
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Presents the mathematical framework, technical language, and control systems know-how needed to design, develop, and instrument micro-scale whole-angle gyroscopes
This comprehensive reference covers the technical fundamentals, mathematical framework, and common control strategies for degenerate mode gyroscopes, which are used in high-precision navigation applications. It explores various energy loss mechanisms and the effect of structural imperfections, along with requirements for continuous rate integrating gyroscope operation. It also provides information on the fabrication of MEMS whole-angle gyroscopes and the best methods of sustaining oscillations.
Whole-Angle Gyroscopes: Challenges and Opportunities begins with a brief overview of the two main types of Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscopes (CVGs): non-degenerate mode gyroscopes and degenerate mode gyroscopes. It then introduces readers to the Foucault Pendulum analogy and a review of MEMS whole angle mode gyroscope development. Chapters cover: dynamics of whole-angle coriolis vibratory gyroscopes; fabrication of whole-angle coriolis vibratory gyroscopes; energy loss mechanisms of coriolis vibratory gyroscopes; and control strategies for whole-angle coriolis vibratory gyro- scopes. The book finishes with a chapter on conventionally machined micro-machined gyroscopes, followed by one on micro-wineglass gyroscopes. In addition, the book:
- Lowers barrier to entry for aspiring scientists and engineers by providing a solid understanding of the fundamentals and control strategies of degenerate mode gyroscopes
- Organizes mode-matched mechanical gyroscopes based on three classifications: wine-glass, ring/disk, and mass spring mechanical elements
- Includes case studies on conventionally micro-machined and 3-D micro-machined gyroscopes
Whole-Angle Gyroscopes is an ideal book for researchers, scientists, engineers, and college/graduate students involved in the technology. It will also be of great benefit to engineers in control systems, MEMS production, electronics, and semi-conductors who work with inertial sensors.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part I
Fundamentals of Whole‐Angle Gyroscopes
1
Introduction
- Industrial applications, such as robotics and automation;
- Automobile stabilization, traction control, and roll‐over detection;
- Gesture recognition and localization in gaming and mobile devices;
- Optical image stabilization (OIS) of cameras;
- Head tracking in Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR);
- Autonomous vehicles, such as self‐driving cars and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs).
1.1 Types of Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscopes
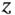
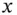
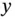
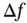
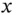
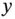
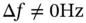
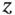
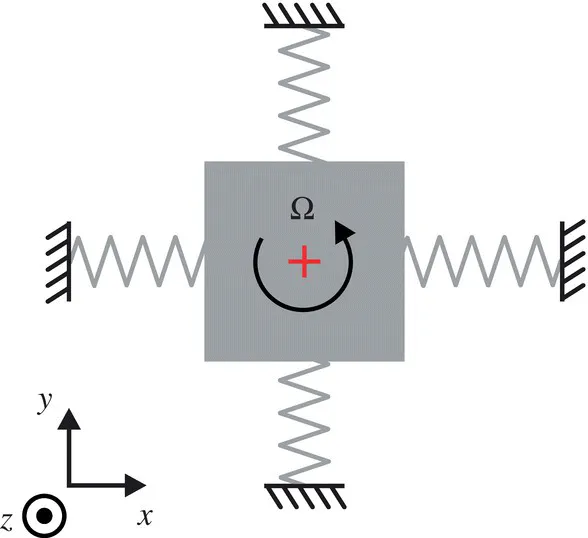
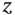
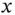
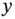
1.1.1 Nondegenerate Mode Gyroscopes
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- List of Abbreviations
- Preface
- About the Authors
- Part I: Fundamentals of Whole‐Angle Gyroscopes
- Part II: 2‐D Micro‐Machined Whole‐Angle Gyroscope Architectures
- Part III: 3‐D Micro‐Machined Whole‐Angle Gyroscope Architectures
- References
- Index
- IEEE Press Series on Sensors
- End User License Agreement