
Microbes for Sustainable Development and Bioremediation
- 368 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Microbes for Sustainable Development and Bioremediation
About this book
Microbes are the predominant form of life on the planet due to their broad range of adaptation and versatile nutritional behavior. The ability of some microbes to inhabit hostile environment incompatible with most forms of life means that their habitat defines the extent of the biosphere and delineates the barrier between the biosphere and geosphere. The direct and indirect role of microbes that include bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes, viruses, mycoplasma, and protozoans are very much important in development of modern human society for food, drugs, textiles, agriculture, and environment. Furthermore, microorganisms and their enzyme system are responsible for the degradation of various organic matters.
Microbes for Sustainable Development and Bioremediation emphasizes the role of microbes for sustainable development of ecosystem. Environmental microbiology role in biogeochemical cycle and bioremediation of environmental waste is major theme, which comprises the following aspects:
- Bacterial phytoextraction mechanism of heavy metals by native hyperaccumulator plants from complex waste-contaminated site for eco-restoration
- Role of microbial enzyme for eco-friendly recycling of industrial waste
- Field-scale remediation of crude oil–contaminated desert soil and treatment technology
- Microbial technology for metal recovery from e-waste printed circuit board
- Impact of genomic data on sustainability of ecosystem
- Methane monooxygenases: their regulations and applications
- Role of microbes in environmental sustainability and food preservation
This book will be directly beneficial to researchers and classroom students, in areas of biotechnology, environmental microbiology, molecular biology, and environmental engineering with specialized collection of cutting-edge knowledge.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 Bacterial-Assisted Phytoextraction Mechanism of Heavy Metals by Native Hyperaccumulator Plants from Distillery Waste–Contaminated Site for Eco-restoration
1.1 Introduction
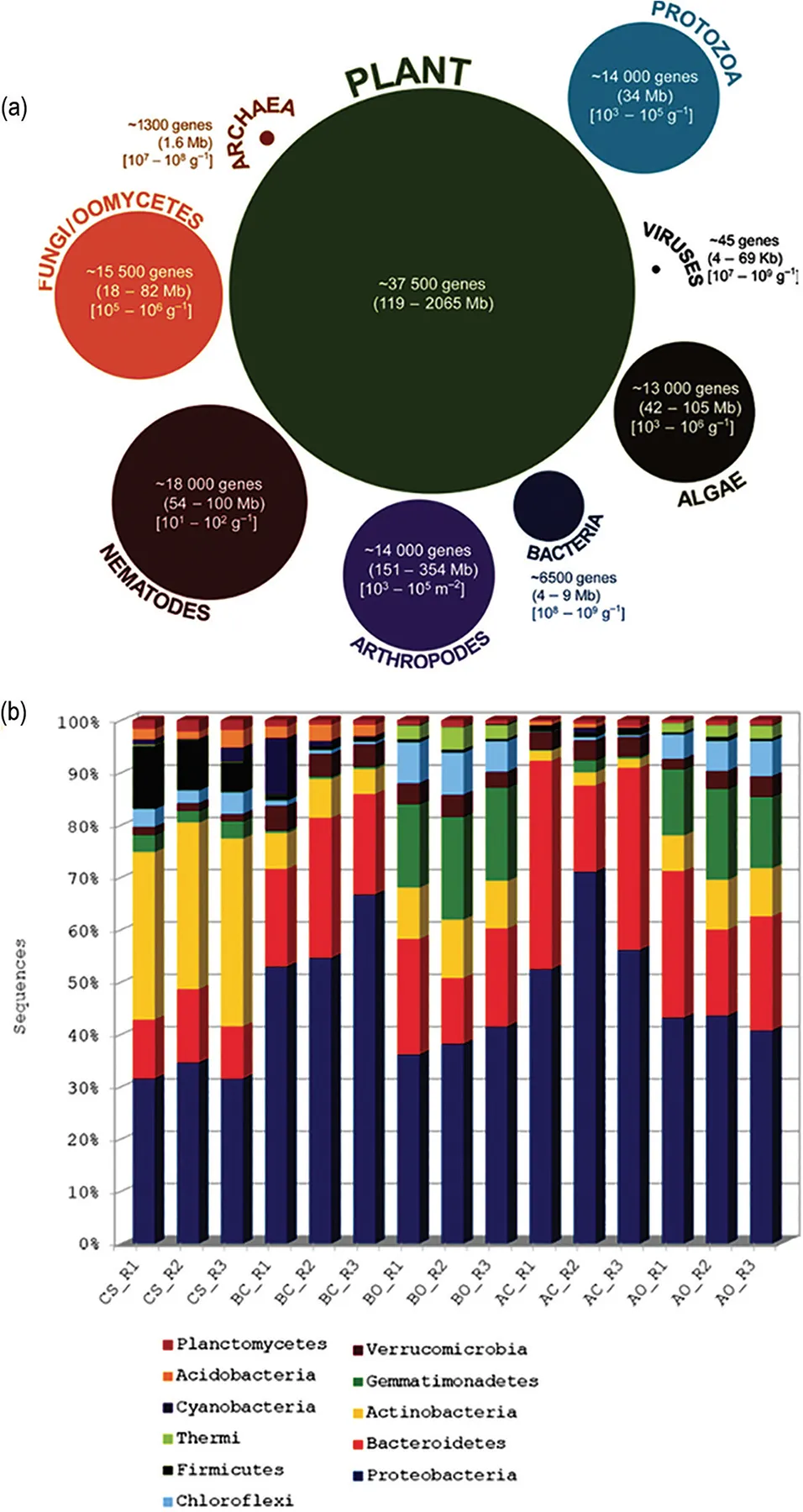

- Phytoextraction involves the use of pollutant-accumulating plants to remove HMs or organics from the soil, sludge, sediment, or water by concentrating them in harvestable parts of the plant. At the end of the growth period, plant biomass is harvested, dried, or incinerated, and the contaminant-enriched material is deposited in a special dump or added into a smelter. The energy gained from burning of the biomass could support the profitability of the technology, if the resultant fumes can be cleaned appropriately.
