
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Cisco expert Todd Lammle prepares you for the NEW Cisco CCNA certification exam!
Cisco, the world leader in network technologies, has released the new Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) exam. This consolidated certification exam tests a candidate's ability to implement and administer a wide range of modern IT networking technologies. The CCNA Certification Study Guide: Volume 2 Exam 200-301 covers every exam objective, including network components, IP connectivity and routing, network security, virtual networking, and much more. Clear and accurate chapters provide you with real-world examples, hands-on activities, in-depth explanations, and numerous review questions to ensure that you're fully prepared on exam day.
Written by the leading expert on Cisco technologies and certifications, this comprehensive exam guide includes access to the acclaimed Sybex online learning system—an interactive environment featuring practice exams, electronic flashcards, a searchable glossary, a self-assessment test, and video tutorials on critical Cisco networking concepts and technologies.
- Covers 100% of all CCNA Exam 200-301 objectives
- Provides accurate and up-to-date information on core network fundamentals
- Explains a broad range of Cisco networking and IT infrastructure
- Features learning objectives, chapter summaries, 'Exam Essentials' and figures, tables, and illustrations
The CCNA Certification Study Guide: Volume 2 Exam 200-301 is the ideal resource for those preparing for the new CCNA certification, as well as IT professionals looking to learn more about Cisco networking concepts and technologies.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
Network Fundamentals
- 1.1 Explain the role and function of network components
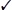
- 1.1.a Routers
- 1.1.b L2 and L3 switches
- 1.1.c Next-generation firewalls and IPS
- 1.2 Describe characteristics of network topology architectures
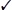
- 1.2.a 2 tier
- 1.2.b 3 tier
- 1.2.c Spine-leaf
- 1.2.d WAN
- 1.2.e Small office/home office (SOHO)
- 1.3 Compare physical interface and cabling types
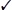
- 1.3.a Single-mode fiber, multimode fiber, copper
- 1.3.b Connections (Ethernet shared media and point-to-point)
- 1.3.c Concepts of PoE


Network Components
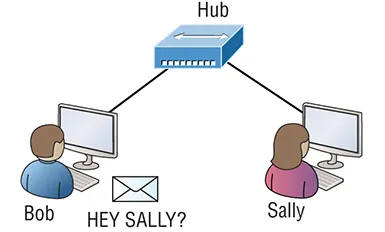
Routers, Switches, and Oh So SOHO!
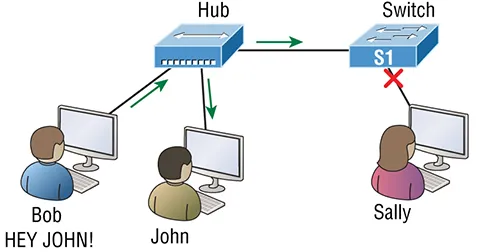
- Too many hosts in a collision or broadcast domain
- Broadcast storms
- Too much multicast traffic
- Low bandwidth
- Adding hubs for connectivity to the network
- A bunch of ARP broadcasts
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Acknowledgments
- About the Author
- Introduction
- Assessment Test
- Answers to Assessment Test
- Chapter 1 Network Fundamentals
- Chapter 2 TCP/IP
- Chapter 3 Easy Subnetting
- Chapter 4 Troubleshooting IP Addressing
- Chapter 5 IP Routing
- Chapter 6 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Chapter 7 Layer 2 Switching
- Chapter 8 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing
- Chapter 9 Enhanced Switched Technologies
- Chapter 10 Access Lists
- Chapter 11 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Chapter 12 IP Services
- Chapter 13 Security
- Chapter 14 First Hop Redundancy Protocol (HSRP)
- Chapter 15 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- Chapter 16 Quality of Service (QoS)
- Chapter 17 Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)
- Chapter 18 Troubleshooting IP, IPv6, and VLANs
- Chapter 19 Wireless Technologies
- Chapter 20 Configuring Wireless Technologies
- Chapter 21 Virtualization, Automation, and Programmability
- Chapter 22 SDN Controllers
- Chapter 23 Configuration Management
- Appendix Answers to Review Questions
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app