
- 202 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This book reviews advances made in recombinant DNA technology as it relates to the techniques employed, and the production and testing of potentially important products such as human interferon, insulin, and growth hormone.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Recombinant DNA Products by Arthur P. Bollon in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medizin & Biotechnologie in der Medizin. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Recombinant DNA Techniques: Isolation, Cloning, and Expression of Genes
A. P. Bolton, E. A. Barron, S. L. Berent, P. W. Bragg, D. Dixon, M. Fuke, C. Hendrix, M. Mahmoudi, R. S. Sidhu, and R. M. Torczynski
Table of Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Enzymes
- A. Restriction Endonucleases
- B. Other Enzymes Used in Gene Isolation and Manipulation
- 1. DNA Polymerase I
- 2. Klenow Fragment of E. coli DNA Polymerase I
- 3. T4 DNA Polymerase
- 4. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase
- 5. T4 Polynucleotide Kinase
- 6. Reverse Transcriptase
- 7. T4 DNA Ligase
- 8. Exonuclease III
- 9. λ Exonuclease
- III. Vectors
- A. E. coli Plasmid Cloning Vectors
- B. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cloning Vectors
- C. Specialized Vectors
- IV. Gene Cloning
- A. Synthesis of cDNA
- B. Gene Libraries
- 1. cDNA Libraries
- 2. Genomic Library
- V. Screening and Enrichment of DNA Clones
- A. Enrichment of DNA Clones
- 1. Chimeric Plasmid Enrichment
- 2. DNA Size Enrichment
- 3. DNA Sequence Enrichment
- B. Screening
- 1. Synthetic Probes
- a. Protein-Probe Strategy
- b. Hybridization Conditions
- c. Screening a Human Genomic Library for Alpha-Interferon Genes Using Two Synthetic Probes
- 2. Differential Hybridization
- 3. Biological Activity and Immunological Screening
- 1. Synthetic Probes
- A. Enrichment of DNA Clones
- VI. Expression
- VII. Summary
- Notes Added in Proof
- Acknowledgments
- References
I. Introduction
The cloning and expression of foreign genes using recombinant DNA technology has permitted access to complex biological mechanisms such as eucaryotic RNA splicing, oncogene dynamics, and developmental systems such as antibody diversity. In addition, the technology has been the foundation for a new bio-technology industry. This chapter contains an analysis of some of the recombinant DNA techniques that have been employed for the manipulation of foreign genes in microorganisms resulting in protein production as diagrammed in Figure 1. Subsequent chapters will address the expression, clinical trials and production of genetically engineered human interferon, insulin, and growth hormone.
II. Enzymes
The isolation and cloning of genes involves a series of linked enzymatic steps. Experience with two-enzyme coupled reactions is enough to sensitize the researcher to the complexity of linking five or more enzyme reactions, that are characteristic of the steps involved in the synthesis and cloning of cDNA. Considering that the substrates as well as the catalysts are biological macromolecules, it is not surprising that there are various opinions as to the most efficient protocols. The purity and correct storage procedures for the substrate and enzymes are clearly very critical. Selected restriction enzymes and other enzymes which are commonly used for cloning procedures will be discussed with emphasis on some of their characteristics and utility.
A. Restriction Endonucleases
Restriction endonucleases are enzymes which have been identified in prokaryotic organisms and recognize specific DNA sequences for their endonucleolytic activity. This mechanism permits organisms to prevent foreign DNA from integrating into their genome, which could jeopardize the genetic integrity of the species. Since bacterial sexuality involves direct movement of DNA between organisms by transformation, conjugation, or transduction, it is not surprising that some mechanism evolved to protect against undesirable DNA (restriction) as well as to protect native endogenous DNA (modification).
Three types of restriction endonucleases have been characterized as indicated in Table 1. Type II enzymes have been most useful for DNA cloning due to the separation of the endonuclease and methylation activities into separate enzymes and the sequence specificity of the endonucleolytic action. A key feature of many restriction endonucleases is their asymmetric cleavage generating single-stranded ends. For example, the commonly used enzyme EcoRI recognizes and cleaves the following sequence at the arrows.
