
- 256 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Electrodynamics and Classical Theory of Fields and Particles
About this book
"We can only hope that more such striking expositions will be written." — Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society
This is a systematic, covariant treatment of the classical theories of particle motion, fields, and the interaction of fields and particles. Particular attention is given to the interaction of charged particles with the electromagnetic field. The treatment throughout the book is relativistic; the author attempts, as much as possible, a coordinate free (or covariant) form of the equations both for particles and the fields. The book opens with an extensive discussion of space-time, Lorentz transformations, Lorentz-group and tensor and spinor fields. This material is essential to the understanding of many branches of theoretical physics, in particular relativistic quantum theory. Chapter II describes various relativistic forms of the fundamental problem of dynamics: describing the trajectories of particles for given external forces. The general dynamical principles to obtain the field equations and the important problems of the conservation laws are discussed in Chapter III.
This is a systematic, covariant treatment of the classical theories of particle motion, fields, and the interaction of fields and particles. Particular attention is given to the interaction of charged particles with the electromagnetic field. The treatment throughout the book is relativistic; the author attempts, as much as possible, a coordinate free (or covariant) form of the equations both for particles and the fields. The book opens with an extensive discussion of space-time, Lorentz transformations, Lorentz-group and tensor and spinor fields. This material is essential to the understanding of many branches of theoretical physics, in particular relativistic quantum theory. Chapter II describes various relativistic forms of the fundamental problem of dynamics: describing the trajectories of particles for given external forces. The general dynamical principles to obtain the field equations and the important problems of the conservation laws are discussed in Chapter III.
The second part of the book (Chapters IV-VI) is devoted to a lucid treatment of the interactions of fields and particles. Chapter IV deals with equations of motion and their solutions (the so-called Cauchy problem), focusing on the solution of field equations with Green's functions using Dirac formalism. The problem of feedback between particles and fields (radiation and radiation reaction) is taken up in Chapter V, as are questions concerning the limitations of classical field theories and classical dynamics. Dr. Barut concludes the book with an excellent exposition of the purely mechanical approach to the problem of the interactions of charged particles — the so-called action-at-a-distance formulation of electrodynamics. Problems, alternate proofs, and additional topics are included at the end of each chapter, where a useful bibliography is also provided. A general bibliography appears at the end of the book.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Electrodynamics and Classical Theory of Fields and Particles by A. O. Barut in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Physics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
PART I
Relativistic Description of Fields and Particles
I.
LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS
1. The Physical Basis of the Lorentz Transformations1
The physical laws governing the behavior of fields and particles are expressed in terms of space-time coordinates x, t and the functions of the coordinates.2 On the other hand, the physical laws describe permanencies in nature that are independent of any coordinate frame: a physical process will take place irrespective of what coordinate frame the observer may choose from which to observe it. The arbitrariness resulting from the choice of the coordinate frames must be eliminated from the formulation of the laws. Consequently, the transformations between different possible frames of reference and the quantities which are invariant under these transformations assume a fundamental importance. The physical laws will be written in such a way that their content and form is the same for a class of observers; for an objectively identical situation only the numerical values of observed quantities may change from observer to observer.
Frames of reference in which free particles move uniformly are called inertial frames of reference. This concept, formally, is the same both in classical mechanics and in the special theory of relativity.3
In classical mechanics the correspondence between different inertial frames is expressed by the Galilean transformation law: two coordinate frames moving with respect to each other with the constant relative velocity w are related by
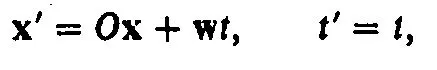
(1.1)
where O is an arbitrary orthogonal transformation and expresses the relative position in space of the two coordinate frames at t = 0. The transformations, Eq. 1.1, which go hand in hand with Newton’s laws, define the class of classical inertial frames. These frames are characterized therefore by the totality of the set (O, w) with w any vector, O any orthogonal transformation. Newton’s laws are the same for all such inertial frames although the numerical values, say, of the coordinates of the particles are different:
Other or more general physical laws (or theories) may not ...
Table of contents
- DOVER BOOKS ON PHYSICS
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- PREFACE TO THE DOVER EDITION
- PREFACE TO THE FIRST EDITION
- Table of Contents
- INTRODUCTION
- PART I - Relativistic Description of Fields and Particles
- PART II - Interactions of Fields and Particles
- RELATED MATHEMATICAL BOOKS
- AUTHOR INDEX
- SUBJECT INDEX