
- 512 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Fundamentals of the Theory of Plasticity
About this book
Based on the author's series of lectures at the Mechanics-Mathematics Faculty of the University of Leningrad, this text is primarily concerned with the plastic deformation of metals at normal temperatures, as applied to the strength of machines and structures. Its focus on delivering a simple presentation of the basic equations of plasticity theory encompasses the best-developed methods for solving the equations; it also considers problems associated with the special nature of plastic state and the most important engineering applications of plasticity theory.
This volume traces the main trends in the theory's development, assuming readers' familiarity with the fundamentals of strength of materials and elasticity theory. Advanced topics are marked with an asterisk and can be omitted on a first reading. Intended as a text for advanced engineering students, as well as a reference book for practicing engineers, it features problems at the end of each chapter that enable readers to test their grasp of the material.
Contents include the fundamentals of continuum mechanics, equations of plastic state and elastic-plastic equilibrium, torsion, plane strain and stress, and axially symmetric strain. Additional topics range from extremum principles and energy methods of solution to theory of shakedown, stability of elastic-plastic equilibrium, dynamic problems, complex media, and viscoplasticity. An extensive bibliography appears at the end of the book. 1971 edition.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Basic Concepts in the Mechanics of Continuous Media
§1. Stress
1.1. Stress
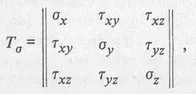
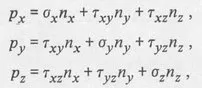
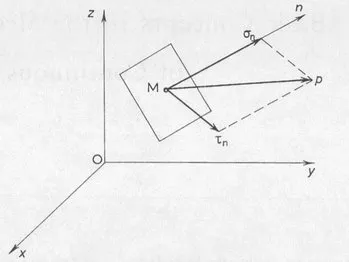
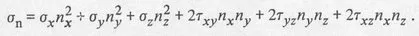
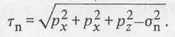
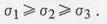

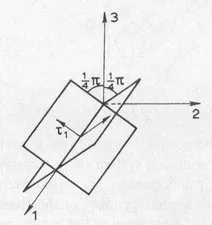
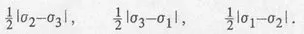

Table of contents
- DOVER BOOKS ON ENGINEERING
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface to the Second Edition
- Basic Notation
- Errata
- Introduction
- 1 - Basic Concepts in the Mechanics of Continuous Media
- 2 - Equations of the Plastic State
- 3 - Equations of Elastic-Plastic Equilibrium. The Simplest Problems
- 4 - Torsion
- 5 - Plane Strain
- 6 - Plane Stress
- 7 - Axisymmetric Strain
- 8 - Extremum Principles and Energy Methods
- 9 - Theory of Shakedown
- 10 - Stability of Elastic-Plastic Equilibrium
- 11 - Dynamical Problems
- 12 - Composite Media. Visco-Plasticity
- Appendix
- Bibliography)
- Subject Index