
- 176 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Stability Theory of Differential Equations
About this book
Suitable for advanced undergraduates and graduate students, this was the first English-language text to offer detailed coverage of boundedness, stability, and asymptotic behavior of linear and nonlinear differential equations. It remains a classic guide, featuring material from original research papers, including the author's own studies.
The linear equation with constant and almost-constant coefficients receives in-depth attention that includes aspects of matrix theory. No previous acquaintance with the theory is necessary, since author Richard Bellman derives the results in matrix theory from the beginning. In regard to the stability of nonlinear systems, results of the linear theory are used to drive the results of Poincaré and Liapounoff. Professor Bellman then surveys important results concerning the boundedness, stability, and asymptotic behavior of second-order linear differential equations. The final chapters explore significant nonlinear differential equations whose solutions may be completely described in terms of asymptotic behavior. Only real solutions of real equations are considered, and the treatment emphasizes the behavior of these solutions as the independent variable increases without limit.
The linear equation with constant and almost-constant coefficients receives in-depth attention that includes aspects of matrix theory. No previous acquaintance with the theory is necessary, since author Richard Bellman derives the results in matrix theory from the beginning. In regard to the stability of nonlinear systems, results of the linear theory are used to drive the results of Poincaré and Liapounoff. Professor Bellman then surveys important results concerning the boundedness, stability, and asymptotic behavior of second-order linear differential equations. The final chapters explore significant nonlinear differential equations whose solutions may be completely described in terms of asymptotic behavior. Only real solutions of real equations are considered, and the treatment emphasizes the behavior of these solutions as the independent variable increases without limit.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Stability Theory of Differential Equations by Richard Bellman in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Mathematics & Geometry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
CHAPTER 1
PROPERTIES OF LINEAR SYSTEMS
1. Introduction. In this introductory chapter we shall consider the fundamental properties of solutions of the system of linear differential equations,
(1)
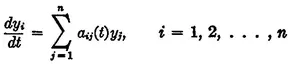
The independent variable t is to range over the interval [0, ∞], and we shall assume that the coefficient functions aij(t) are piecewise-continuous over any finite subinterval. Under this assumption, we may consider all integrals that appear to be Riemann integrals. For our purposes there is very little to be gained from the sophistication of the Lebesgue integral, and we prefer, in consequence, to keep our discussion on as elementary a level as possible.
We furthermore postulate that the coefficients are real functions. Occasionally, particularly in the discussion of linear systems with constant coefficients and with coefficients close to constant, we shall introduce complex solutions. For example, we may use (eit,e-it) as a basic set of solutions of d2u/dt2 + u = 0, rather than (cos t, sin t). This is purely a matter of convenience, however, and we shall always be primarily interested in real solutions of real systems.
The only way to study the behavior of solutions of systems of linear algebraic equations or linear differential equations in any systematic fashion is to make use of the concepts of vectors and matrices. In this chapter we shall introduce these concepts and demonstrate the few results required for the theory of differential equations. No prior knowledge of vector or matrix theory will be assumed.
Exercise
Show that the nth-order linear equation
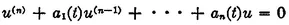
may be converted into a linear system of the type of (1) above by means of the substitutions u = u1,, u′ = u2, . . . , u(n−1) = un....
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Dedication
- Copyright Page
- PREFACE
- Table of Contents
- CHAPTER 1 - PROPERTIES OF LINEAR SYSTEMS
- CHAPTER 2 - STABILITY, BOUNDEDNESS, AND ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS
- CHAPTER 3 - THE EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS OF NONLINEAR SYSTEMS
- CHAPTER 4 - THE STABILITY OF SOLUTIONS OF NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
- CHAPTER 5 - THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF THE SOLUTIONS OF SOME NONLINEAR EQUATIONS OF THE FIRST ORDER
- CHAPTER 6 - THE SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
- CHAPTER 7 - THE EMDEN-FOWLER EQUATION
- INDEX