
- 348 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Staircases - Structural Analysis and Design
About this book
In recent years both free-standing and geometric staircases have become quite popular. Many variations exist, such as spiral, helical, and elliptical staircases, and combinations of these. A number of researchers have come forward with different concepts in the fields of analytical and numerical design and of experimental methods and assessments. The aim of this book is to cover all these methods and to present them with greater simplicity to practising engineers.
Staircases is divided into five chapters: Specifications and basic data on staircases; Structural analysis of staircases – Classical methods; Structural analysis of staircases – Modern methods; Staircases and their analysis – A comparative study; Design analysis and structural detailing. Charts and graphs are included and numerous design examples are given of freestanding and other geometric staircases and of their elements and components. These examples are related to the case studies which were based on staircases that have already been constructed. All examples are checked using various Eurocodes.
The book includes bibliographical references and is supported by two appendices, which will be of particular interest to those practising engineers who wish to make a comparative study of the different practices and code requirements used by various countries; detailed drawings are included from the USA, Britain, Europe and Asia. Staircases will serve as a useful text for teachers preparing design syllabi for undergraduate and post graduate courses. Each major section contains a full explanation which allows the book to be used by students and practising engineers, particularly those facing the formidable task of having to design/ detail complicated staircases with unusual boundary conditions. Contractors will also find this book useful in the preparation of construction drawings and manufacturers will be interested in the guidance given.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
Specifications and basic data on staircases
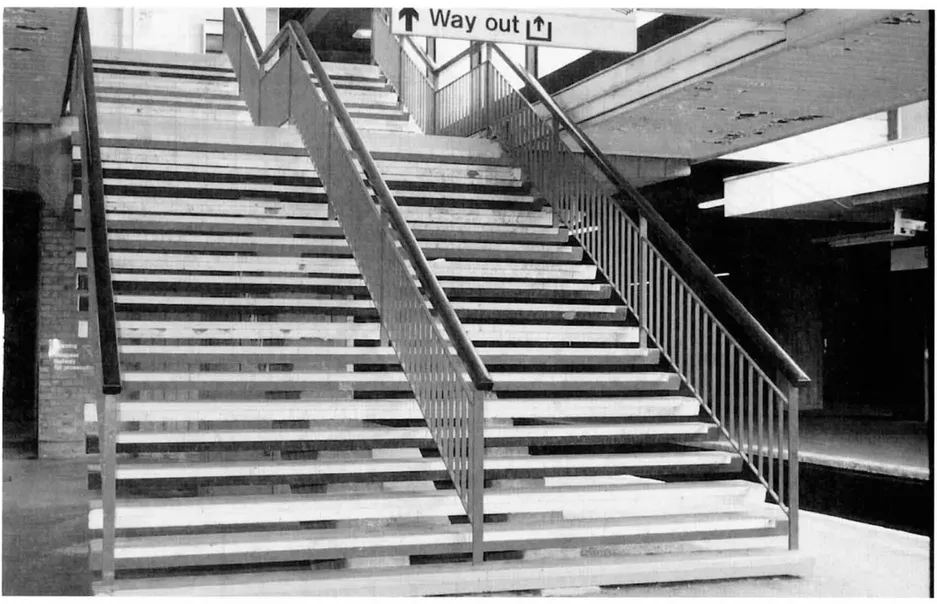
1.1 Introduction to Staircases
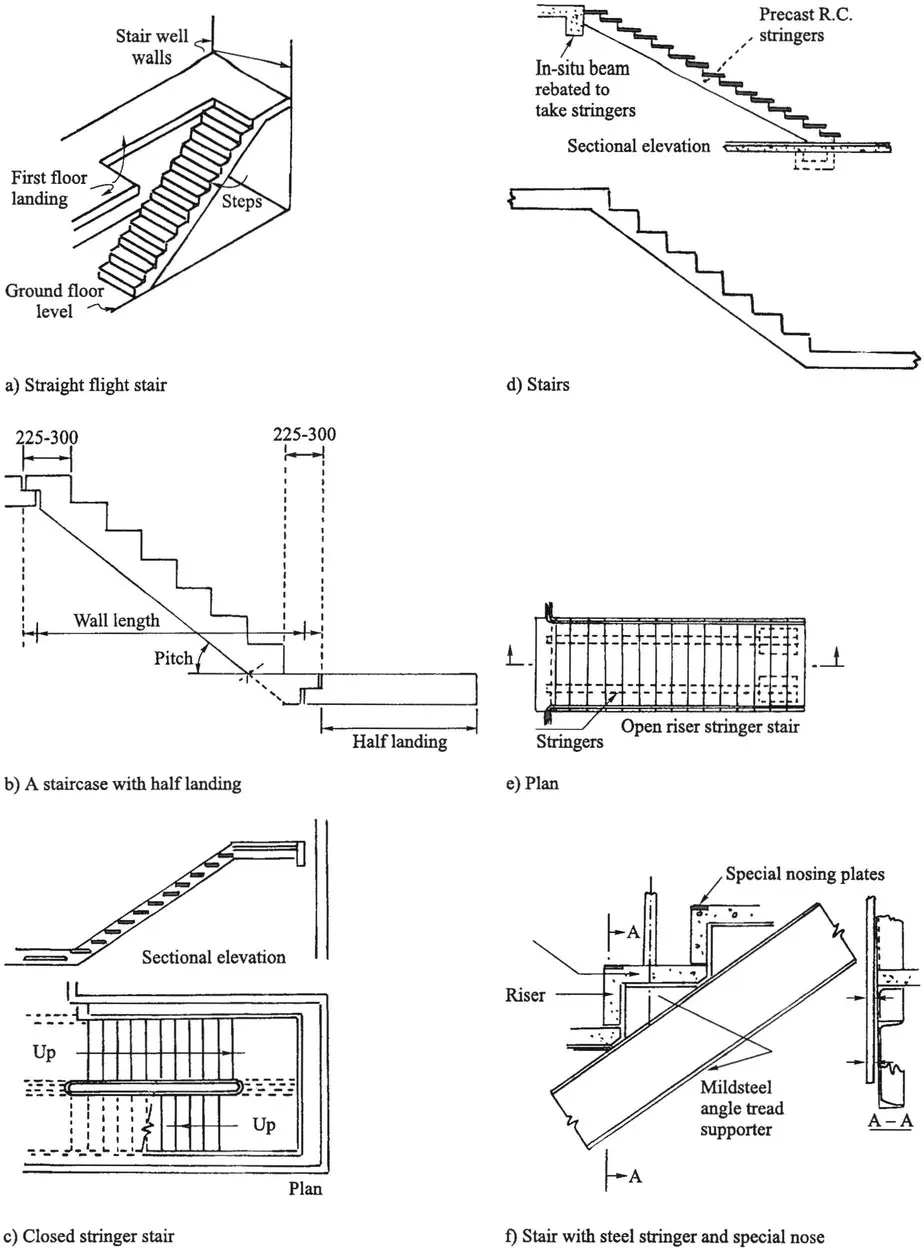
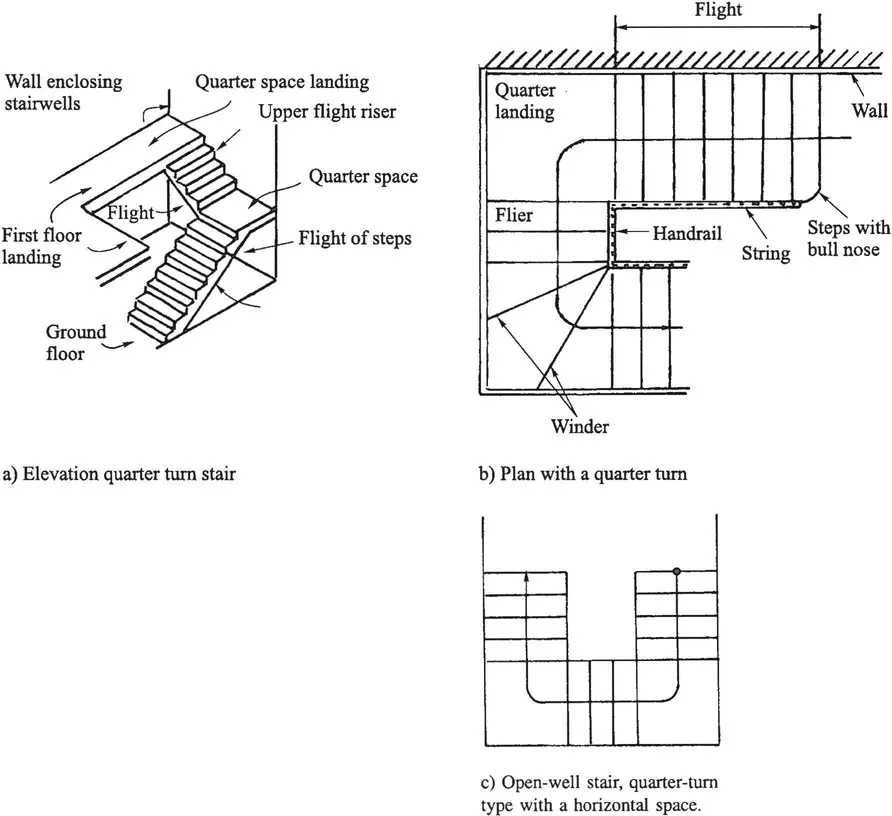
1.2 Stairway Layouts
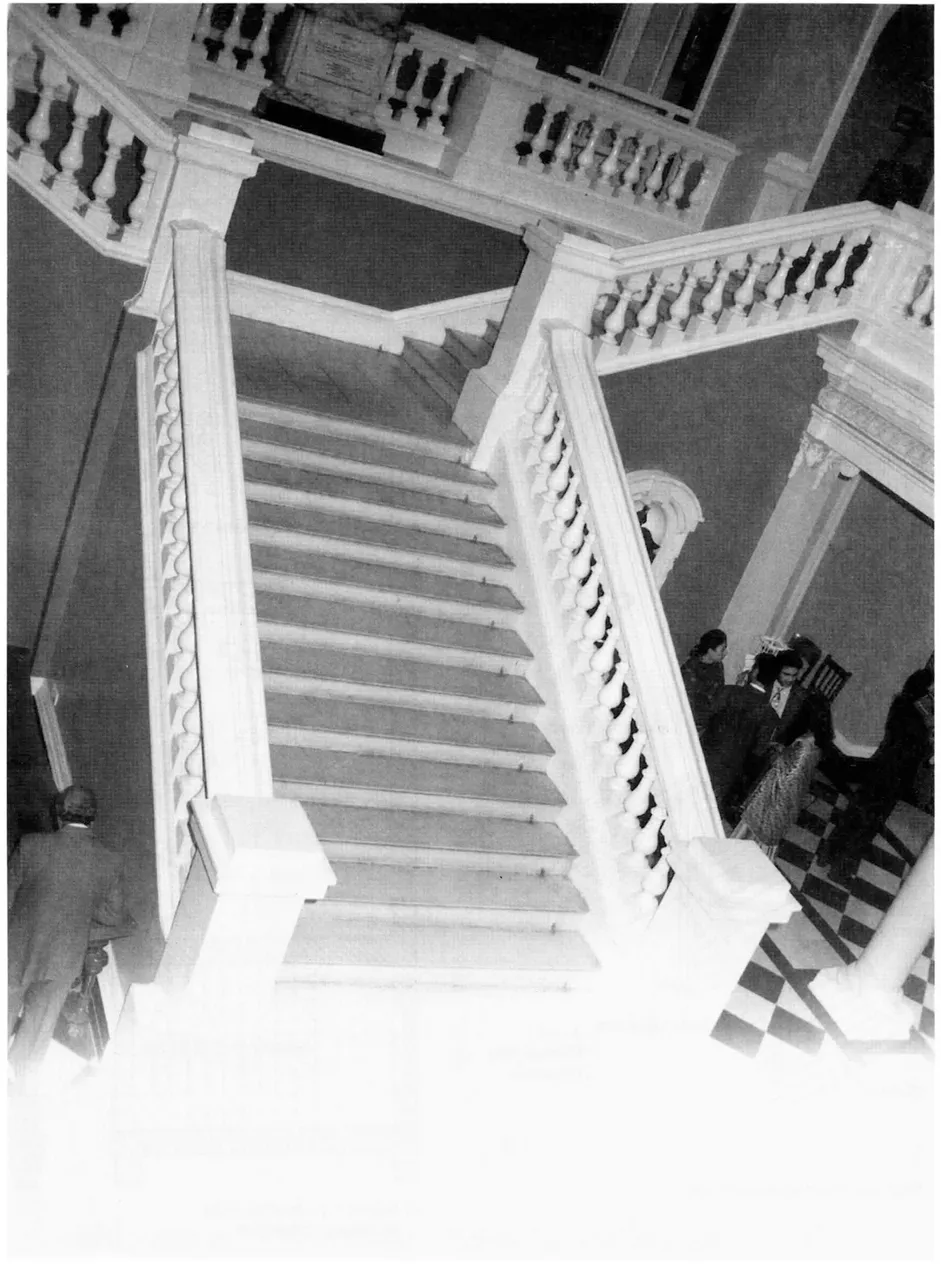
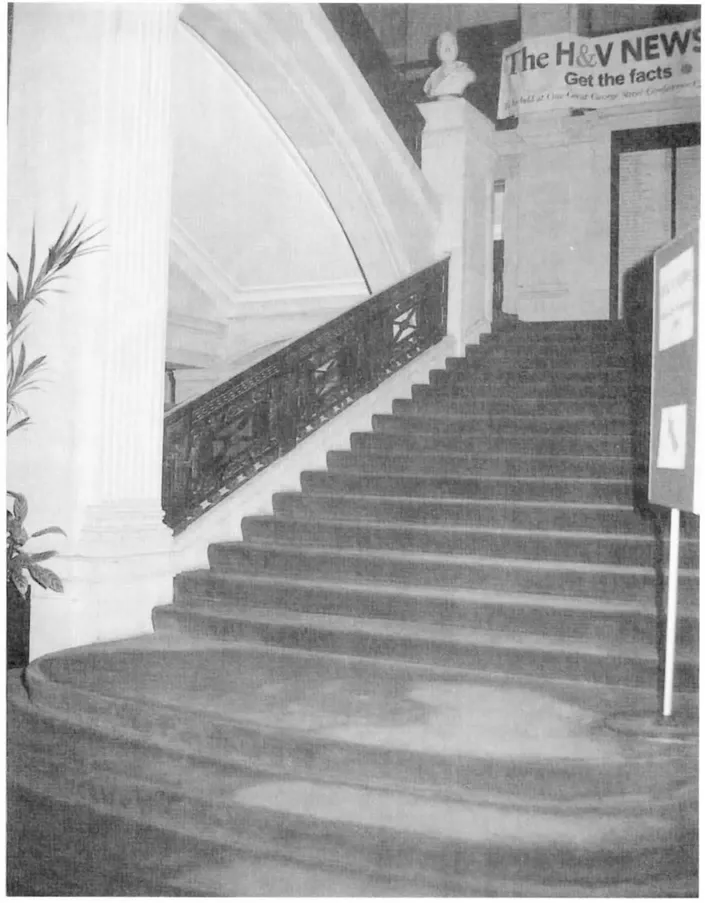



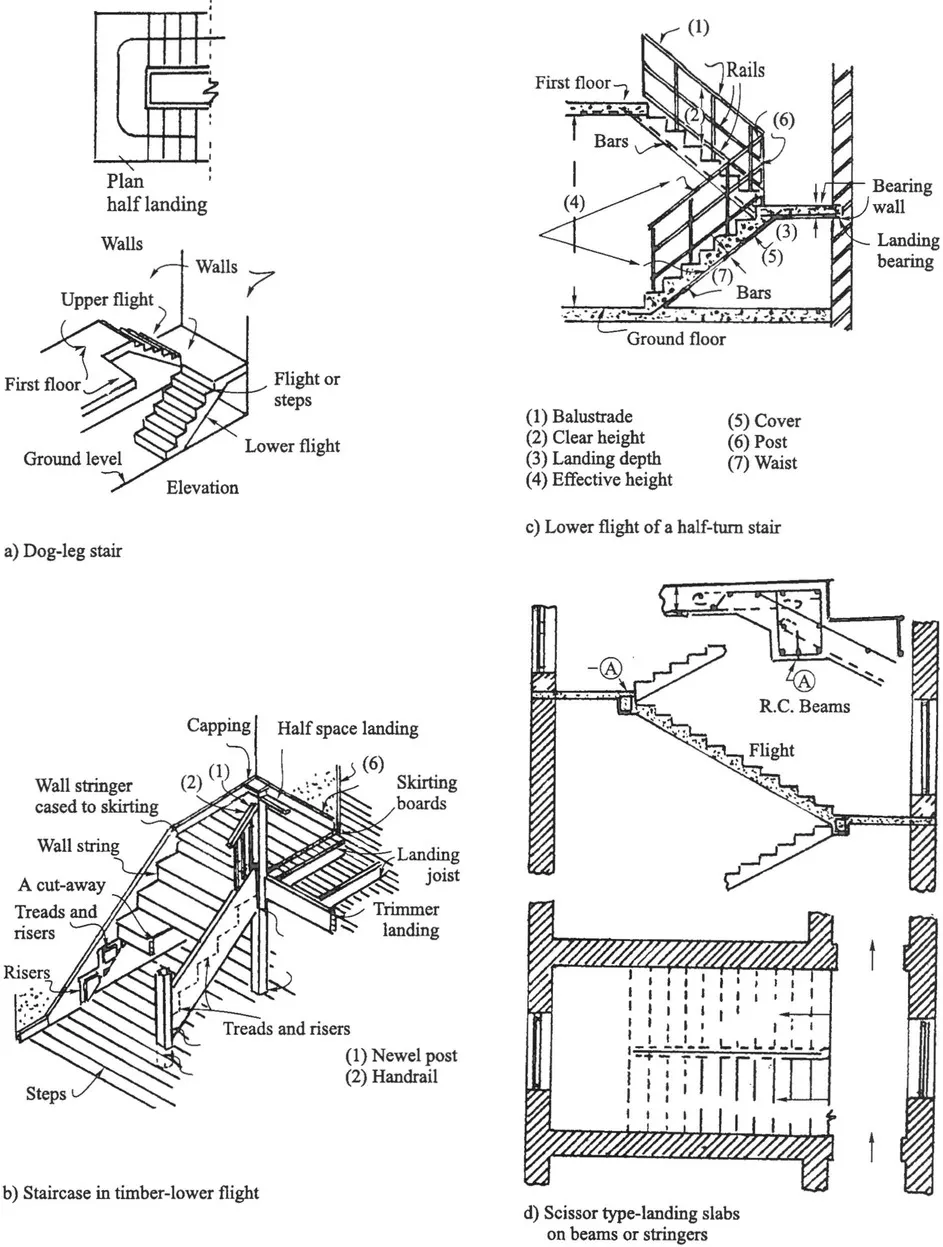

