
- 224 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
English Legal System
About this book
Key Facts Key Cases: English Legal System will ensure you grasp the main concepts of your English Legal System module with ease. This book explains in concise and straightforward terms:
• Discussion of the courts system, both civil and criminal;
• Details of the tribunal system
• The doctrine of precedent
• Statutory interpretation
• Personnel in the legal system, both professional and lay
Key Facts Key Cases is the essential series for anyone studying law at LLB, postgraduate and conversion courses and professional courses such as ILEX. The series provides the simplest and most effective way to absorb and retain all of the material essential for passing your exams. Each chapter includes:
-
- diagrams at the start of chapters to summarise key points
-
- structured headings and numbered points to allow for clear recall of the essential points
-
- charts and tables to break down more complex information
Where relevant, chapters also contain a Key Cases section which provides the simplest and most effective way to absorb and memorise essential cases needed for exam success.
-
- Essential and leading cases are explained
-
- The style, layout and explanations are user friendly
-
- Cases are broken down into key components by use of a clear system of symbols for quick and easy visual recognition
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 | What is law? |

a) | rules that forbid certain conduct and rules that compel certain conduct on pain of sanctions; |
b) | rules requiring people to compensate those whom they injure; |
c) | rules stating what needs to be done in certain ‘mechanical’ areas of law, such as making a contract or making a will; |
d) | a system of courts to determine what the rules are, whether they have been broken, and what the appropriate sanction is; |
e) | a body whose responsibility it is to make rules and amend or repeal them when necessary. |

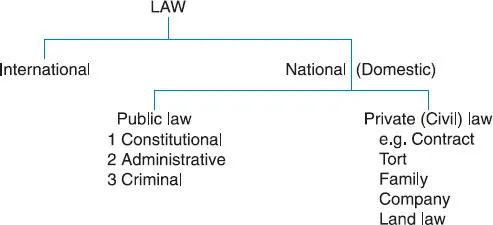
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- PREFACE
- TABLE OF CASES
- Chapter 1 WHAT IS LAW?
- Chapter 2 JUDICIAL PRECEDENT
- Chapter 3 LEGISLATION
- Chapter 4 STATUTORY INTERPRETATION
- Chapter 5 EUROPEAN UNION LAW
- Chapter 6 LAW REFORM
- Chapter 7 THE CIVIL JUSTICE SYSTEM
- Chapter 8 TRIBUNALS AND INQUIRIES
- Chapter 9 POLICE POWERS
- Chapter 10 THE CRIMINAL PROCESS AND COURTS
- Chapter 11 SENTENCING
- Chapter 12 THE LEGAL PROFESSION
- Chapter 13 THE JUDICIARY
- Chapter 14 LAY MAGISTRATES
- Chapter 15 JURIES
- Chapter 16 LEGAL SERVICES AND FUNDING
- INDEX