
- 480 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
The Battle with the Slum
About this book
Splendid sequel to author's 1902 classic, How the Other Half Lives. Compelling real-life tales, accompanied by rare photographs and engravings, report on the status of living conditions among New York City's poor and exploited, including successful efforts to demolish breeding grounds of crime and the removal from power of Boss Tweed and the Tammany organization.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access The Battle with the Slum by Jacob A. Riis in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Storia & Storia nordamericana. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
CHAPTER I
BATTLING AGAINST HEAVY ODDS
THE slum I speak of is our own. We made it, but let us be glad we have no patent on the manufacture. It is not, as one wrote with soul quite too patriotic to let the Old World into competition on any terms, “the offspring of the American factory system.” Not that, thank goodness! It comes much nearer to being a slice of original sin which makes right of might whenever the chance offers. When to-day we clamor for air and light and water as man’s natural rights because necessary to his being, we are merely following in the track Hippocrates trod twenty-five centuries ago. How like the slums of Rome were to those of New York any one may learn from Juvenal’s Satires and Gibbon’s description of Rome under Augustus. “I must live in a place where there are no fires, no nightly alarms,” cries the poet, apostle of commuters. “Already is Ucalegon shouting for water, already is he removing his chattels; the third story in the house you live in is already in a blaze. You know nothing about it. For if the alarm begin from the bottom of the stairs, he will be the last to be burned whom a single tile protects from the rain where the tame pigeons lay their eggs.” (Clearly they had no air-shafts in the Roman tenements!) “Codrus had a bed too small for his Procula; six little jugs, the ornament of his sideboard, and a little can, besides, beneath it. . . . What a height it is from the lofty roofs from which a potsherd tumbles on your brains. How often cracked and chipped earthenware falls from the windows. . . . Pray and bear about with you the miserable wish that they may be contented with throwing down only what the broad basins have held. . . . If you can tear yourself away from the games in the circus, you can buy a capital house at Sora, or Fabrateria, or Frasino, for the price at which you are now hiring your dark hole for one year. There you will have your little garden . . . live there enamoured of the pitchfork. . . . It is something to be able in any spot to have made oneself proprietor even of a single lizard. . . . None but the wealthy can sleep in Rome.”5
One reads with a grim smile of the hold-ups of old: “‘Where do you come from?’ he (policeman?) thunders out. ‘You don’t answer? Speak or be kicked! Say, where do you hang out?’ It is all one whether you speak or hold your tongue; they beat you just the same, and then, in a passion, force you to give bail to answer for the assault. . . . I must be off. Let those stay . . . for whom it is an easy matter to get contracts for building temples, clearing rivers, constructing harbors, cleansing sewers, etc.“6 Not even in the boss and his pull can we claim exclusive right.
Rome had its walls, as New York has its rivers, and they played a like part in penning up the crowds. Within space became scarce and dear, and when there was no longer room to build in rows where the poor lived, they put the houses on top of one another. That is the first chapter of the story of the tenement everywhere. Gibbon quotes the architect Vitruvius, who lived in the Augustan age, as complaining of “the common though inconvenient practice of raising houses to a considerable height in the air. But the loftiness of the buildings, which often consisted of hasty work and insufficient material, was the cause of frequent and fatal accidents, and it was repeatedly enacted by Augustus as well as by Nero that the height of private dwellings should not exceed the measure of seventy feet above the ground.”
“Repeatedly” suggests that the jerry-builder was a hard nut to crack then as now. As to Nero’s edict, New York enacted it for its own protection in our own generation.