1.2.1 Landings, landing beams and flights
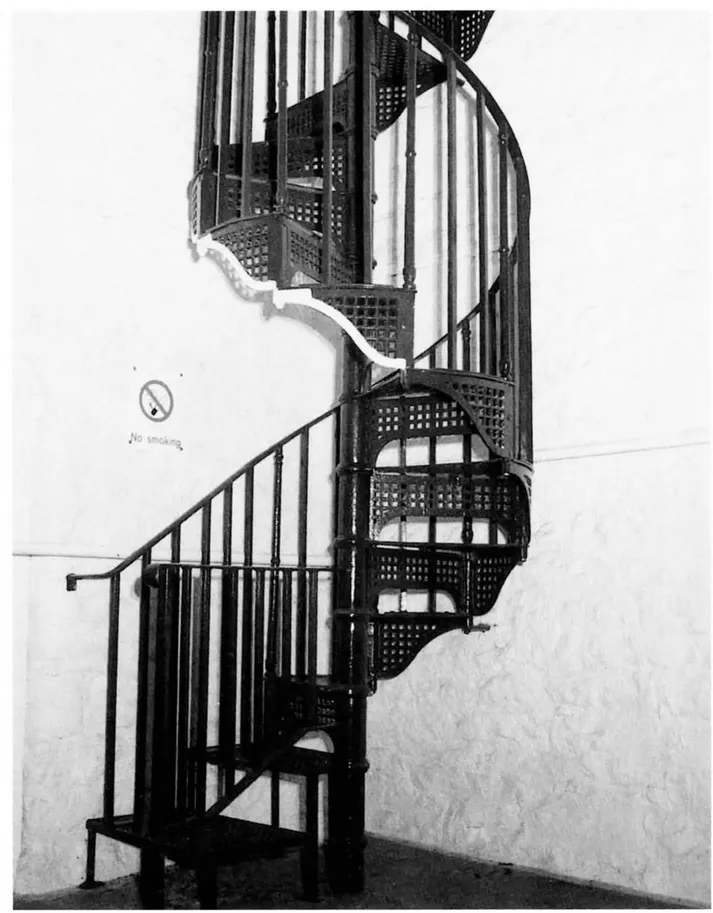

1.2.2 Strings or stringers
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Definitions
- Major notations
- Comparison of notations
- Conversion factors (units)
- 1 Specifications and basic data on staircases
- 2 Structural analysis of staircases: Classical methods
- 3 Structural analysis of staircases
- 4 Staircases and their analyses
- 5 Design analysis and structural detailing
- Appendix 1 Supporting analyses
- Appendix 2 Structural details for practising engineers
- References
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app