendix I: Inductors: Commercial ValuesInductors: Commercial Values
- Appendix J: Simulation ToolsSimulation Tools
- Appendix K: GlossaryGlossary
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app