Step now across eighteen centuries and all the chapters of the dreary story to the middle of the century we have just left behind, and look upon this picture of the New World’s metropolis as it was drawn in public reports at a time when a legislative committee came to New York to see how crime and drunkenness came to be the natural crop of a population “housed in crazy old buildings, crowded, filthy tenements in rear yards, dark, damp basements, leaking garrets, shops, outhouses, and stables converted into dwellings, though scarcely fit to shelter brutes,” or in towering tenements, “often carried up to a great height without regard to the strength of the foundation walls.” What matter? They were not intended to last. The rent was high enough to make up for the risk — to the property. The tenant was not considered. Nothing was expected of him, and he came up to the expectation, as men have a trick of doing. “Reckless slovenliness, discontent, privation, and ignorance were left to work out their inevitable results, until the entire premises reached the level of tenant-house dilapidation, containing, but sheltering not, the miserable hordes that crowded beneath smouldering, water-rotted roofs, or burrowed among the rats of clammy cellars.”7
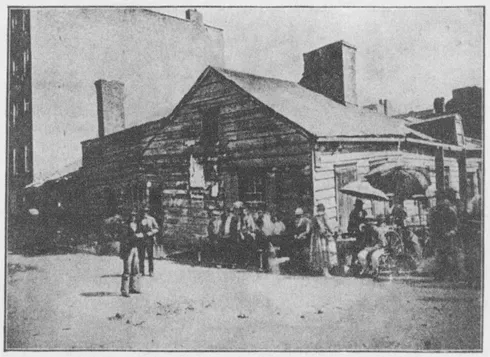
One of the Five Points Fifty Years ago.
We had not yet taken a lesson from Nero. That came later. But otherwise we were abreast. No doubt the Roman landlord, like his New York brother of a later day, when called to account, “urged the filthy habits of his tenants as an excuse for the condition of the property.” It has been the landlord’s plea in every age. “They utterly forgot,” observes the sanitarian who was set to clean up, “that it was the tolerance of those habits which was the real evil, and that for this they themselves were alone responsible.”8
Those days came vividly back to me last winter, when in a Wisconsin country town I was rehearsing the story of the long fight, and pointing out its meaning to us all. In the audience sat a sturdy, white-haired, old farmer who followed the recital with keen interest, losing no word. When he saw this picture of one of the Five Points, he spoke out loud: “Yes! that is right. I was there.” It turned out that he and his sister had borne a hand in the attack upon that stronghold of the slum by the forces of decency, in 1849 and 1850, which ended in the wiping out of the city’s worst disgrace. It was the first pitched battle in the fight. Soon after he had come west and taken homestead land; but the daily repetition during a lifetime of the message to men, which the woods and the fields and God’s open sky have in keeping, had not dulled his ears to it, and after fifty years his interest in his brothers in the great city was as keen as ever, his sympathies as quick. He had driven twenty miles across the frozen prairie to hear my story. It is his kind who win such battles, and a few of them go a long way.
A handful of Methodist women made the Five Points decent. To understand what that meant, look at the “dens of death” in Baxter Street, which were part of it, “houses,” says the health inspector,9 “into which the sunlight never enters . . . that are dark, damp, and dismal throughout all the days of the year, and for which it is no exaggeration to say that the money paid to the owners as rent is literally the ‘price of blood.’“ It took us twenty-four years after that to register the conviction in the form of law that that was good cause for the destruction of a tenement in cold blood; but we got rid of some at that time in a fit of anger. The mortality officially registered in those “dens of death” was 17.5 per cent of their population. We think now that the death-rate of New York is yet too high at 19 or 20 in a thousand of the living.
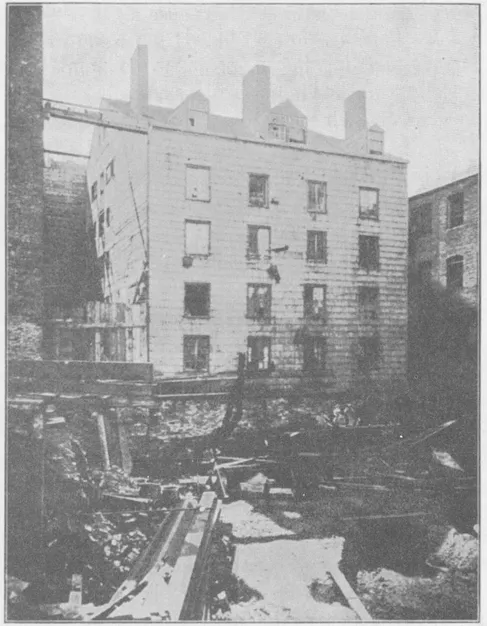

The “Old Church” Tenement.
