
Python GUI Programming Cookbook
Develop functional and responsive user interfaces with tkinter and PyQt5, 3rd Edition
- 486 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Python GUI Programming Cookbook
Develop functional and responsive user interfaces with tkinter and PyQt5, 3rd Edition
About this book
Over 90 recipes to help you develop widgets, forms, layouts, charts, and much more using the latest features of Python 3
Key Features
- Use object-oriented programming to develop impressive GUIs in Python
- Create interesting charts to visually represent data using Matplotlib
- Develop GUIs with the latest versions of tkinter, PyQt5, and wxPython frameworks
Book Description
Python is a multi-domain, interpreted programming language that is easy to learn and implement. With its wide support for frameworks to develop GUIs, you can build interactive and beautiful GUI-based applications easily using Python. This third edition of Python GUI Programming Cookbook follows a task-based approach to help you create effective GUIs with the smallest amount of code. Every recipe in this book builds upon the last to create an entire, real-life GUI application. These recipes also help you solve problems that you might encounter while developing GUIs. This book mainly focuses on using Python's built-in tkinter GUI framework. You'll learn how to create GUIs in Python using simple programming styles and object-oriented programming (OOP). As you add more widgets and expand your GUI, you will learn how to connect to networks, databases, and graphical libraries that greatly enhance the functionality of your GUI. You'll also learn how to use threading to ensure that your GUI doesn't become unresponsive. Toward the end, you'll learn about the versatile PyQt GUI framework, which comes along with its own visual editor that allows you to design GUIs using drag and drop features. By the end of the book, you'll be an expert in designing Python GUIs and be able to develop a variety of GUI applications with ease.
What you will learn
- Create amazing GUIs with Python's built-in tkinter module
- Customize GUIs using layout managers to arrange GUI widgets
- Advance from the typical waterfall coding style to an OOP style using Python
- Develop beautiful charts using the free Matplotlib Python module
- Use threading in a networked environment to make GUIs responsive
- Discover ways to connect GUIs to a MySQL database
- Understand how unit tests can be created and internationalize GUI
- Delve into the world of GUI creation using PyQt5
Who this book is for
If you're a programmer or developer looking to enhance your Python skills by writing powerful GUI applications, this book is for you. Familiarity with the Python programming language is necessary to get the most out of the book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Best Practices
-
- Avoiding spaghetti code
- Using __init__ to connect modules
- Mixing fall-down and OOP coding
- Using a code naming convention
- When not to use OOP
- How to use design patterns successfully
- Avoiding complexity
- GUI design using multiple notebooks
Avoiding spaghetti code
Getting ready
How to do it...
- Create a new module: GUI_Spaghetti.py.
- Add the following code:
# Spaghetti Code #############################
def PRINTME(me):print(me)
import tkinter
x=y=z=1
PRINTME(z)
from tkinter import *
scrolW=30;scrolH=6
win=tkinter.Tk()
if x:chVarUn=tkinter.IntVar()
from tkinter import ttk
WE='WE'
import tkinter.scrolledtext
outputFrame=tkinter.ttk.LabelFrame(win,text=' Type into the scrolled text control: ')
scr=tkinter.scrolledtext.ScrolledText(outputFrame,width=scrolW,height=scrolH,wrap=tkinter.WORD)
e='E'
scr.grid(column=1,row=1,sticky=WE)
outputFrame.grid(column=0,row=2,sticky=e,padx=8)
lFrame=None
if y:chck2=tkinter.Checkbutton(lFrame,text="Enabled",variable=chVarUn)
wE='WE'
if y==x:PRINTME(x)
lFrame=tkinter.ttk.LabelFrame(win,text="Spaghetti")
chck2.grid(column=1,row=4,sticky=tkinter.W,columnspan=3)
PRINTME(z)
lFrame.grid(column=0,row=0,sticky=wE,padx=10,pady=10)
chck2.select()
try: win.mainloop()
except:PRINTME(x)
chck2.deselect()
if y==x:PRINTME(x)
# End Pasta #############################
- Run the code and observe the output, as follows:
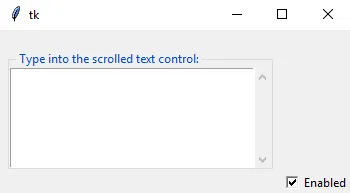
- Compare the preceding GUI to the intended GUI design, as follows:
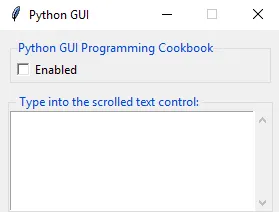
- Create a new module, GUI_NOT_Spaghetti.py, and add the following code:
#======================
# imports
#======================
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import scrolledtext
#======================
# Create instance
#======================
win = tk.Tk()
#======================
# Add a title
#======================
win.title("Python GUI")
#=========================
# Disable resizing the GUI
#=========================
win.resizable(0,0)
- Next, add some controls:
#=============================================================
# Adding a LabelFrame, Textbox (Entry) and Combobox
#=============================================================
lFrame = ttk.LabelFrame(win, text="Python GUI Programming Cookbook")
lFrame.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky='WE', padx=10, pady=10)
#=============================================================
# Using a scrolled Text control
#=============================================================
outputFrame = ttk.LabelFrame(win, text=' Type into the scrolled text
control: ')
outputFrame.grid(column=0, row=2, sticky='E', padx=8)
scrolW = 30
scrolH = 6
scr = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(outputFrame, width=scrolW,
height=scrolH, wrap=tk.WORD)
scr.grid(column=1, row=0, sticky='WE')
- Add some more widgets:
#=============================================================
# Creating a checkbutton
#=============================================================
chVarUn = tk.IntVar()
check2 = tk.Checkbutton(lFrame, text="Enabled", variable=chVarUn)
check2.deselect()
check2.grid(column=1, row=4, sticky=tk.W, columnspan=3)
#======================
# Start GUI
#======================
win.mainloop()
- Run the code and observe the following output:
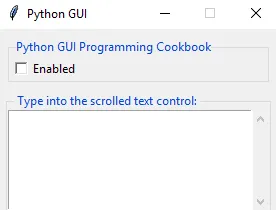
How it works...
def PRINTME(me):print(me)
import tkinter
x=y=z=1
PRINTME(z)
from tkinter import *
#======================
# imports
#======================
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
#-----------------------------------
import tkinter.scrolledtext
outputFrame=tkinter.ttk.LabelF...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- About Packt
- Contributors
- Preface
- Creating the GUI Form and Adding Widgets
- Layout Management
- Look and Feel Customization
- Data and Classes
- Matplotlib Charts
- Threads and Networking
- Storing Data in Our MySQL Database via Our GUI
- Internationalization and Testing
- Extending Our GUI with the wxPython Library
- Building GUIs with PyQt5
- Best Practices
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app