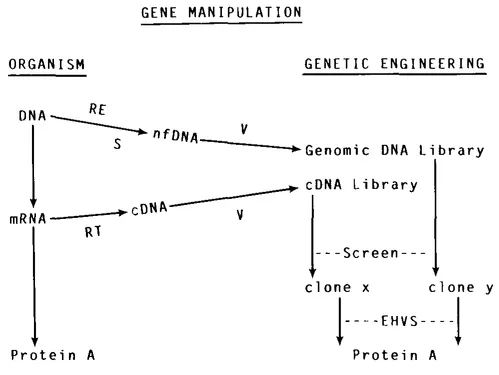
FIGURE 1. cDNA, copy DNA; EHVS, expression host-vector system; nf DNA, natural fragmented DNA; RE, restriction endonuclease; S, sheared; V, vector. Protein A is a protein made either naturally by the organism or by genetic engineering. Clone X is a single clone identified from a cDNA library containing Protein A cDNA. Clone Y is a single clone identified from a genomic library containing a Protein A natural gene.
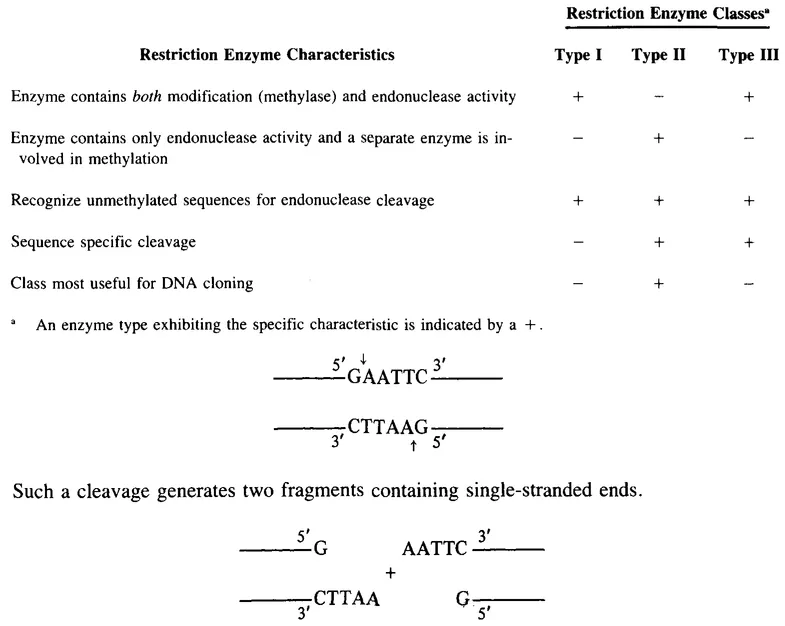
Table 1 RESTRICTION ENZYME TYPES
Since the enzyme cuts between the GA and the recognition sequence is an...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- The Editor
- Contributors
- Table of Contents
- Chapter 1 Recombinant DNA Techniques: Isolation, Cloning, and Expression of Genes A. P. Bollon, E. A. Barron, S. L. Berent, P. W. Bragg, D. Dixon, M. Fuke, C. Hendrix, M. Mahmoudi, R. S. Sidhu, and R. M. Torczynski
- Chapter 2 From Somatostatin to Human Insulin Arthur D. Riggs, Keiichi Itakura, and Herbert W. Boyer
- Chapter 3 Yeast: An Alternative Organism for Foreign Protein Production Ronald A. Hitzeman, Christina Y. Chen, Frank E. Hagie, June M. Lugovoy, and Arjun Singh
- Chapter 4 Background to Human Interferon Norwood O. Hill
- Chapter 5 Preclinical Assessment of Biological Properties of Recombinant DNA Derived Human Interferons Nowell Stebbing and Phillip K. Weck
- Chapter 6 Human Clinical Trials of Bacteria-Derived Human α Interferon Zofia E. Dziewanowska, Leon L. Bernhardt, and Seymour Fein
- Chapter 7 Large-Scale Production of Human Alpha Interferon from Bacteria W. Courtney McGregor and Armin H. Ramel
- Chapter 8 Direct Expression of Human Growth Hormone in Escherichia coli with the Lipoprotein Promoter Nancy G. Mayne, Hansen M. Hsiung, John D. Baxter, and Rama M. Belagaje
- Chapter 9 Biological Actions in Humans of Recombinant DNA Synthesized Human Growth Hormone Raymond L. Hintz
- Chapter 10 The NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules Elizabeth Ann Milewski
- Chapter 10A Appendix: Viral Vectors and the NIH Guidelines Stanley Barban
- Chapter 11 FDA'S Role in Approval and Regulation of Recombinant DNA Drugs Wanda deVlaminck
- Index