
eBook - ePub
Multiband Non-Invasive Microwave Sensor
Design and Analysis
- 134 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This monograph focuses on the design, implementation and characterization of a concurrent dual band RF sensor for non-invasive detection of human vital signs.
Exclusive title on multiband short range sensors and their biomedical applications, offers detailed analysis of subsystems based on fabricated and measured prototypes and verifies and discusses the system in the real-time environment.
Discusses the practical difficulties of the design process and offers case studies based on the design.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1Introduction
1.1Introduction: Background and Driving Forces
Recently, thousands of people have lost their lives due to heavy flooding and landslides in Sri Lanka and the hilly area of Uttarakhand, India. Similar situations were reported in Japan, where thousands of people were buried under debris from frequent earthquakes. Under these conditions, the quick search-and-rescue operation was negatively affected due to a lack of suitable portable wireless sensors to ascertain human life under the debris as the electric power supply system, roads, and communication networks in those regions were destroyed due to natural calamity. The necessity of wireless and non-invasive sensors in such a situation was heavily felt by the rescue team as well as the research community.
Another important application scenario is in southern Asia, where a large number of unattended and uncovered bore well pits are the cause of human life disasters. Due to a lack of literacy and awareness, young children often fall inside these, which can be fatal. With existing rescue mechanisms, one cannot ascertain life until the rescue operation is over. With a wireless non-invasive sensor, it may be possible to keep track of human life during the rescue operation, thereby guiding the rescue team to decide its course of action.
A wireless and non-invasive sensor may also be useful in a variety of applications, such as through-the-wall detection for the presence of human beings, remote monitoring of patients’ health in hospitals and infant care units, for ascertaining the life of wounded soldiers in battlefields, for the home care of elderly people, in structural health monitoring systems, and to decide the viability of a particular construction.
Motivated from these day-to-day life requirements, this book reports the design and development of a handheld portable wireless sensor to detect the existence of human life non-invasively. The presence of human life is ascertained by the virtue of vital signs such as respiration rate and heartbeat. Hence, they are used as vital signs to indicate the existence of a human life by the proposed sensor. For successful deployment of the device as a sensor for the aforementioned applications, it must fulfill the various criteria:
- The device should be sensitive and capable of detecting even a minute variation of human vital signs.
- The prediction accuracy of the device must be very high, that is, it should be robust against any variation in the measurement conditions.
- The device should be portable enough to be easily carried from one place to another.
- The power consumption of the device should be minimum.
- Most importantly, the device must be cost-effective and reproducible.
As per the records available in the literature, efforts were initiated in the early 1970s toward the non-invasive detection of human vital signs using radio frequency (RF) systems. In 1975, RF systems were used for the first time in the assessment of vital signs of human beings and animals [1]. The high-sensitivity and miniaturized RF systems based on the Doppler principle have been employed as wireless sensors in numerous day-to-day applications; for example, in sleep disorder detection, location and distance estimation, detection of food contamination, characterization of materials and substances, and human vital sign detection in battlefields and sports fields [2–7], among others. These systems have also been found to be very useful by law enforcement agencies to inflict through-the-wall human detection and direction of arrival estimation and in hospitals for non-invasive human healthcare monitoring. Recently, the sensors based on the radar principle have been employed for structural health monitoring [8–13].
However, most of these reported systems are focused on the use of a particular single-band radio or instrument-based bulky systems. The challenging issue in the reported systems is the compromise between the detection sensitivity and the noise content in the signals. This factor has hindered the deployment of such systems as a portable sensor with high detection accuracy. In view of this, the book reports on the design, development, and analysis of a concurrent dualband RF sensor for remote monitoring of human vital signs to detect and ascertain the presence of human life. Figure 1.1 depicts the motivation for development of a non-invasive RF sensor.

