
Model-Based Testing for Embedded Systems
- 688 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Model-Based Testing for Embedded Systems
About this book
What the experts have to say about Model-Based Testing for Embedded Systems:
"This book is exactly what is needed at the exact right time in this fast-growing area. From its beginnings over 10 years ago of deriving tests from UML statecharts, model-based testing has matured into a topic with both breadth and depth. Testing embedded systems is a natural application of MBT, and this book hits the nail exactly on the head. Numerous topics are presented clearly, thoroughly, and concisely in this cutting-edge book. The authors are world-class leading experts in this area and teach us well-used and validated techniques, along with new ideas for solving hard problems.
"It is rare that a book can take recent research advances and present them in a form ready for practical use, but this book accomplishes that and more. I am anxious to recommend this in my consulting and to teach a new class to my students."
—Dr. Jeff Offutt, professor of software engineering, George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia, USA
"This handbook is the best resource I am aware of on the automated testing of embedded systems. It is thorough, comprehensive, and authoritative. It covers all important technical and scientific aspects but also provides highly interesting insights into the state of practice of model-based testing for embedded systems."
—Dr. Lionel C. Briand, IEEE Fellow, Simula Research Laboratory, Lysaker, Norway, and professor at the University of Oslo, Norway
"As model-based testing is entering the mainstream, such a comprehensive and intelligible book is a must-read for anyone looking for more information about improved testing methods for embedded systems. Illustrated with numerous aspects of these techniques from many contributors, it gives a clear picture of what the state of the art is today."
—Dr. Bruno Legeard, CTO of Smartesting, professor of Software Engineering at the University of Franche-Comté, Besançon, France, and co-author of Practical Model-Based Testing
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
Introduction
1
A Taxonomy of Model-Based Testing for Embedded Systems from Multiple Industry Domains
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Definition of Model-Based Testing
1.2.1 Test dimensions
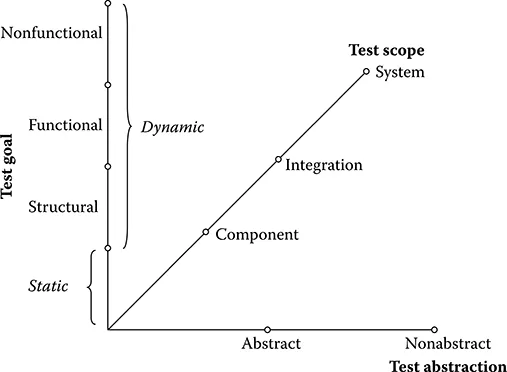
Selected test dimensions.
1.2.1.1 Test goal
- Static test: Testing is often defined as the process of finding errors, failures, and faults. Errors in a program can be revealed without execution by just examining its source code (International Software Testing Qualification Board 2006). Similarly, other development artifacts can be reviewed (e.g., requirements, models, or the test specification itself).
- Structural test: Structural tests cover the structure of the SUT during test execution (e.g., control or data flow), and so the internal structure of the system (e.g., code or model) must be known. As such, structural tests are also called white-box or glass-box tests (Myers 1979; International Software Testing Qualification Board 2006).
- Functional test: Functional testing is concerned with assessing the functional behavior of an SUT against the functional requirements. In contrast to structural tests, functional tests do not require any knowledge about system internals. They are therefore called black-box tests (Beizer 1995). A systematic, planned, executed, and documented procedure is desirable to make them successful. In this category, ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- MATLAB Statement
- Contributors
- Technical Review Committee
- Book Introduction
- Part I Introduction
- Part II Automatic Test Generation
- Part III Integration and Multilevel Testing
- Part IV Specific Approaches
- Part V Testing in Industry
- Part VI Testing at the Lower Levels of Development
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app