- In phytodegradation, contaminants are taken up from soil or water, metabolized in plant tissues, and broken up to less toxic or nontoxic compounds within the plant by several metabolic processes via the action of compounds produced by the plant. Besides, the contaminants are also degraded in the rhizopshere by the proteins or enzymes pro...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- List of Contributors
- Chapter 1 Bacterial-Assisted Phytoextraction Mechanism of Heavy Metals by Native Hyperaccumulator Plants from Distillery Waste–Contaminated Site for Eco-restoration
- Chapter 2 Microbial Enzymes for Eco-friendly Recycling of Waste Paper by Deinking
- Chapter 3 Advances in Industrial Wastewater Treatment
- Chapter 4 Microbial Degradation of Pesticides in the Environment
- Chapter 5 Dissimilatory Iron-Reducing Bacteria: A Template for Iron Mineralization and Nanomaterial Synthesis
- Chapter 6 Heat and Chemical Pretreatment of Bacterial Cells to Enhance Metal Removal
- Chapter 7 Field-Scale Remediation of Crude Oil–Contaminated Desert Soil Using Various Treatment Technologies: A Large Remediation Project Case Study
- Chapter 8 Microbial Processes for Treatment of e-Waste Printed Circuit Boards and Their Mechanisms for Metal(s) Solubilization
- Chapter 9 Application of Thermostable Enzymes for Retaining Sustainable Environment: Improvement of the Enzymatic Activities of Two Thermophilic Archaeal Enzymes without Decreasing Their Stability
- Chapter 10 Metagenomics: A Genomic Tool for Monitoring Microbial Communities during Bioremediation of Environmental Pollutants
- Chapter 11 Microbial Capacities for Utilization of Nitroaromatics
- Chapter 12 Methane Monooxygenases: Their Regulations and Applications in Biofuel Production
- Chapter 13 Plant Growth–Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) and Bioremediation of Industrial Waste
- Chapter 14 Fungi Treatment of Synthetic Dyes by Using Agro-industrial Waste
- Chapter 15 Beneficial Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture
- Chapter 16 Detoxification of Biomedical Waste
- Chapter 17 Immobilized Enzyme-Based Biocatalytic Cues: An Effective Approach to Tackle Industrial Effluent Waste
- Chapter 18 Lipase of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Diversity and Application
- Chapter 19 Role of Microbes in Environmental Sustainability and Food Preservation
- Chapter 20 Bioinformatics and Applications in Biotechnology
- Chapter 21 Microbial Bioinoculants for Sustainable Agriculture: Trends, Constraints, and Future Perspectives
- Index