
eBook - ePub
Understanding Traffic Systems
Data Analysis and Presentation
- 484 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Road traffic and its impacts affect all aspects of modern life, leisure and industry, with safety, congestion and pollution being of greatest public concern. Transport planning increasingly emphasises travel demand management (TDM) and traffic calming - aided by dynamic, lower cost data from Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) - to enable real time monitoring, control and traveller information. This second edition of a highly successful work has been fully updated since its first publication in 1996 to reflect developments in technology available to the traffic analyst and in the social, ecological and economic environment. New sections are included on shockwaves, data capture without surveys, traffic incidents, delay estimation, off-line use of on-line data, environmental sensitivity, and controlled crash tests. The authors introduce and demonstrate techniques with which the analyst, engineer or planner can examine traffic problems. The underlying theme is that proper understanding of traffic systems performance and traffic problems can only come from the intelligent processing, refinement, appraisal and evaluation of traffic data. Arranged in five parts, the book offers an integrated approach to tackling road traffic problems: ¢ How to gain information and understanding about traffic ¢ The theories of traffic flow ¢ The principles of good survey planning and management ¢ Specific types of traffic studies ¢ Analytical techniques for transforming raw data into useful information. Understanding Traffic Systems provides cogent insights into the techniques of traffic data collection and analysis, the application of traffic theory and the role of data in analysis and decision making. Its breadth and use of examples from several countries make it a useful reference text for students and researchers, as well as an essential tool for practising traffic engineers and planners.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part E
Data Analysis and Modelling
15
From data to information
The results of traffic analysis must be transmitted to the user or client in a form that is understandable and efficient. Chapter 2 described the recent developments in database systems, spreadsheets and statistical packages that assist in this process. These tools are of considerable assistance in developing a picture of what a data set is trying to tell us. The important step is the transformation of data into information. To do this requires appropriate examination of the data, for which methods of data presentation, often graphically based, are used.
The first task in any analysis is to become familiar with the data. It is useful to have answers to questions such as: are there any outliers? Is the distribution of the data symmetric? Do data values accumulate in the middle or at the end? Are any values repeated? Answers to these questions can often be obtained by having a look at the data. Data may be viewed through the astute use of tables (Section 15.1), but one of the most powerful methods is the construction of diagrams (Section 15.2). This forms the basis of Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA, see Section 15.3).
The correct analytical procedure with any data set is to undertake EDA and then move into statistical analysis. EDA can also be used throughout the statistical analysis process to enrich understanding and interpretation (see Chapter 17). Modem methods of interactive data analysis allow analysts the opportunity to have many different views of the data, quickly. Then follows the use of descriptive statistics (Section 15.4).
15.1 Tables
The tabular form of presentation is a common and useful first step in data analysis. The simplest table is just a simple listing of the data. The listing of vehicle speeds in Table 15.1 is an example of this form of presentation. These speeds are those from the data set presented in Appendix B.
Table 15.1 Vehicle speeds (km/h) in residential streets

The unsystematic manner in which the data are presented in Table 15.1 makes it difficult to gain insights into the character of the data. A better view may be gained by arranging the data in some manner. The ordering of the data from the lowest to the highest value is presented in Table 15.2. This table provides more insight. It shows the extremes of the data and provides an indication of where the data tend to group together.
Table 15.2 Table of speeds (km/h) sorted in increasing order
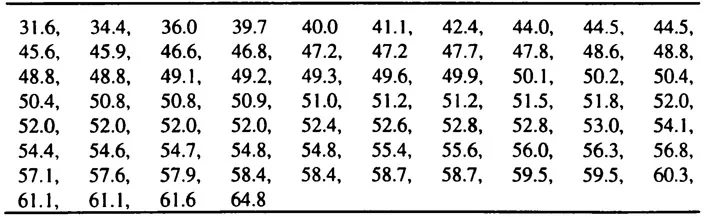
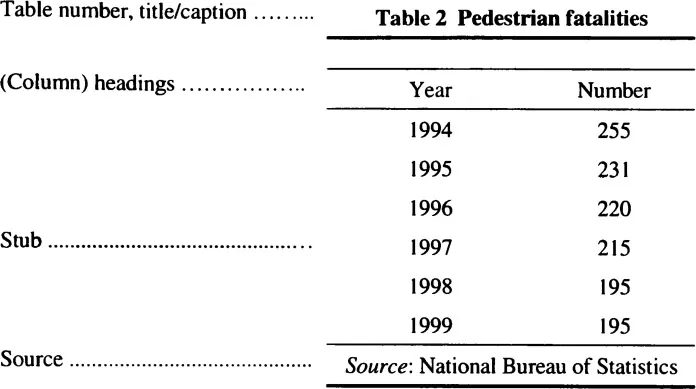
These tables present information on one variable and are, therefore, referred to as one-dimensional tables. One-dimensional tables can be divided into the following components: the table number, the title or caption, the (column) headings, the stub (or left-hand column – a vertical listing of categories about which data are given in the other columns of the table) and, if necessary, the source. The table number, title/caption, column headings, stub and other columns of data make up the body of the table. Table 15.3 is an example of a simple one-dimensional table with the components marked.
Table 15.3 One-dimensional table
Two-way classification tables can be obtained by subdividing the stub. Two-way classifications are sometimes referred to as cross-tabulations. They are possibly the most common analytical method in the social sciences. The first step in the construction of cross-classification tables is to determine the primary emphasis. The data with the primary emphasis should be place...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- List of figures
- List of tables
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Part A: INTRODUCTION
- Part B: BASIC TRAFFIC THEORY
- Part C: DATA CAPTURE
- Part D: TRAFFIC STUDIES
- Part E: DATA ANALYSIS AND MODELLING
- Appendix A: Statistical tables
- Appendix B: Database of vehicle speeds on residential streets
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Understanding Traffic Systems by Michael A.P. Taylor,Peter W. Bonsall in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Geography. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.