
- 254 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Wide-Range Antennas
About this book
Expanding the range of antenna frequency is the main objective of this book. Solutions proposed are based on the development of new theoretical methods for analyzing and synthesizing antennas. The book shows that concentrated capacitive loads connected along linear and V-antennas provide a high level of matching with a cable over a wide frequency range and improves directional characteristics of antennas, i.e. increases the communication distance.
New theoretical methods are proposed for analysis and synthesis of antennas under consideration: 1) method of calculating directional characteristics of radiators with a given current distribution, and 2) method of electrostatic analogy for calculating mutual and total fields of complex multi-element radiating structures. These methods allow us to obtain optimal directional characteristics for director-type antennas (arrays of Yagi-Uda) and log-periodic antennas with concentrated capacitances and show that use of capacitors makes it possible to extend the frequency range of the director antennas and to decrease dimensions of the log-periodic antennas
Multi-element (flat and three-dimensional) self-complementary antennas with different variants of connecting generator poles and cable wires to antenna elements are proposed, which improves the matching with a cable. Characteristics of flat structures are compared with characteristics of volume structures: conical, parabolic, and located on a pyramid edges.
The book describes new versions of transparent antennas, antennas for cellular communication, multi-tier and multi-radiator antennas, and much more.
Information
(1.1) |
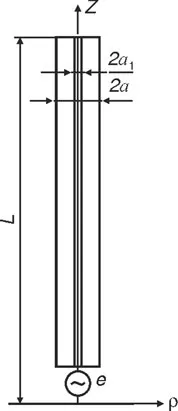
(1.2) |
(1.3) |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- PART 1: WIDE-RANGE ANTENNAS
- PART 2: MULTI-FREQUENCY ANTENNAS
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app