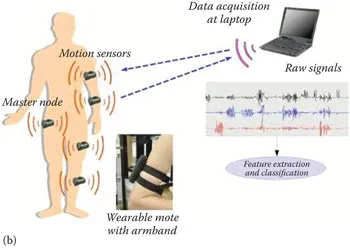
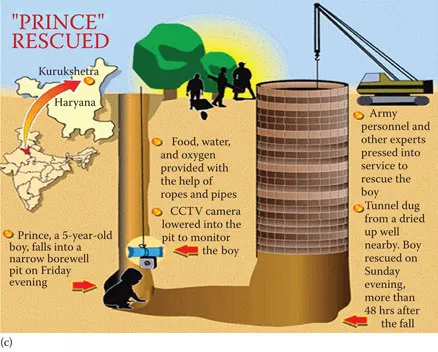

Figure 1.1Motivation for the book: (a) Disaster management, (b) healthcare applications. (c) social aspects, (d) battlefields and law enforcement applications. (From U Turn Foundation, Rehabilitation of Villages Devastated in Uttarakhand Flood, http://uturnfoundation.org/wputurn/rehabilitation-of-villages-devastated-in-uttarakhand-flood [14]; CodeBlue Project, http://www.eecs.Harvard.edu/~mdw/proj/codeblue [15]; Prince Rescued, KBK Infographics, http://im.rediff.com/news/2006/jul/23prince.gif [16]; RANGE-R, Theory of Operation, http://www.range-r.com/tech/theory.htm [17].)
1.2Theory of Non-Invasive VSD Radar
Vital signs are the symptoms of physiological information, frequently used to evaluate the fundamental body functionality. In healthcare terminology, measurements of vital signs are classified into two types: in vivo (on or within a human body) and in vitro (exterior of human body) [18]. Measurement of vital signs, in principle, involves recording of heartbeat and respiration rate, body temperature, and blood pressure. Among these, the respiration rate and heartbeat are more significantly used vital signs to predict physical health of a human being since a close nonlinear relation exists between the respiratory and the cardiovascular systems. Both the heartbeat and respiration rate are modified by the target activity (i.e., the human being).
Vital signs vary continuously with the age of the human being. In general, measurement of the human vital signs may be principally carried out by either using the bioelectric energy generated within the cardiac muscle (direct method) or measurement of periodic displacement of the chest wall surface due to the heart’s contractions (indirect method). The direct method of assessment requires a measuring device capable of detecting changes in the surrounding electric field. The indirect method works on the principle of the Doppler phase shift.
1.2.1Working Principle
With advancements in technology, the traditional invasive vital sign monitoring systems are becoming less invasive and more sophisticated. RF systems with non-invasive monitoring of respiration and heartbeat provide a choice over well-known invasive techniques. The non-invasive vital sign detection (NIVSD) system works on the principle of change in phase of electromagnetic waves due to partial reflection at the separation of two mediums and propagation all the way through the medium. Such RF-based non-invasive measurement methods neither confine nor cause distress, as conventional vital sign measurement methods do, to the human being. Table 1.1 provides a comparison between the traditional invasive systems and the NIVSD system.
Table 1.1Comparison of Invasive and Non-Invasive VSD System
VSD System | Invasive | Wireless Detection | Cooperation from Subject | Detection Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Invasive (traditional) | Yes | Not Possible | Essential | Using starchy electrodes |
NIVSD | No | Possible | Optional | Using RF Signals |
This aspect of non-invasive detection becomes predominantly significant for long-term continuous monitoring of the vital signs of a human being. Radio detection and ranging...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- Authors
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Preliminaries and Review
- Chapter 3 Design and Characterization of the Radiating Elements
- Chapter 4 Concurrent Dualband Front-End Elements for NIVSD Sensors
- Chapter 5 Characterization of a Concurrent Dualband NIVSD Sensor
- Chapter 6 Occupancy Sensors
- Chapter 7 Conclusions and Future Scope
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Multiband Non-Invasive Microwave Sensor by Brijesh Iyer,Nagendra Prasad Pathak in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Service Industry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.