A dozen steps away in Mulberry Street, called “Death’s Thoroughfare” in the same report, were the “Old Church Tenements,” part of the Five Points and nearly the worst part. “One of the largest contributors to the hospitals,” this repulsive pile had seen the day when men and women sat under its roof and worshipped God. When the congregation grew rich, it handed over its house to the devil and moved uptown. That is not putting it too strong. Counting in the front tenements that shut out what little air and sunshine might otherwise have reached the wretched tenants, it had a population of 360 according to the record, and a mortality of 75 per thousand!
The sketches of the Fourth Ward and Wooster Street barracks are reproduced from an old report of the Association for Improving the Condition of the Poor. They rightly made out, those early missionaries, that the improvement must begin with the people’s homes, or not at all, and allowed no indifference on the part of the public to turn them from their path. It is worth the while of Chicago and the other Western cities that are growing with such joyful metropolitan ambitions, to notice that their slums look to-day very much as New York’s did then. In fifty years how will it be? “The offspring of municipal neglect” the Assembly Committee of 1857 called our “tenement-house” system. “Forgetfulness of the poor” was the way a citizens’ council put it. It comes to the same thing. Whether seen from the point of view of the citizen, the philanthropist, or the Christian, the slum is the poorest investment a city can make, and once made it is not easily unmade. In a Mississippi river town, when pleading for the turning over to the people’s use of some vacant land on the river-shore that would make a fine breathing space, I was told that by and by they would consider it. Just now it was too valuable for factory purposes. When the city had grown opulent, in say twenty-five years, they would be willing to hand it over. Fatal delusion! Men do not grow that kind of sense as they grow rich. The land will be always “too valuable.” When we in New York were scandalized at last into making a park of the Mulberry Bend, it cost us a million and a half, and it had made the slum a fixture, not to be dislodged. No! the way to fight the slum is to head it off. It is like fighting a fire. Chasing it up is hard and doubtful work; the chances are that you will not overtake it till the house is burned down.

An Old Wooster Street Court.

A Fourth Ward Colony in the Bad Old Days.
There were those who thought when the Civil War was over, that a big fire would not be the worst thing that could happen to New York; and, if it could have burned sense into men’s minds as it burned up the evidence of their lack of it, they would have been right. But forty per cent — the rent some of the barracks brought — is a powerful damper on sense and conscience, even with the cholera at the door. However, the fear of it gave us the Citizens’ Council of Hygiene, and New York heard the truth for once.
“Not only,” it ran, “does filth, overcrowding, lack of privacy and domesticity, lack of ventilation and lighting, and absence of supervision and of sanitary regulation still characterize the greater number of the tenements; but they are built to a greater height in stories; there are more rear houses built back to back with other buildings, correspondingly situated on parallel streets; the courts and alleys are more greedily encroached upon and narrowed into unventilated, unlighted, damp, and well-like holes between the many-storied front and rear tenements; and more fever-breeding wynds and culs-de-sac are created as the demand for the humble homes of the laboring poor increases.”10 The Council, which was composed of sixteen of New York’s most distinguished physicians, declared that by ordinary sanitary management the city’s death-rate should be reduced thirty per cent. Its judgment has been more than borne out. In the thirty-five years that have passed since, it has in fact been reduced over fifty per cent.
Men and women were found living in cellars deep down under the ground. One or two of those holes are left still in Park Street near the Five Points Mission, but they have not been used as living-rooms for a generation. In cellars near the river the tide rose and fell, compelling the tenants “to keep the children in bed till ebb-tide.” The plumber had come upon the field, but his coming brought no relief. His was not a case of conscience. “Untrapped soil pipes opened into every floor and poisoned the tenants.”
