
- 361 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Dichroic Dyes for Liquid Crystal Displays
About this book
This book provides a systematic presentation of issues pertaining to the development of dichroic dyes applied in electrooptical systems for displaying and processing data. It explains the theory of the guest-host effect and the methodology of engineering dichroic dye (DD) molecules with specified characteristics. The book then examines the properties of currently known DDs, including the most interesting examples of synthesis. Various aspects of designing LCM for guest-host devices and available designs of guest-host LCDs are considered as well. Characteristics of dichroic dyes are presented in the Appendix as an added benefit to readers.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Dichroic Dyes for Liquid Crystal Displays by Aleksandr V. Ivashchenko in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Chemistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Types of Dichroic Dyes and Their Order Parameters
When a dye with geometric anisotropy is dissolved in a liquid crystal the dye molecules tend to arrange in such a way that their long molecular axes align along the LC director, (the direction of the predominant orientation of the LC long molecular axes). One of the main criteria of the DD eff iciency is the degree of ordering (or, in other words, the order parameter), S, of the long-wave electron transition oscillator (LETO), responsible for the color of the dye, with respect to . S can be easily found from the electron polarization spectra of the DD solution in LC using the following formula:
where D|| and D⊥ are optical densities of the aligned solution of DD in LC measured for light polarizations parallel and normal to . As a rule, DN and Dx are measured at the maximum of the absorption band. Often, to characterize the DD efficiency, the dichroic ratio N = D||/D⊥ is used which is related to S as follows:
If LETO coincides with the long geometrical axis x of the DD molecule (Figure 1a), then the value of S is equal to that of the geometrical ordering (SG) of the DD long molecular axes in LC and can be found in the same way as the LC order parameter3,14
where θ is the angle between LETO (long axis) of an individual DD molecule and averaged over all the DD molecules in the sample.
In the overwhelming majority of cases the DD LETO is polarized at an angle β relative to the axis x (Figure lb), hence the relationship between S and S° can be given by11
Dependence of S on the angles β and θ, and relationships between S and SG for such dyes are presented in Figure 2. As can be seen from Figure 2b, for θ = 0 the order parameter decreases with β, and S >0 for the angles in the range 0° ≤ β < 54°44′8″. The dyes with S >0 are called DD of positive dichroism, or L-dyes (L = longitudinal). The L-dyes can be exemplified by 4-dialkylamino-4’-cyanoazobenzenes (Structure 1). The dyes with S <0 (54°44′8″ (< β ≤ 90°) are called DD of negative dichroism, or T-dyes (T = transverse), for example, 3,6-disubstituted tetrazines (Structure 2).
Also known are dyes with S = 0 (β = 54°44′8″ for θ = 0, or β = 90° for θ = 54°44′8″). They are referred to as isotropic dyes, orl-dyes, because in the electron polarization spectra of their aligned LC solutions the values of D|| and D⊥ are equal. DD of Structure 3 is an example of such a dye. Further below, dyes with -0.05 ≤ S ≤ 0.1 will be called I-dyes.
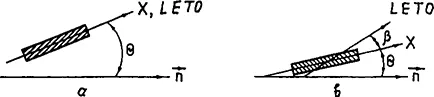
Figure 1 Types of dichroic dyes: (a) LETO coincides with the long molecular axis x of the DD molecule; (b) LETO does not coincide with the axis x.
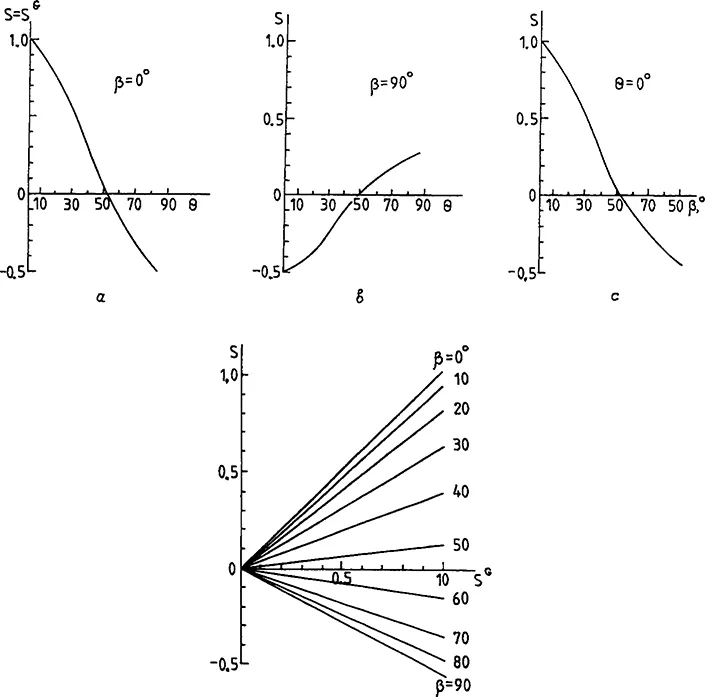
Figure 2 Dependence of the DD order parameter, S, on the angles β and θ (a to c) and on the DD geometric ordering in LC (d).
Finally, there are dichromatic DD having in the visible spectral range two or more absorption bands with opposite signs of S. Such dyes are named L,T- and T,L-dyes, respectively. It should be noted that, similarly, there can be other dichromatic dyes, namely, LI- and IL- or IL- and TI-dyes, the latter, however, being represented by only a few examples. This type can be exemplified by the bism...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter 1 Types of Dichroic Dyes and Their Order Parameters
- Chapter 2 Design of a Dichroic Dye Molecule
- Chapter 3 Dichroic Dyes
- Chapter 4 Liquid Crystalline Materials
- Chapter 5 Electrooptical Effects and Color Displays Based on Them
- Chapter 6 Commercial Dichroic Dyes and Liquid Crystalline Materials
- References
- Appendix 1. Bis(Arylideneamino)Anthraquinones
- Index