
- 552 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Engineering Science will help you understand the scientific principles involved in engineering.
Focusing primarily upon core mechanical and electrical science topics, students enrolled on an Engineering Foundation degree and Higher National Engineering qualification will find this book an invaluable aid to their learning.
The subject matter covered includes sections on the mechanics of solids, dynamics, thermodynamics, electrostatics and electromagnetic principles, and AC and DC circuit theory.
Knowledge-check questions, summary sections and activities are included throughout the book, and the necessary background mathematics is applied and integrated alongside the appropriate areas of engineering being studied. The result is a clear, straightforward and easily accessible textbook that encourages independent study and covers most of the scientific principles that students are likely to meet at this level.
It is supported with a companion website at http://www.key2engineeringscience.com for students and lecturers:
- Solutions to the Test your Knowledge questions in the book
- Further guidance onessential mathematics
- Extra chapters on vapour properties, cycles and plants
- Downloadable SCILAB scriptsthat helps simplifyadvanced mathematical content
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part I
Mechanics of materials
Chapter 1
Fundamentals

1.1 Force
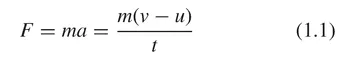
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- PART I MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- PART II DYNAMICS
- PART III THERMODYNAMICS
- PART IV ELECTROSTATICS AND ELECTROMAGNETISM
- PART V DIRECT CURRENT
- PART VI TRANSIENTS
- PART VII ALTERNATING CURRENT
- Index