
Electrochemical Supercapacitors for Energy Storage and Delivery
Fundamentals and Applications
- 373 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Electrochemical Supercapacitors for Energy Storage and Delivery
Fundamentals and Applications
About this book
Although recognized as an important component of all energy storage and conversion technologies, electrochemical supercapacitators (ES) still face development challenges in order to reach their full potential. A thorough examination of development in the technology during the past decade, Electrochemical Supercapacitors for Energy Storage and Delivery: Fundamentals and Applications provides a comprehensive introduction to the ES from technical and practical aspects and crystallization of the technology, detailing the basics of ES as well as its components and characterization techniques.
The book illuminates the practical aspects of understanding and applying the technology within the industry and provides sufficient technical detail of newer materials being developed by experts in the field which may surface in the future. The book discusses the technical challenges and the practical limitations and their associated parameters in ES technology. It also covers the structure and options for device packaging and materials choices such as electrode materials, electrolyte, current collector, and sealants based on comparison of available data.
Supplying an in depth understanding of the components, design, and characterization of electrochemical supercapacitors, the book has wide-ranging appeal to industry experts and those new to the field. It can be used as a reference to apply to current work and a resource to foster ideas for new devices that will further the technology as it becomes a larger part of main stream energy storage.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 History
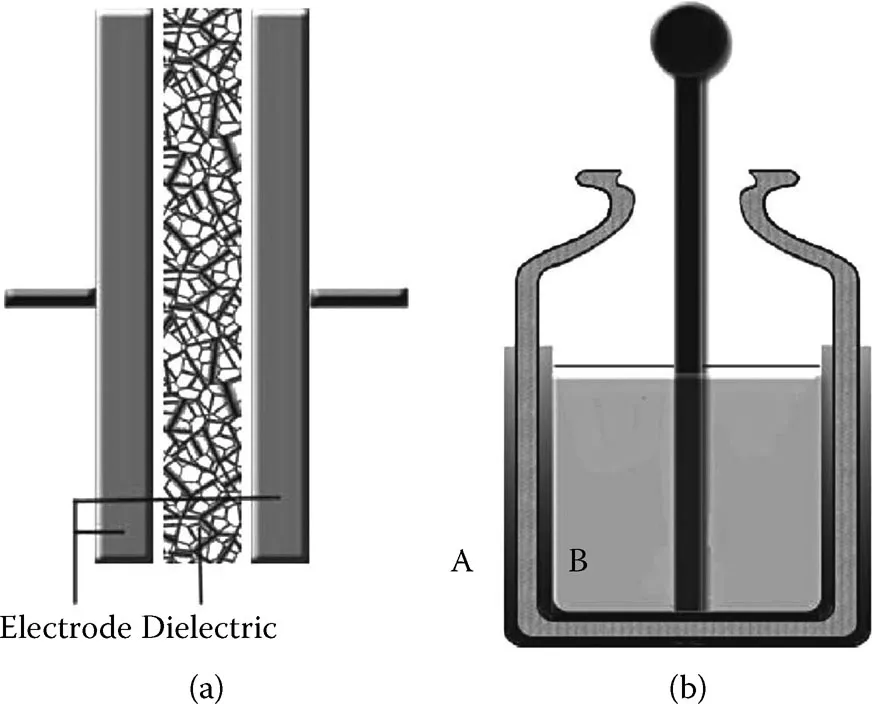
(See color insert.) (a) Simplified schematic of capacitor design. (b) Cross-sectional schematic of Leyden jar (water-filled glass jar containing metal foil electrodes on its inner and outer surfaces, (denoted A and B).
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Series Preface
- Preface
- Authors
- 1 Fundamentals of Electric Capacitors
- 2 Fundamentals of Electrochemical Double-Layer Supercapacitors
- 3 Fundamentals of Electrochemical Pseudocapacitors
- 4 Components and Materials for Electrochemical Supercapacitors
- 5 Electrochemical Supercapacitor Design, Fabrication, and Operation
- 6 Coupling with Batteries and Fuel Cells
- 7 Characterization and Diagnosis Techniques for Electrochemical Supercapacitors
- 8 Applications of Electrochemical Supercapacitors
- 9 Perspectives and Challenges
- Index