
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Essentials of MRI Safety
About this book
Essentials of MRI Safety is a comprehensive guide that enables practitioners to recognise and assess safety risks and follow appropriate and effective safety procedures in clinical practice. The text covers all the vital aspects of clinical MRI safety, including the bio-effects of MRI, magnet safety, occupational exposure, scanning passive and active implants, MRI suite design, institutional governance, and more.
Complex equations and models are stripped back to present the foundations of theory and physics necessary to understand each topic, from the basic laws of magnetism to fringe field spatial gradient maps of common MRI scanners. Written by an internationally recognised MRI author, educator, and MRI safety expert, this important textbook:
- Reflects the most current research, guidelines, and MRI safety information
- Explains procedures for scanning pregnant women, managing MRI noise exposure, and handling emergency situations
- Prepares candidates for the American Board of MR Safety exam and other professional certifications
- Aligns with MRI safety roles such as MR Medical Director (MRMD), MR Safety Officer (MRSO) and MR Safety Expert (MRSE)
- Contains numerous illustrations, figures, self-assessment tests, key references, and extensive appendices
Essentials of MRI Safety is an indispensable text for all radiographers and radiologists, as well as physicists, engineers, and researchers with an interest in MRI.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Systems and safety: MR hardware and fields
INTRODUCTION

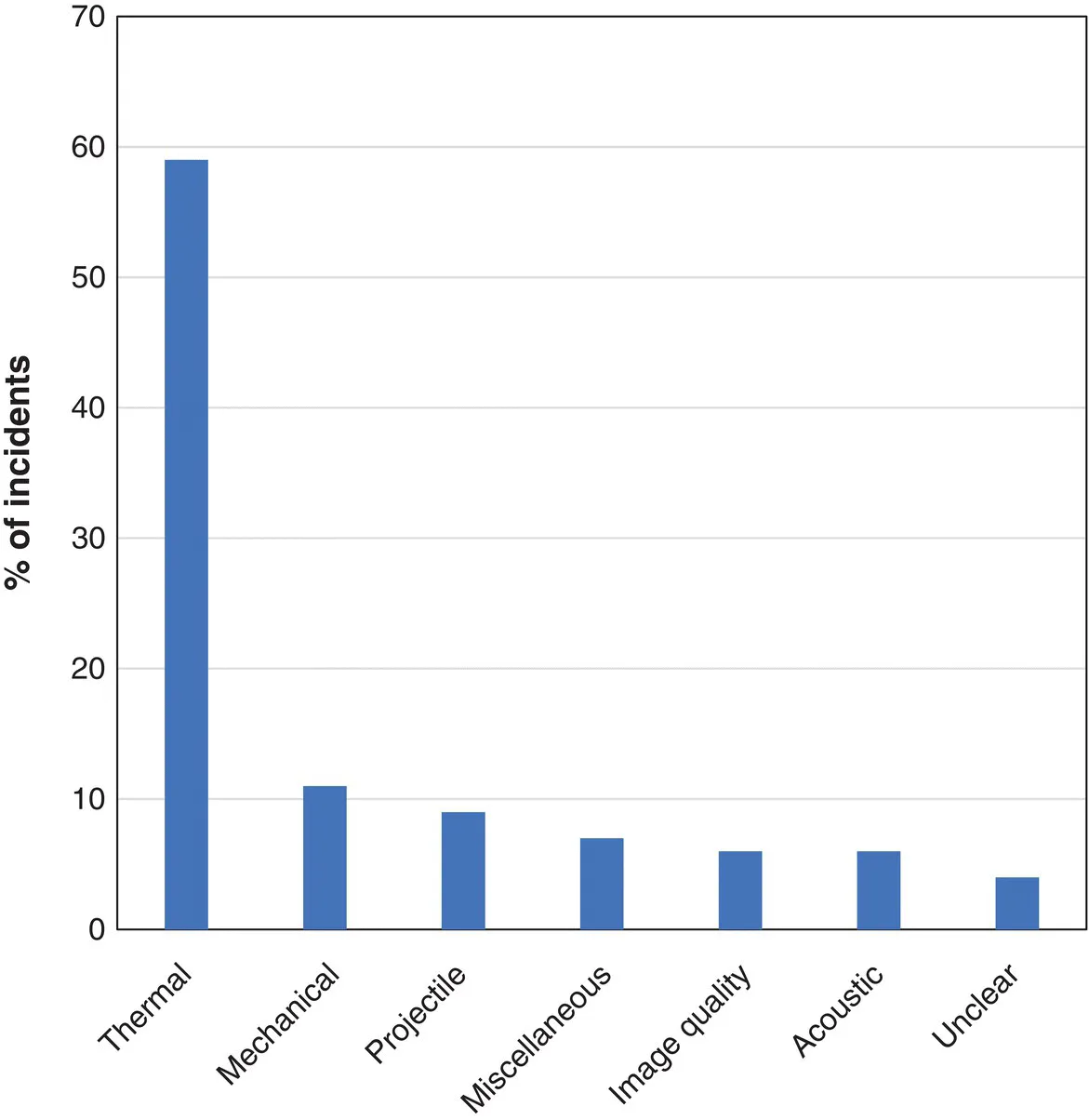
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Foreword: essentials
- Acknowledgments
- 1 Systems and safety: MR hardware and fields
- 2 Let’s get physical: fields and forces
- 3 Bio‐effects 1: static field
- 4 Bio‐effects 2: time‐varying gradient fields
- 5 Bio‐effects 3: radio‐frequency fields
- 6 Acoustic noise
- 7 Pregnancy
- 8 Contrast agents
- 9 Passive implants
- 10 Active implants
- 11 Would you scan this? Understanding the conditions
- 12 Location, location, location
- 13 But what about us? Occupational exposure
- 14 Organization and management
- Appendix 1: One hundred equations you need to know
- Appendix 2: Maths toolkit
- Appendix 3: Symbols and constants
- Answers to revision questions
- Index
- End User License Agreement