Where the “dens of death” were in Baxter Street, big barracks crowded out the old shanties. More came every day. I remember the story of those shown in the picture. They had been built only a little while when complaint came to the Board of Health of smells in the houses. A sanitary inspector was sent to find the cause. He followed the smell down in the cellar and, digging there, discovered that the waste pipe was a blind. It had simply been run three feet into the ground and was not connected with the sewer.
The houses were built to sell. That they killed the tenants was no concern of builder’s. His name, by the way, was Buddensiek. A dozen years after, when it happened that a row of tenements he was building fell down ahead of time, before they were finished and sold, and killed the workmen, he was arrested and sent to Sing Sing for ten years, for manslaughter.

Dens of Death.
That time he had forgotten to put lime in the mortar. It was just sand. When the houses fell in the sight of men, the law was at last able to make him responsible. It failed in the matter of the soil pipe. It does sometimes to this very day. Knocking a man in the head with an axe, or sticking a knife into him, goes against the grain. Slowly poisoning a hundred so that the pockets of one be made to bulge may not even banish a man from respectable society. We are a queer lot in some things. However, that is hardly quite fair to society. It is a fact that that part of it which would deserve the respect of its fellow-citizens has got rid of its tenement-house property in recent years. It speculates in railway shares now.
Twenty cases of typhoid fever from a single house in one year was the record that had gone unconsidered. Bedrooms in tenements were dark closets, utterly without ventilation. There couldn’t be any. The houses were built like huge square boxes, covering nearly the whole of the lot. Some light came in at the ends, but the middle was always black. Forty thousand windows, cut by order of the Health Board that first year, gave us a daylight view of the slum: “damp and rotten and dark, walls and banisters sticky with constant moisture.” Think of living babies in such hell-holes; and make a note of it, you in the young cities who can still head off the slum where we have to wrestle with it for our sins. Put a brand upon the murderer who would smother babies in dark holes and bedrooms. He is nothing else. Forbid the putting of a house five stories high, or six, on a twenty-five foot lot, unless at least thirty-five per cent of the lot be reserved for sunlight and air. Forbid it absolutely, if you can. It is the devil’s job, and you will have to pay his dues in the end, depend on it.
And while you are about it make a note of a fact we let go unheeded too long to our harm, and haven’t grasped fully yet. The legislative committee of 1857 said it: “to prevent drunkenness provide every man with a clean and comfortable home.” Call it paternalism, crankery, any other hard name you can think of, all the same it goes down underneath the foundation of things. I have known drunkards to wreck homes a p...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- PREFACE
- Table of Contents
- INTRODUCTION
- WHAT THE FIGHT IS ABOUT
- CHAPTER I - BATTLING AGAINST HEAVY ODDS
- CHAPTER II - THE OUTWORKS OF THE SLUM TAKEN
- CHAPTER III - THE DEVIL’S MONEY
- CHAPTER IV - THE BLIGHT OF THE DOUBLE-DECKER
- CHAPTER V - “DRUV INTO DECENCY”
- CHAPTER VI - THE MILLS HOUSES
- CHAPTER VII - PIETRO AND THE JEW
- CHAPTER VIII - ON WHOM SHALL WE SHUT THE DOOR?
- CHAPTER IX - THE GENESIS OF THE GANG
- CHAPTER X - JIM
- CHAPTER XI - LETTING IN THE LIGHT
- CHAPTER XII - THE PASSING OF CAT ALLEY
- CHAPTER XIII - JUSTICE TO THE BOY
- CHAPTER XIV - THE BAND BEGINS TO PLAY
- CHAPTER XV - “NEIGHBOR” THE PASSWORD
- CHAPTER XVI - REFORM BY HUMANE TOUCH
- CHAPTER XVII - THE UNNECESSARY STORY OF MRS. BEN WAH AND HER PARROT
- INDEX
- A CATALOG OF SELECTED DOVER BOOKS IN ALL FIELDS OF INTEREST
- DOVER BOOKS ON NEW YORK