
- 520 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Introduction to Electromagnetic Theory
About this book
A direct, stimulating approach to electromagnetic theory, this text employs matrices and matrix methods for the simple development of broad theorems. The author uses vector representation throughout the book, with numerous applications of Poisson’s equation and the Laplace equation (the latter occurring in both electronics and magnetic media). Contents include the electrostatics of point charges, distributions of charge, conductors and dielectrics, currents and circuits, and the Lorentz force and the magnetic field. Additional topics comprise the magnetic field of steady currents, induced electric fields, magnetic media, the Maxwell equations, radiation, and time-varying current circuits.
Geared toward advanced undergraduate and first-year graduate students, this text features a large selection of problems. It also contains useful appendixes on vector analysis, matrices, elliptic functions, partial differential equations, Fourier series, and conformal transformations. 228 illustrations by the author. Appendixes. Problems. Index.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Appendix
A. Vectors and Geometry
1. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
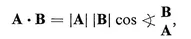
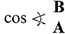
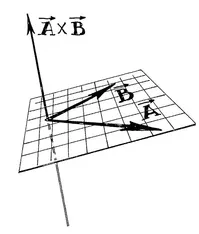
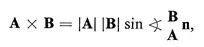
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Preface
- Table of Contents
- Notation
- I. Preliminaries
- II. The Electrostatics of Point Charges
- III. Distributions of Charge
- IV. Conductors and Dielectrics
- V. Currents and Circuits
- VI. The Lorentz Force and the Magnetic Field
- VII. The Magnetic Field of Steady Currents
- VIII. Induced Electric Fields
- IX. Magnetic Media
- X. The Maxwell Equations
- XI. Radiation
- XII. Time- Varying Current Circuits
- Appendix
- Problems
- Index