
- 190 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Practical Guide for Oracle SQL, T-SQL and MySQL
About this book
SQL is a widely used to access most databases, therefore database developers and system administrators should be familiar with it. This hands-on SQL book will help beginner and intermediate users to write queries that apply complex conditions on a table. The book's unique side by side approach makes it easy for the reader to learn three major query languages in the IT industry. The author has over 20 years of experience in database design.
KEY FEATURES:
- Contains numerous practical screenshots of Oracle SQL, T-SQL, MySQL statements and results.
- Shows the differences between Oracle SQL, T-SQL and MySQL side by side.
- Gives a real world experience for SQL developers and database administrators.
- Sample data is available to work on (available on our website).
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction to SQL and Relational Databases
Relational database management systems (RDBMS) have become the standard database type for various industries since the 1980s. These systems allow the users to store data and access data in graphic user interfaces. It also allows users to set security rules.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a standard computer language for relational database management systems. SQL has different dialects. For example, Oracle SQL is called PL/SQL, MS SQL Server SQL is called T-SQL (Transact-SQL).
SQL is a very useful tool for database developers and database administrators. Database developers use SQL to select, insert, and update data. Database administrators (DBAs) apply their SQL skills to support Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL and other database systems.
The highlights of this chapter include
• Brief History of SQL and Database Systems
• SQL Standards
• Oracle, SQL Server and MySQL Versions
• Introduction to RDBMSs
• Relational Database Basic Concepts
• Entity Relational Diagram Used in This Book
Brief History of SQL and Database Systems
Table 1.1 History of SQL and Database Systems
Year | SQL and Database Development |
1970 to 1972 | Dr. E.F. Codd in IBM introduced in his paper the term “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks”. In the paper he defined RDBMs by Codd’s 12 rules. |
1970s | Ingres and System R were created at IBM San Jose. System R used the SEQUEL query language. The development of SQL/DS, DB2, and Oracle were based on the SEQUEL query language. |
1976 | Dr. Peter Chen developed the entity-relationship model. This model becomes the foundation of many systems analysis and design methods. |
1980s | Structured Query Language became the standard query language. Computer sales increased rapidly. Relational database systems became a commercial success. IBM’s DB2 and IBM PC resulted in the launches of many new developments of database systems such as PARADOX, dBase III and IV. |
1990s | Successful Online businesses let to demand for database accessing tools. MySQL and Apache became open source solution for the Internet. Application development tools including Oracle Developer, Power Builder, and Visual Basic were released. |
2000s | The three leading relational database systems in the world are Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server and MySQL. |
SQL Standards
Table 1.2 SQL Standards
Year | SQL Standard |
1974 | Original SQL (SEQUEL) |
1986 | SQL became a standard by ANSI (American National Standards Institute) and ISO (International Standards Organization) |
SQL/96 | Major modification (ISO 9075) |
SQL/99 | Added many features including recursive queries, triggers, procedural and control-of-flow statements, and some object-oriented structures |
SQL/2003 | Introduced XML-related features |
SQL/2006 | Defined ways for importing and storing XML data in database |
SQL/2008 | Added TRUNCATE TABLE statement and INSTEAD OF triggers |
Oracle, SQL Server and MySQL Versions
Table 1.3 Different versions for the three database systems
Oracle | SQL Server | MySQL |
1979–Oracle 2 | 1989–SQL Server 1.0 | 1995–First Release |
1983–Oracle 3 | 1991–SQL Server 1.1 | 1996–MySQL 3.19 |
1984–Oracle 4 | 1993–SQL Server 4.21 | 1997–MySQL 3.20 |
1985–Oracle 5 | 1995–SQL Server 6.0 | 1998–MySQL 3.21 |
1988–Oracle 6 | 1996–SQL Server 6.5 | 2000–MySQL 3.23 |
1992–Oracle 7 | 1998–SQL Server 7.0 | 2002–MySQL 4.0 |
1997–Oracle 8 | 2000–SQL Server 2000 | 2003–MySQL 4.01 |
1998–Oracle 8i | 2005–SQL Server 2005 | 2004–MySQL 4.1 |
2001–Oracle 9i | 2008–SQL Server 2008 | 2005–MySQL 5.0 |
2003–Oracle 10g | 2010–SQL Server 2008 R2 | 2010–MySQL 5.5 |
2007–Oracle 11g | 2012–SQL Server 2012 | 2013–MySQL 5.6 |
2013–Oracle 12C | 2014–SQL Server 2014 | 2015–MySQL 5.7 |
2016–SQL Server 2016 | 2016–MySQL 8.0 |
Relational Database Basic Concepts
■ Databases
Relational Database Management System consists of one or more databases. For example, the following SQL Server has HR and Sample databases.
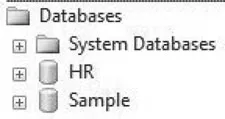
Figure 1.1 Data...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Chapter 1. Introduction to SQL and Relational Databases
- Chapter 2. Data Types
- Chapter 3. Installation of Oracle, SQL Server and MySQL
- Chapter 4. Database Development Tools
- Chapter 5. Data Definition Language (DDL)
- Chapter 6. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- Chapter 7. Aggregate Functions and GROUP BY Clause
- Chapter 8. Functions
- Chapter 9. Advanced SQL
- Chapter 10. Joins
- Chapter 11. Views
- Chapter 12. Data Import and Export
- Chapter 13. Stored Procedures
- Index
- About the Author
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Practical Guide for Oracle SQL, T-SQL and MySQL by Preston Zhang in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Databases. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.