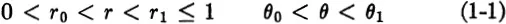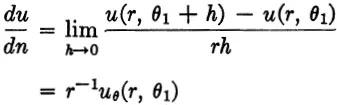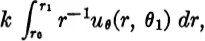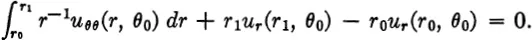![]()
Dirichlet's Problem and
Poisson’s Theorem
This entire chapter discusses a single problem that lies at the heart of the subject of Fourier series. In physical terms, it is to determine the steady state temperature distribution in a disk when the boundary temperatures are known; the mathematical formulation is known as Dirichlet's problem. Starting from scratch, we arrive at a solution in the form of a series Σ anr|n|einθ, called a trigonometric series. The attempt to verify that this can actually be made to solve the heat problem leads to Poisson’s theorem, one of the most important and attractive elementary theorems of analysis. A number of important consequences are evolved below, but these few only suggest the importance of Poisson’s theorem. Echoes of the proof, and of the integral representation on which it is based, appear frequently in mathematics even today.
1-1. THE EQUATION OF STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION
The first step in solving heat problems (as in most problems of mathematical physics) is to find a differential equation governing the situation. Since we are concerned with a disk, the natural coordinates are polar. The temperature at the point with coordinates (r, θ) is denoted by u(r, θ).
In order to find the relevant equation, consider any section of the disk given by
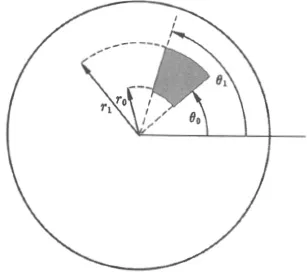
(see Fig. 1-1). Since we are considering a steady state, the rate at which heat flows into this section must be 0; otherwise the average temperature would change with time. Now it is a basic postulate of heat conduction that the rate at which heat crosses a curve C is proportional to the integral along C of the normal derivative ∂u/∂n of the temperature distribution. Here ∂u/∂n is the derivative of u with respect to arc length along any curve perpendicular to C. When C is the side θ — θ1 of the portion given in (1-1), we can take these perpendicular curves to be given by r = constant. Then, since the length of a circular arc is the angle times the radius, along
FIGURE 1-1.Derivation of the heat equation in polar coordinates.
θ = θ1 the normal derivative is
and the rate at which heat flows into the section in Fig. 1-1 along the boundary θ = θ1 is
where k is the conductivity. Adding corresponding expressions for the other three boundaries and setting the net flow equal to zero, we get
If we divide by θ1 — θ0 and let θ1 θ0this yields
(The first term comes from Leibnitz’s rule, and the second from the fundam...